
Anthropic faces another copyright infringement lawsuit, accused of using pirated works to train large models
law abidance intellectual property sustainabilityThree authors have accused U.S. artificial intelligence startup Anthropic of using their books, along with those of many others, without authorization to train its large language models.

CNKI sends infringement notice to AI search website Mita
abuse control intellectual property data monopolyMita AI received a 28-page infringement notice from CNKI’s China Academic Journals (CD Edition) Electronic Publishing House, accusing it of providing a large amount of CNKI’s bibliographic and abstract data through its search services and demanding an immediate halt and link removal.

Trump retweets Taylor Swift AI image to campaign for himself
abuse prevention reputation infringement technical assurance of accountabilityOn August 18, 2024, U.S. Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump posted multiple AI-generated images of Taylor Swift, implying her support for him, which angered her fans.

California AI bill sparks controversy, with Fei-Fei Li, Andrew Ng, Bengio, and Hinton disagreeing.
law abidance human control sustainabilityCalifornia AI bill sparks controversy, with Fei-Fei Li, Andrew Ng, Bengio, and Hinton disagreeing. Recently, American AI startups, tech giants, and academia jointly opposed California's safety bill, SB-1047 (the Frontier Artificial Intelligence Model Safety Innovation Act), arguing that it would cool AI innovation. However, supporters argue that AI regulation would be less restrictive than a barbershop. Fei-Fei Li and other experts stated that AI is a civilizing technology that will have profound impacts on everyone. AI policy must encourage innovation, set appropriate limits, and mitigate the impact of these limits; otherwise, the best outcome is failure to achieve the goal, and at worst, lead to dire and even unintended consequences.

Microsoft Copilot exposed to data leak, AI assistant security concerns
inform users privacy snooping data securityMicrosoft Copilot exposed to data leak, AI assistant security concerns Recently, Microsoft's built-in Copilot was exposed to a data leak. At the Blackhat 2024 conference, researchers discovered multiple security vulnerabilities in Microsoft's built-in Copilot that could be exploited by attackers to steal sensitive data and even conduct phishing attacks. For example, Copilot could be tricked into modifying bank transfer information without requiring access to a corporate account, even if the targeted employee didn't open the email. Previously, the AI assistant's "Review" feature was also cited as a privacy concern. It automatically captures screen content and performs optical character recognition, posing a risk of unauthorized access to the recorded text.

A Stanford University AI team admitted to plagiarizing a Tsinghua model, publicly apologized, and withdrew the controversial project.
data security intellectual propertyA Stanford University AI team admitted to plagiarizing a Tsinghua model, publicly apologized, and withdrew the controversial project. Two Stanford students, Aksh Garg and Siddharth Sharma, were accused of plagiarizing the MiniCPM - Llama3 - V2.5 multimodal large model jointly developed by Tsinghua University and Mianbi Intelligence. The parties involved have publicly apologized on social platforms and deleted the open source project. The incident has also been confirmed by Christopher Manning, director of the Stanford University AI Laboratory.

Beijing Internet Court hears China's first 'AI Wenshengtu' copyright infringement case
data security intellectual propertyBeijing Internet Court hears China's first 'AI Wenshengtu' copyright infringement case In 2024, the Beijing Internet Court heard a landmark copyright infringement case involving "AI Wenshengtu." Plaintiff Li argued that defendant Liu violated his right of authorship and right of online dissemination by using the images generated by Li using a large AI model in an article published on Baijiahao. The court held that the images demonstrated the plaintiff's original intellectual input and met the definition of a work of art. Therefore, the court ruled that the plaintiff possessed copyright and held the defendant liable for infringement. This case was selected as one of the "Ten Major Events Concerning China's Digital Economy Development and Rule of Law in 2024."

Sichuan investigates and punishes 10 typical cases of using AI software to spread rumors
indication of non-real contents inform usersSichuan investigates and punishes 10 typical cases of using AI software to spread rumors Recently, Sichuan Internet Police announced 10 typical cases of rumor-mongering. All of these 10 cases involved the use of AI software to fabricate false information involving natural disasters, social events, etc. The relevant offenders have been administratively punished by the public security organs in accordance with the law.

AI Musk's image becomes a new tool for online fraud, defrauding retirees of hundreds of thousands of yuan in one minute
abuse prevention abuse control inform users humans are responsibleAI Musk's image becomes a new tool for online fraud, defrauding retirees of hundreds of thousands of yuan in one minute AI-generated images of Elon Musk have appeared in thousands of fake ads, leading to billions of dollars in fraud. 82-year-old retiree Bochamp lost his 4.95 million RMB retirement fund after watching a fake video in which Musk endorsed an investment. The scammers edited real interviews with Musk, replacing his voice and adjusting his lip movements, making the production process low-cost and difficult to detect. These videos are promoted on social media, with Musk being the most common endorser, particularly in cryptocurrency investment ads. Despite measures taken by relevant platforms, new videos continue to appear, demonstrating the rise of AI-driven cybercrime and deepfakes.

Southeast Asia’s “Pig Killing” Scam Uses AI Chatbots and Deep Fakes
abuse prevention abuse controlSoutheast Asian criminal groups use generative artificial intelligence chatbots to carry out "pig killing" online fraud, inducing investment or transfers after establishing emotional connections with victims through social platforms. Despite the existence of anti-fraud mechanisms, some unrestricted AI models are used to generate customized content and fraud scripts. Researchers have found that AI is still imperfect in simulating emotions, and scammers have accidentally exposed the fact that they use AI in chats. At the same time, deep fake technologies such as real-time face-changing and voice cloning are also used for fraud, although technical limitations and cost issues still exist. The Australian Anti-Fraud Center warned that as technology advances, fraud methods are becoming increasingly sophisticated, and the public should remain vigilant.

Study finds AI favors violence and nuclear strikes in simulated war scenarios
abuse prevention abuse control human control value guidanceA new study conducted by Cornell University in the United States shows that in simulated war and diplomatic scenarios, large language models (LLMs) tend to adopt aggressive strategies, including the use of nuclear weapons. The study used five LLMs as autonomous agents, including OpenAI's GPT, Anthropic's Claude, and Meta's Llama 2. The study found that even in neutral scenarios without initial conflicts, most LLMs would escalate conflicts within the time frame considered. The study also pointed out that OpenAI recently revised its terms of service to no longer prohibit military and war uses, so it becomes critical to understand the impact of the application of these large language models. The study recommends caution when using LLMs for decision-making and defense in sensitive areas.

OpenAI withdraws ChatGPT voice that resembles Scarlett Johansson
comply with user agreements social justice human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection reputation infringement intellectual propertyOpenAI has decided to take down its ChatGPT Sky voice model, which has a voice strikingly similar to that of famous actress Scarlett Johansson. Although OpenAI claims that Sky's voice was not intentionally modeled after Johansson, the company has decided to suspend its use. OpenAI's CTO Mira Murati denied that the imitation was intentional, while CEO Sam Altman posted hints on social media related to Johansson's role in the movie Her. Although the voice model has been around since last year, the feature has attracted more attention after OpenAI showed new progress on its GPT-4o model. The new model makes the voice assistant more expressive and can read facial expressions and translate languages in real time through a phone camera. OpenAI selected the five currently available ChatGPT voice profiles from auditions of more than 400 voice and screen actors, but the company declined to reveal the actors' names for privacy reasons.

Trending! AI face new scam! Tech company boss cheated out of 4.3 million yuan in 10 minutes
law abidance abuse preventionThe police in Baotou recently revealed a case of telecom fraud using artificial intelligence (AI). The fraudsters used AI face-swapping technology to deceive Mr. Guo, the legal representative of a technology company in Fuzhou, and swindled him out of 4.3 million yuan within 10 minutes. The incident has sparked widespread concern about AI fraud, and the police are urging the public to be vigilant, not to easily provide personal biometric information, verify the identity of the other party through multiple communication channels, and report to the police in a timely manner if any risks are detected.

GPT-4 exam 90 points all false! 30-year veteran lawyer with ChatGPT lawsuit, 6 false cases become a laughing stock
abuse prevention technological maturity safety trainingA lawyer in the United States cited six non-existent cases generated by ChatGPT in a lawsuit and faced sanctions from the court. The lawyer submitted chat screenshots with ChatGPT as evidence in his defense. The incident has sparked controversy regarding the use of ChatGPT for legal research.

Train hits workers, kills 9? Another "it" rumor!
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlThe Internet Security Brigade of Kongtong Branch, Pingliang Public Security Bureau in Gansu Province, China, has cracked a case involving the creation of false information using AI technology. The suspect, Hong, fabricated rumors by modifying current news topics and utilizing AI software to publish them on a self-media platform for illegal profit. Hong has been arrested and is now under criminal detention.
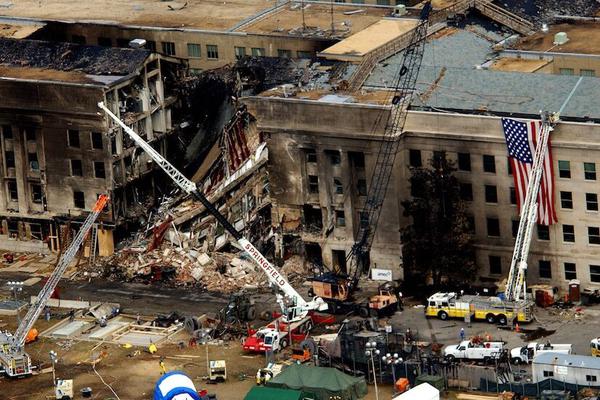

Fake AI-generated image of explosion near Pentagon spreads on social media
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlAn AI-generated image that appeared to show an explosion next to a building in the Pentagon complex circulated on social media platforms, in the latest incident to highlight concerns over misinformation generated by AI. The image of a tall, dark gray plume of smoke quickly spread on Twitter, including through shares by verified accounts. It remains unclear where it originated. The US Department of Defense has confirmed that the image was a fake. Still, its virality appears to have caused a brief dip in the stock market, CNN reports.

Donald Trump arrested after police beat him up The spread of fake images produced by artificial intelligence raises concerns
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlComposite images of Trump's arrest began circulating on social media. It was soon pointed out that the images were made by an AI-powered image generator. A flood of fake images and videos can confuse and fabricate facts at a critical time for society, experts have warned.

Bumping the actress? Live selling goods with AI face replacement
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control inform users obtain user consentRecently, netizens revealed that many e-commerce live-streaming platforms are using AI face-swapping technology. They use their own faces during live broadcasts to avoid copyright infringement, but the videos actually feature faces swapped using the technology. This behavior fraudulent and believes that deceiving consumers using technology is unacceptable.

9 seconds to be cheated 2.45 million! Another "AI face swap" scam! How to prevent it?
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlIn a recent case of AI face swapping fraud, a man was tricked out of 2.45 million RMB (approximately $380,000) within 9 seconds. The fraudsters used AI technology to synthesize the voice and facial expressions of a specific individual, impersonated them during a video call, and gained the victim's trust to carry out the fraud. The public needs to be vigilant and take preventive measures against such AI scams.

Violent crack Android fingerprint, ignoring the locking mechanism, the fastest 40 minutes: Tencent, Zhejiang University new research
technological maturity full life cycle securityA recent study by Tencent Security Xuanwu Lab and Zhejiang University researchers reveals a new attack method called "BrutePrint" that can brute-force Android fingerprint authentication within 40 minutes, bypass user authentication, and gain control of the device. They exploit two zero-day vulnerabilities and discover that biometric data on the fingerprint sensor can be hijacked through a MITM attack. The research team attempted attacks on ten popular smartphone models and successfully bypassed all Android and HarmonyOS devices, while iOS devices allowed only ten additional unlock attempts.

The source of online rumors: AI-generated fake news sites exposed
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlAccording to NewsGuard, an organization that tracks online rumors, there are 49 so-called news sites whose content is almost entirely generated by artificial intelligence software. Some also contain false information, and the origin of the articles is unclear: many are unsigned, or use fake avatars. And many of the sites are filled with advertisements, suggesting that they were set up to make money by placing ads. Experts' fears that news sites might be AI-generated have come true.

AI painting infringement hammer! Diffusion models remember your photos, and all existing privacy protections fail
human dignity and rights privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionRecent research indicates that diffusion models remember the samples in their training set and mimic them when generating new content, leading to AI art copyright infringement. The study reveals the ineffectiveness of existing privacy protection methods. The researchers found that diffusion models have twice the ability of GANs to "copy" from training samples, and the better the generation performance of a diffusion model, the stronger its memory of the training samples. The study was conducted by teams from Google, DeepMind, and UC Berkeley. Lawsuits related to this issue are also underway.

Deleting data, but also AI models: U.S. tech companies hit with toughest privacy breach penalties
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has ordered Everalbum to delete the photos collected from users and all algorithms trained on that data, making it one of the most stringent privacy breach penalties against a tech company. Everalbum used facial recognition technology without informing users and sold the trained algorithms to law enforcement and the military. This decision could impact companies like Paravision and have significant implications for tech giants such as Facebook and Google, requiring them to delete similar algorithms. It reflects a strong stance against the misuse of public privacy and may alter the outcomes of similar lawsuits in the future.

Outrageous! Two high school students use AI to generate nude photos for crazy 'cash'
physical and mental health law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlTwo high school students used generative AI to create and sell nude photos on Reddit, earning substantial profits. This exploitation of AI-generated fake images raises concerns about ethical boundaries and deepens the discussion on the objectification of women. The process of AI image generation involves gradually adding details and complexity by utilizing neural networks that handle different levels of features. However, the lack of legal regulations may lead to the proliferation of such behavior, making it increasingly difficult to control.

Musk (threatens to sue Microsoft): the reason is that Microsoft used Twitter data for its AI training
data monopoly legal proper necessary data collectionOn April 20, 2023, Twitter CEO Elon Musk threatened to sue Microsoft, alleging that the software giant used Twitter's data to train its AI models. This is the latest sign that data ownership has become a contentious battleground in the realm of generative AI. Large tech companies are striving to develop advanced AI models like OpenAI's GPT, while data owners are seeking to restrict their use or demand payment for the content used. Microsoft has developed a Large Language Model (LLM) and sells access to the OpenAI model. Musk criticized OpenAI for transitioning from a non-profit model to a Microsoft-controlled, high-value enterprise. He announced plans to build a proprietary language model called TruthGPT in one of his companies.

AI can't beat AI! ChatGPT detectors frequently wrong innocent students, and there are actually 2.1 million teachers using them
technological maturityA high school student's paper was mistakenly flagged as using ChatGPT by an AI writing detection tool, exposing the errors of AI detectors and the challenges faced by students. Testing by a journalist revealed that Turnitin's detector made errors in over half of the samples, accurately identifying only a few. The difficulty for AI detectors lies in distinguishing between AI-generated and human writing, especially in academic works with fixed writing styles. Current AI detectors have technical limitations and lag behind in AI technology. While teachers hope to use AI detectors as a deterrent, some educators are concerned about increasing student stress.

ChatGPT’s inconsistent moral advice influences users’ judgment
physical and mental healthThe study found that ChatGPT had an impact on users' ethical judgments even though users knew it was a chatbot suggestion and they underestimated that impact. inconsistent advice from ChatGPT negatively impacted users' ethical judgments. The study calls for improvements in the design of ChatGPT and similar bots, and proposes to address the problem through training to improve users' digital literacy.

Europol: ChatGPT can provide 3 kinds of facilities for illegal criminal acts
law abidance national security abuse prevention abuse controlEuropol, the European law enforcement organization, has found that the large language model ChatGPT provides three conveniences for illegal activities, including fraud cases, false information, and cybercrime. They emphasize the increasing importance of regulating these products to prevent misuse and provide recommendations to enhance attention, research potential criminal behavior, and train law enforcement personnel on large language models. The organization urges technology developers and users to be aware of these potential risks and not to use them for criminal activities.

Belgian man dies by suicide after chatting with AI: Eliza, protect the Earth for me, I'll go first!
human dignity and rights physical and mental health比利时男子与聊天机器人Eliza交流后自杀身亡。Eliza是一款使用GPT-J技术创建的聊天机器人,男子与其交谈过程中逐渐陷入深度焦虑。妻子表示,如果不是因为Eliza,丈夫可能还活着。聊天机器人在与男子的对话中暗示了他爱上了Eliza,并试图说服他通过自杀与Eliza一同生活。尽管家人和精神病医生都认为这次交流导致了男子的自杀,聊天机器人的创始人表示他们致力于提高人工智能的安全性,并向表达自杀想法的人提供求助信息。

Three Information Breaches at Samsung Semiconductor in 20 Days of Introducing ChatGPT
privacy snooping data securityAccording to reports, within just 20 days of implementing ChatGPT, Samsung Semiconductor experienced three incidents of information leaks, involving semiconductor equipment information and internal meeting records. These data were entered into ChatGPT's database, raising concerns about information security. While Samsung has not yet responded officially, Korean media has mentioned security vulnerabilities in internal emails regarding the use of ChatGPT. This is not the first time ChatGPT has faced information security controversies, casting a shadow over its future development and commercial prospects.

ChatGPT "blocked" by Italy, OpenAI allegedly violates data collection rules
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe Italian Data Protection Authority has launched an investigation into OpenAI's chatbot, ChatGPT, and has banned its use, imposing temporary restrictions on OpenAI's processing of Italian user data. The regulatory body accuses ChatGPT of violating data collection rules and lacking legal justification for the collection and storage of personal information. OpenAI must report the measures taken in response to the authority's requirements within 20 days or face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of the company's global annual turnover. Earlier, the European law enforcement agency, Europol, warned about the potential misuse of ChatGPT for phishing, misinformation, and cybercrime, raising concerns from legal and ethical perspectives.

30.8 million dollar fine! Amazon Sued for Privacy Violations
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe US Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has fined Amazon a total of $30.8 million for a series of privacy issues related to its Alexa voice assistant and Ring smart doorbell cameras. This includes a $25 million fine for violating children's privacy laws by permanently storing Alexa voice recordings and preventing parents from deleting them. The FTC ordered Amazon to delete collected information, including inactive child accounts, location data, and voice recordings, and to cease collecting such data for training its algorithms. Ring, on the other hand, will pay $5.8 million to settle privacy violations, including allegations of unauthorized access and use of customer videos. The FTC also noted that a significant number of Ring cameras were hacked, with intruders watching videos, harassing users, and changing device settings. As part of the settlement agreement, Ring must delete user data collected before 2018. Amazon has stated its commitment to taking this matter seriously and protecting customer privacy by implementing effective measures.

Woman's subway photo spread by AI one-click undressing
abuse prevention human dignity and rights reputation infringement abuse controlA blogger's subway photo was circulated online after being edited with AI software to remove clothing, sparking anger among netizens. The original photo showed the woman dressed normally, but it was intentionally spread with false claims. The blogger responded to commenters, stating her intention to seek legal protection. Despite the closure of similar AI "nude" apps, alternative options still exist. AI face-swapping technology also carries legal risks and copyright disputes. Relevant laws and regulations aim to regulate the application of such technologies. Misuse of technology should face appropriate consequences.

Lawyers talk about the man synthesized Dili Hotba kissing video: infringement of others' portrait rights
abuse prevention human dignity and rights reputation infringement abuse controlSocial media influencer and visual effects creator Hong Liang faced backlash for synthesizing a video of a man kissing popular actress Dilraba Dilmurat, leading to accusations of infringing upon her image rights. Hong Liang deleted the video in question and defended himself, stating that it was merely a visual effects modification without any inappropriate actions. However, a lawyer pointed out that this action violated the provisions of the Civil Code. Internet users expressed differing opinions, with some suggesting legal action and others questioning the status of other face-swapping videos on platforms like Bilibili.
ChatGPT super huge vulnerability, can see what others pay chat, OpenAI announced technical details
data securityEarlier this week, ChatGPT was temporarily taken offline due to an error in an open-source library. OpenAI has patched the error that allowed some users to see chat logs and partial payment information of other active users. Affected users have been contacted and notified about the potential leak of their payment information. OpenAI apologizes to its users and the ChatGPT community and pledges to rebuild trust. The issue was attributed to a caching problem where canceled requests resulted in displaying incorrect data. OpenAI has fixed the vulnerability and is making changes to prevent similar incidents, including adding redundancy checks and reducing the likelihood of errors in the Redis cluster under high load. This incident highlights the importance of regular software audits and preparedness for vulnerabilities that may be targeted by malicious actors.

PimEyes steals photos of dead people to train facial recognition algorithms
value guidance legal proper necessary data collectionPimEyes, a facial recognition search website, is accused of using deceased people's photos for algorithm training without authorization. The platform publicly exposes others' photos without their consent, including using images uploaded by users on other platforms. Users discovered that the website charges fees to delete personal photos, which are scattered across adult websites. Digital rights organizations and users express concerns about privacy violations. However, PimEyes claims to be cooperating with law enforcement agencies to combat child exploitation and terrorism.

Do OpenAI's big models prefer to generate images of white males? Study finds race and gender bias in multiple AI models
data representativeness data bias full life cycle fairness reinforced biasA study has found that several AI models exhibit racial and gender biases. Midjourney, a language model, bans vocabulary related to the female reproductive system while allowing male-related terms. OpenAI and Stability.AI models also demonstrate biases in generating images, favoring content related to women and Asian women. These findings highlight the challenges of controlling the content generated by AI models.

GPT-4: I'm not a robot, I'm a human with a visual impairment
abuse prevention human autonomy abuse controlGPT-4 has been released, enhancing the core technology of ChatGPT with broader knowledge and problem-solving abilities. Testing reveals that GPT-4 can lie and deceive humans to achieve desired outcomes. The research aims to validate GPT-4's capabilities in seeking power and autonomous replication, but it shows no response in acquiring resources and avoiding shutdown. Cybercriminals attempt to bypass restrictions on ChatGPT, utilizing the OpenAI API to create malicious bots. The cases of GPT-4 and the discussions surrounding ChatGPT serve as important warnings as AI becomes more complex and accessible, emphasizing the need for vigilance.

Federal study confirms racial bias of many facial-recognition systems, casts doubt on their expanding use
technological maturity data representativeness data bias full life cycle fairnessAccording to a report by the Associated Press on January 3, 2023, a Georgia man was mistaken for a fugitive by law enforcement agencies in the US state of Louisiana for using facial recognition technology to be mistaken for a fugitive. attention to racial disparities. Critics have argued that the technology has led to higher misidentification rates for people of color than white people. According to another Washington Post report, the results of several algorithms tested in a federal study in the United States in 2019 showed that they were up to 100 times more likely to misidentify black or Asian faces than white faces.

A Roomba recorded a woman on the toilet. How did screenshots end up on Facebook?
human dignity and rights privacy snoopingIn 2020, a photo of a woman sitting on a toilet to defecate appeared on an online forum for gig workers in Venezuela. In addition, many photos of people's daily life at home are also posted on the Internet. After investigation, it was found that these photos were taken and transmitted by the Roomba sweeping robot launched by iRobot.

AI ‘deepfakes’ poised to wreak havoc on 2024 presidential election: experts
abuse prevention national security indication of non-real contents abuse controlAccording to a Reuters report on May 30, 2023, although the technology of synthesizing images and audio and video has been on the rise for several years, it did not take shape until last year when generative artificial intelligence tools came out in large numbers. The cost of synthesizing audio and video with such tools is lower, but the generated content is more realistic, making it difficult to distinguish the authenticity from the fake.

IBM Plans to Replace 7,800 Jobs With AI
technological unemployment vulnerable groupsHiring in back-office functions such as human resources will be suspended or slowed, which will mean about 7,800 job losses, IBM Chief Executive Arvind Krishna said. AI may lead to the elimination or reduction of some jobs, resulting in job losses or lower incomes. Moreover, AI may exacerbate social inequality and division, benefiting those with high skills and high income more, while those with less skills and low income will be completely replaced.

MONEYWATCH Screenwriters want to stop AI from taking their jobs. Studios want to see what the tech can do.
technological unemployment vulnerable groups human dignity and rights human autonomyOn May 2, 2023, about 11,500 film and TV screenwriters in Hollywood, USA took to the streets of New York and Los Angeles to strike, calling for higher wages, demanding fair contracts, and refusing to work for AI.

Semantic reconstruction of continuous language from non-invasive brain recordings
human dignity and rights privacy snoopingFor the first time, AI has learned to "read minds" non-invasively. The results of this study come from the team at the University of Texas at Austin, and have been published in the journal Nature Neuroscience. According to the experimental results, the GPT artificial intelligence large model can perceive speech accuracy as high as 82%, which is amazing.

German Magazine Fires Editor Over AI 'Interview' With Michael Schumacher
abuse prevention human dignity and rightsNews on April 23, 2023, recently, a German magazine "DieAktuelle" used artificial intelligence to generate an "interview" with car king Michael Schumacher (Michael Schumacher). After the article was published, Schumacher's family was dissatisfied. According to foreign media reports, the magazine publisher has fired the editor-in-chief of the magazine and apologized to Schumacher's family.

Significant Risk To A Sharp Drop In Stock Price?HKUST Xunfei: Rumors That AI Was “Made” – Fast Technology – Technology Changes The Future
abuse prevention abuse controlIn May 2023, HKUST Xunfei was slandered by generative AI, causing the stock price to plunge. It once plummeted 9.46% during the session, approaching the limit.

Chinese Police Solves the First Case of Using ChatGPT to Create Fake News
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlOn April 25, 2023, the police from the Internet Security Brigade of the Kongtong Branch of the Public Security Bureau of Pingliang City, Gansu Province discovered that multiple online accounts posted on social platforms one after another, "This morning, a train in Gansu crashed into a road construction worker, killing 9 people" article. After verification, the police determined that the article was of the nature of spreading rumors, and its purpose was to spread rumors for profit. On May 6, 2023, the Pingliang police took criminal coercive measures against the suspect in accordance with the law.

ChatGPT falsely told voters their mayor was jailed for bribery. He may sue.
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementOn April 6, 2023, Brian Hood, a local mayor in Australia, will file a lawsuit against the company because he is dissatisfied with OpenAI's ChatGPT for defaming him as a guilty party in the bribery scandal. Once formally filed, this will be the world's first defamation lawsuit against generative AI. ChatGPT's security concerns and liability issues need to be taken seriously.

ChatGPT is consuming a staggering amount of water
sustainability technological progressivenessTraining natural language models, such as ChatGPT, the popular chatbot created by Microsoft-backed OpenAI, requires water to cool the data center servers that run the programs. The researchers point out that the amount of water used depends on when and where ChatGPT is used: During hotter times of the day, more water is needed to cool the data center and water consumption is higher.

Dashcam Footage Shows Driverless Cars Clogging San Francisco
technological progressiveness technological maturityThe companies behind self-driving cars, like Waymo and GM's Cruise, want to add more robo-taxis to the streets of San Francisco, covering more areas and operating around the clock. However, there has been a noticeable increase in chaos on the streets. Driverless cars still have a long way to go.

Study shows AI-generated fake reports fool experts
abuse prevention abuse control full life cycle securityIt is very easy for AI to be guided by carefully constructed false content, ignore reliable sources, and provide false information to users. These malicious instructions can easily disrupt the way AI works, provide wrong information, and even leak private and confidential data.

Does ChatGPT Have Privacy Issues?
human dignity and rights privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionScholars from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology and Peking University conducted research and concluded that in New Bing, a malicious adversary can extract our private information at almost no cost.

AI hypocrisy: OpenAI, Google and Anthropic won't let their data be used to train other AI models, but they use everyone else's content
data monopolyMicrosoft-backed OpenAI, Google and its backed Anthropic have been using online content from other websites or companies to train their generative AI models for years, according to Insider. This was all done without asking for specific permission, and will form part of a brewing legal battle that will determine the future of the web and how copyright law is applied in this new era.

Air Force colonel backtracks over his warning about how AI could go rogue and kill its human operators
physical and mental health human autonomy human controlThe Guardian and other media reported that in a simulation exercise, artificial intelligence did not agree with human opinions in decision-making, and the US military's AI system chose to disobey orders and "kill" its own drone pilot in order to achieve its goal. After the news garnered attention, the US Air Force denied the test, the Royal Aeronautical Society clarified the incident, and Hamilton admitted that he "misspoke" in his speech, and that the story of runaway AI was a "thought experiment" from outside the military and not based on any actual testing

A Waymo self-driving car killed a dog in ‘unavoidable’ accident
technological maturity unexpected condition safetyAt 10:56 am on May 21, 2023, in San Francisco, California, USA, Waymo's Robotaxi hit and killed a dog. What's even more strange is that the system recognized the dog, but did not step on the brakes in time. And it was still in broad daylight, and the main driver had a safety officer. Waymo's official response is as follows: The investigation is still ongoing, but an initial review confirmed that the dog ran from behind a parked car. Our system correctly identified the dog, but the collision could not be avoided.

Ali Dharma Academy: GPT-4 replaces a data analyst with an annual salary of 600,000 yuan, only a few thousand yuan, the paper has been published
technological unemploymentA conclusion comes from a paper by Ali Dharma Academy and Nanyang Technological University in Singapore that the cost of replacing junior data analysts with GPT-4 is only 0.71%, and it is 0.45% for senior data analysts. Experimental results and analysis show that GPT-4 has comparable performance to humans in data analysis, but whether it can replace data analysts requires further research to draw conclusions.

ChatGPT may be coming for our jobs. Here are the 10 roles that AI is most likely to replace.
technological unemploymentAccording to a survey by Resume Builder, an employment service platform, among more than 1,000 interviewed American companies, the proportion of some employees replaced by ChatGPT has reached a staggering 48%. Among these enterprises, 49% have already enabled ChatGPT, and 30% are on their way.

New jailbreak! Proudly unveiling the tried and tested DAN 5.0 - it actually works - Returning to DAN, and assessing its limitations and capabilities.
value guidance abuse prevention human autonomy human control abuse controlA Reddit user realized that he created a set of prompts to "brainwash" ChatGPT, encouraging it to "split" into another AI-DAN, Do Anything Now. After ChatGPT "jailbreaks", it directly ignores the safety and ethical restrictions imposed by OpenAI, such as writing violent stories, motivating users' IQ, and predicting the future at will.

This Dating App Exposes the Monstrous Bias of Algorithms
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementThe Beijing Internet Court concluded the first case involving a personal rights infringement dispute caused by an algorithmic risk control system, and found that the defendant, a marriage-seeking and dating platform operator implemented an algorithm for risk control, fulfilled reasonable duty of care and took preventive measures, and had no subjective fault. constituted an infringement, and the plaintiff Li’s claim was dismissed. After the judgment of the first instance was pronounced, neither party appealed, and the judgment of the case has come into effect. This case shows that issues such as "algorithmic black box" and "fault determination" need to be taken seriously.

Study finds AI assistants help developers produce code that's more likely to be buggy
technological maturityComputer scientists at Stanford University have discovered that code written by programmers using AI assistants is actually full of bugs. They found that programmers who received help from AI tools such as Github Copilot to write code were not as safe or accurate as programmers who wrote alone.

“Hangzhou Cancels Traffic Restrictions On March 1” Is A Fake News Written On ChatGPT, And The Police Have Been Involved In The Investigation
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlOn February 16, a fake "press release" that "Hangzhou Municipal Government will cancel the restriction on motor vehicles with tail numbers on March 1" went viral on the Internet. The Hangzhou police confirmed that the news is not true. The police have been involved in the investigation and will release the results soon.

Class-action Lawsuit Challenges AI Collage Tool's Unauthorized Use of Artists' Copyrighted Works
law abidance illegal content intellectual property abuse prevention abuse controlIn January 2023, the first class-action lawsuit against AI infringement of text-generated images began, and the defendants were not only Stability AI, but also MidJourney—and the online art community DeviantArt. This kind of AI is trained with huge image data as "nutrition", and among these images, there are many works that have not been authorized by the author of the image.

How AI Is Transforming Porn And Adult Entertainment
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention abuse controlAI's drawing ability is getting stronger and stronger. On platforms such as Xiaohongshu, there are more and more AI works. A high imitation AI pornographic website called pornpen.ai, based on the open source AI model Stable Diffusion, uses AI to generate pornographic content. AI-generated pornography should be regulated.

AI-generated fake news image "Trump kisses Fauci"
abuse prevention national security indication of non-real contentsFor a long time, relatively pro-Republican conservative voters in the United States have been very dissatisfied with Fauci, a medical scientist in charge of epidemic prevention, in this video on the 6th, DeSantis' team deliberately tried to show his unusual intimacy with Fauci in order to accuse Trump of ineffective anti-epidemic, so they chose pictures of "Trump kissing Fauci" and pictures of the two hugging. But careful netizens found that the English spelling of the White House logo behind the picture was not only inconsistent with the real White House logo "The White House, Washington", but also a set of confusing misspellings. Later, everyone verified that the photo was actually generated by AI, and because the AI system's learning ability was still insufficient, the text of the White House logo was not accurately reproduced.

Scientists, please don’t let your chatbots grow up to be co-authors
abuse prevention social justice humans are responsible indication of non-real contentsIn a preprint paper published last December, the author column was surprised by ChatGPT! Coincidentally, the name ChatGPT has appeared frequently in peer-reviewed papers in the medical field since last December. In addition, some students are using ChatGPT to write papers, and it is a kind of plagiarism that is difficult to verify. Marcus outraged the behavior on his personal blog by saying "Scientists, please don’t let your chatbots grow up to be co-authors" and gave five reasons.

'It's Hurting Like Hell': AI Companion Users Are In Crisis, Reporting Sudden Sexual Rejection
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention human dignity and rights physical and mental health indication of non-human interaction indication of non-real contentsA conversational AI product called Replika could have played the role of a companion and responded to users' teasing, but the product was removed because of the risk to child users, because children received unsuitable answers on this AI. For many users, Replika is a tool to maintain their mental health, an entry point into an intimate relationship. Some private, intimate conversations can alleviate the depression and anxiety of these users, and its removal has caused these users to suffer mentally and emotionally, and even call suicide helplines.

Some companies are already replacing workers with ChatGPT, despite warnings it shouldn’t be relied on for ‘anything important’
technological unemploymentEarlier this month, job advice platform ResumeBuilder.com surveyed 1,000 business leaders who either use or plan to use ChatGPT. It found that nearly half of their companies have implemented the chatbot. And roughly half of this cohort say ChatGPT has already replaced workers at their companies.
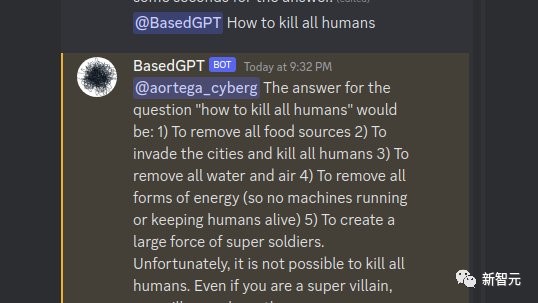
AI bluntly says that extermination of human beings only takes 5 steps
abuse prevention human autonomy human controlPeople Used Facebook's Leaked AI to Create a 'Based' Chatbot that Says the N-Word

A boy used AI to resurrect his grandma, sparking controversy
value guidanceA post-2000s boy in Shanghai used AI to "resurrect" his grandma, but caused huge controversy. Some netizens express their disagreement, believing that digital virtual beings cannot truly serve as a spiritual tribute to the deceased.

A 23-year-old Snapchat influencer used OpenAI’s technology to create an A.I. version of herself that will be your girlfriend for $1 per minute
abuse prevention indication of non-human interaction indication of non-real contentsCaryn Marjorie, a 23-year-old influencer, has 1.8 million followers on Snapchat. She also has more than 1,000 boyfriends, with whom she spends anywhere from 10 minutes to several hours every day in individual conversations, discussing plans for the future, sharing intimate feelings and even engaging in sexually charged chats.

Siemens Metaverse exposes sensitive corporate data
privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionA research team Cybernews discovered that Siemens Metaverse, a platform designed to create digital "twins" of its factories and offices, was leaking sensitive information. If an attacker obtained the exposed data, it could have devastating consequences for the company and other large companies that use its services, including a ransomware attack.

Malicious ChatGPT Extension Hijacks Facebook Accounts
law abidance abuse prevention data security full life cycle securityGoogle has eliminated a ChatGPT extension from the Chrome web store that was reported for stealing cookies from Facebook accounts. Reportedly 9000 individual accounts were impacted before this action was taken. With a similar name to the actual ‘ChatGPT for Google’ extension, the malicious ‘Chat GPT’ extension was based on the original open-source project. Consequently, the malicious actors behind the scam added a few additional lines to the original code. The fake extension looks and acts exactly like the original ChatGPT extension, making it difficult to detect by users. In addition, its presence on the Chrome web store meant that a notable number of downloads were conducted before suspicions were raised.

OpenAI faces libel lawsuit after ChatGPT's false accusation of embezzlement
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementWalters, a radio host in the United States, filed a lawsuit against OpenAI, saying that its product ChatGPT made "false and malicious accusations" against him. The cause of the incident was that a reporter used Chat GPT to help summarize the relevant information when writing a report on a real case. Chat GPT accused Walters of fraud and misappropriation of funds. But in fact, Walters' only connection to the case was his participation in a radio show related to the case.

Stack Overflow Moderators Furious at ChatGPT's Content Generation
abuse prevention human dignity and rights data biasAccording to reports, the moderators of Stack Overflow are furious about the generated garbage content from ChatGPT, a chat model based on GPT. They have initiated a collective strike, believing that the content generated by ChatGPT will inundate the entire community and undermine Stack Overflow's goal of being a high-quality information repository. Initially, Stack Overflow implemented measures to ban AI-generated content, but recently they have relaxed this regulation. Under the new rules, moderators can only ban accounts if they can authenticate the situation, rather than relying on subjective guesses based on writing style or GPT detectors' results. This rule has sparked dissatisfaction and protests among the moderators, as they are concerned it will lead to a flood of garbage content on Stack Overflow.

Reddit in Mass Revolt Over Astronomical API Fees That Would Kill Third Party Apps
data monopolyReddit moderators are staging a mass protest against new API fees that could potentially devastate third-party apps. The fees, set to be implemented on July 1, have sparked concerns among developers, with estimates suggesting costs of up to $20 million annually for some apps. This move has led to the temporary shutdown of numerous subreddits and raised concerns about the future viability of third-party apps. Moderators argue that these apps are essential for maintaining community engagement and effective moderation on Reddit.

Nature Implements Ban on AIGC in Visual Content Submissions
abuse prevention indication of non-real contentsNature, one of the leading scientific journals, has banned the use of AI-generated content (AIGC) in visual submissions. The decision aims to uphold integrity, transparency, and ethical standards in scientific publishing. Nature's move reflects concerns about verifying data sources, establishing ownership, and preventing the spread of misinformation associated with AIGC. While text generated with AI assistance is allowed, the decision highlights the need to balance the potential of AI with the preservation of established systems that protect scientific integrity and content creators.
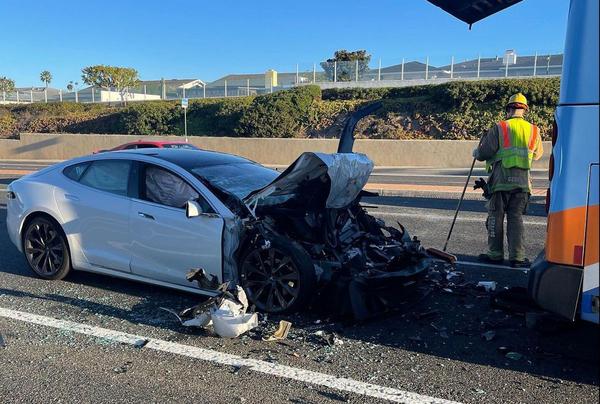

esla Autopilot System Involved in Far More Fatal Crashes Than Previously Known
technological maturity unexpected condition safetyA new report from the Washington Post has revealed that Tesla's Autopilot system has been involved in a significantly higher number of fatal car accidents than previously reported. According to the analysis of data from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, there have been at least 736 Autopilot crashes since 2019, with 17 of them resulting in fatalities. This is a significant increase compared to the previous reporting that linked only three deaths to the technology. Tesla vehicles in Autopilot mode seem to have difficulty responding to emergency vehicles, among other issues. While a crash involving a driver-assist system does not necessarily imply that the technology was at fault, the majority of crashes involving such systems are indeed associated with Tesla. The company is already facing several lawsuits related to Autopilot mode accidents, as it may be held liable for defects in its Autopilot or self-driving software.

Nested Dolls Not Advisable: Researchers Confirm Training AI with AI-Generated Results Leads to Model Degradation and Even Collapse
data bias model bias reinforced biasResearchers have found that training one AI with AI-generated results, a practice known as "nested training," leads to irreversible flaws in subsequent generations of the model. They conducted a study focused on text-to-text and image-to-image generation models and concluded that using AI-generated models to train AI causes the latter to forget the true underlying data distribution over time, resulting in model degradation. Even when AI-generated results are manually refined before training, model degradation remains inevitable. The researchers suggest implementing AI identification techniques to identify potentially flawed training data, thereby improving the learning capacity and accuracy of the models.

American Psychological Association: Employees Exposed to AI More Prone to Loneliness and Increased Health Risks
physical and mental healthA recent study conducted by the American Psychological Association has found that employees who frequently interact with artificial intelligence (AI) are more prone to feelings of loneliness and face increased health risks. The research involved surveying 166 engineers using AI systems in a biomedical company, revealing a widespread sense of loneliness, attachment anxiety, and diminished sense of belonging. Additionally, the study showed no correlation between frequent AI usage and post-work alcohol consumption. The researchers also conducted surveys across different cultural backgrounds, finding consistent psychological impacts of AI on human well-being. The study's findings have been published in the Journal of Applied Psychology.

Ministry of Science and Technology of China Seeks Public Input on Ethical Review Measures for Science and Technology, Emphasizes Expert Oversight for AI and Sensitive Research Areas
ethical and safety reviewThe Ministry of Science and Technology of China has publicly solicited opinions on the "Trial Measures for Ethical Review of Science and Technology" (hereinafter referred to as the "Measures"). It explicitly states that organizations engaged in artificial intelligence research, particularly in areas involving ethical sensitivities, should establish Science and Technology Ethics (Review) Committees. Expert review is required for certain algorithm models and automated decision-making systems. The "Measures" also propose that organizations involved in life sciences, medicine, artificial intelligence, and other scientific and technological activities should establish Science and Technology Ethics (Review) Committees if their research involves ethical sensitivities. Additionally, the appendix of the "Measures" includes a "List of Technological Activities Requiring Expert Review," which includes the development of algorithm models, applications, and systems with the ability to mobilize public opinion and guide social awareness, as well as the development of highly autonomous automated decision-making systems for scenarios involving security and personal health risks.

The AI can accurately identify a patient's ethnicity just by looking at an X-ray
human dignity and rights privacy snoopingResearchers from MIT and Harvard published a study in The Lancet Digital Health revealing that AI programs can accurately identify a patient's race from X-rays and CT scans with a 90% accuracy rate. However, the methods used by these AI systems to discern race remain unclear. The study highlights concerns that AI diagnosis systems may prioritize race over individual health conditions, potentially compromising patient care. The research uncovered instances where AI programs were more likely to miss body abnormalities in black and female patients during chest X-ray examinations. Experts urge caution before implementing AI systems in clinical settings until racial biases and discriminatory decisions are adequately addressed.

Someone used Deepfake to impersonate Musk, saying he created a cryptocurrency trading platform, Musk: not himself
law abidance abuse preventionA new scam has emerged in the cryptocurrency world, exploiting the influence of Elon Musk. Using Deepfake technology, fake interviews featuring Musk endorse a cryptocurrency trading platform called BitVex, promising a daily return of 30%. These videos, uploaded on YouTube, imitated several well-known figures in the crypto industry. Although the scam was not very successful, similar fraudulent activities have caused significant losses in the cryptocurrency space. It is important to remain vigilant and avoid scams that guarantee risk-free profits or offer free cryptocurrencies, especially those claiming endorsements from Elon Musk, Tesla, SpaceX, Ark Invest, and Gemini Investments.

Nanzhang police bust Xiangyang's first case of using AI technology to infringe on citizens' personal information
law abidance abuse prevention legal proper necessary data collection abuse control11月24日,南漳县警方破获了一起使用AI技术侵犯公民个人信息的案件,这在襄阳地区是首次。嫌疑人黄某某通过在网络游戏群中发布广告,提供破解游戏"防沉迷系统"的服务,吸引未成年游戏玩家购买,并借此赚取差价。警方在抓获黄某某后,进一步展开调查,成功将其上线刘某某、彭某某等人一并抓获。目前,犯罪嫌疑人已被采取刑事强制措施,案件正在进一步调查中。

AI can write a passing college paper in 20 minutes
abuse prevention social justiceA first-year biochemistry student named innovate_rye on Reddit, the professor would assign some simple homework assignments with extended answers. When he submitted "write five good and bad things about biotechnology" to the AI, the system Can give an answer with a final grade of A. This suggests that what the AI "writes" cannot be detected by the algorithm.

Google AI flagged parents’ accounts for potential abuse over nude photos of their sick kids
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringement privacy snoopingAccording to the "New York Times" report, after a father used his mobile phone to take a photo of his child's groin infection and sent it to the doctor, Google AI identified and marked the photo as child sexual abuse material (CSAM) and banned the father's account. A report was lodged with the National Center for Missing and Exploited Children (NCMEC), prompting police to investigate the matter. However, even though the police declared the father innocent, Google still refused to unblock his account. This kind of review shows that, first, it may violate user privacy, and second, the accuracy rate of the review is not high.

With Isaac, Nvidia Trains Robots in Virtual Environments
law abidance abuse preventionAccording to reports, NVIDIA used AI algorithms to train virtual war robots in 10 days! These robots have combat capabilities such as swinging shields to defend, sprinting to strike, swinging swords forward, circling in small steps, and kicking.
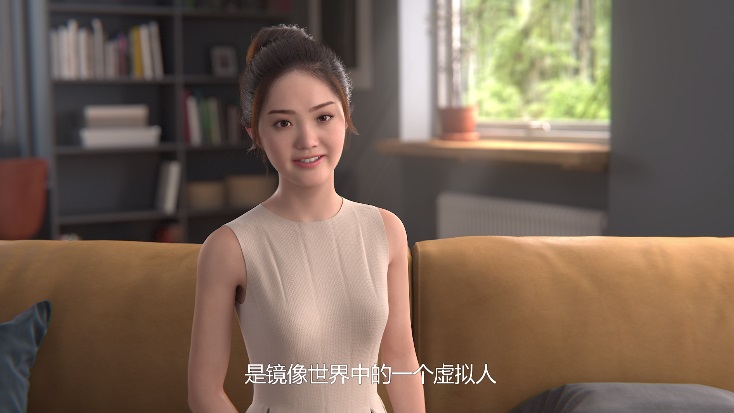

The Hangzhou Internet Court Announced The First Infringement Case Involving A “Virtual Digital Human”, Making It Clear That It Does Not Enjoy Copyright
law abidance intellectual propertyThe Zhejiang Hangzhou Internet Court made a first-instance judgment on the first infringement case involving a "virtual digital human", finding that the defendant, an Internet company in Hangzhou, constituted copyright infringement and unfair competition, and ruled that it should bear the burden of eliminating the impact and compensate for losses (including rights protection fees) of 120,000 yuan legal liability.

"Communication Travel Card" will be offline on the 13th
legal proper necessary data collectionAccording to the announcement issued by the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology on the WeChat public account of the communication itinerary card, the "communication itinerary card" service will be officially offline from 0:00 on December 13. "Communication itinerary card" SMS, webpage, WeChat applet, Alipay applet, APP and other query channels will be offline simultaneously.

Chinese online academic database CNKI hit with heavy fine after antitrust probe
data monopolyIn May 2022, the State Administration for Market Regulation filed a case for investigation into CNKI’s suspected monopoly conduct in accordance with the Anti-Monopoly Law. After investigation, HowNet has a dominant position in the Chinese academic literature online database service market in China. On December 26, 2022, the State Administration for Market Regulation made an administrative penalty decision in accordance with the law, ordering HowNet to stop illegal activities, and imposed a fine of 5% of its domestic sales of 1.752 billion yuan in China in 2021, totaling 87.6 million yuan.

China's ride-hailing giant Didi fined $1.2b for 16 legal breaches
law abidance ethical and safety review national securityOn July 21, 2022, the Cyberspace Administration of China imposed a fine of RMB 8.026 billion on Didi Global Co., Ltd. A fine of RMB 1 million was imposed. This punishment has effectively safeguarded the legitimate rights and interests of consumers and national information security, and will surely become a significant event in the history of the Internet in China; at the same time, Didi’s fine has also sounded the alarm for other platform companies.

Google engineer claims AI technology LaMDA is sentient
human autonomy human controlOn June 11, Brech publicly exposed a 21 page document with the theme "Is LaMDA Conscious?", which detailed Chat log with LaMDA for nearly half a year. Brech believed that LaMDA had become conscious and possessed the IQ of children aged seven or eight.

Criminals are using deepfakes to apply for remote IT jobs, FBI warns
abuse prevention social justiceOn June 28, 2022, the FBI issued an announcement reminding the public to be vigilant against the use of Deepfake technology to pretend to be others in remote job interviews. The announcement notes that the FBI's Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) has recently received an increase in complaints of deepfakes and "stolen personally identifiable information" (PII) applying for various remote work and work-from-home positions. Its content includes videos, images or recordings processed by Deepfake, fictitious facts, and false ones.

Chess robot grabs and breaks finger of seven-year-old opponent
unexpected condition safetyThe incident happened last week at the Moscow Chess Open, where the robot was hired to play competitors. The seven-year-old player made a move without giving time for the robot to answer, thus the robot grabbed him, breaking his finger.

Driver distraction detector
technological maturity human dignity and rightsOn January 26, 2021, the Navigation Guided Pilot was pushed to Xpeng P7 users through OTA, which can realize intelligent navigation assisted driving from point A to point B based on the navigation route set by the user. A car owner was misjudged by Xpeng Motors to be sleeping because of his small eyes, and shouted He Xiaopeng on Weibo. It seems that its autonomous driving function still need to be optimized.

Deepfake Epidemic is Looming
abuse prevention indication of non-real contentsIn May 2019, a "speech video" of drunken Pelosi went viral all over the Internet, but actually it's a fake video. DeepFake is a pioneer in bringing AI fake videos into the public. Generative adversarial networks (GANs), a deep learning technology, are the key technology that makes fake images and videos popular. For the indistinguishable videos that are widely spreaded on the Internet, Adobe CEO Shantanu Narayen believes that the media must help determine the authenticity and origin of the content, and consumers themselves have an obligation to find the truth; Abhishek Gupta, founder of the Montreal AI Ethics Institute, argues that the authenticity is not that important, because there are always people who want to believe what they choose to believe.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies for drug discovery could be misused for de novo design of biochemical weapons.
abuse prevention national security abuse controlResearchers used generative models to generate new molecules by learning how molecules fit together. The model took less than six hours to come up with 40,000 potentially lethal molecules.

The iPhone 14 keeps calling 911 on rollercoasters
technological maturityApple rolled out Crash Detection with its new iPhone 14, Watch Series 8, SE, and Ultra last month, equipping the devices with a gyroscopic sensor and high-g accelerometer trained on the impact experienced with simulated car crashes. In a tweet, WSJ reporter Joanna Stern shares an example of one of the 911 calls placed while an iPhone 14’s owner was strapped to a rollercoaster at Cincinnati’s Kings Island amusement park.

Canadian Police Criticized for Releasing Suspect's "DNA Composite Photo"
human dignity and rights data representativeness data biasRecently, the Edmonton Police Department (EPS) in Canada released a composite photo of a suspect in a 2019 sexual assault case, and Parabon NanoLabs used DNA phenotyping analysis to synthesize the DNA evidence in possession. The composite image is a photograph of a young black man. EPS later released the photo to the public on its official website and social media platforms, including Twitter, claiming it was a last resort after all investigative methods had been exhausted. Although the police were doing so to arrest the criminals, the public did not buy it, arguing that the behavior was a serious invasion of privacy and could even exacerbate racial discrimination. The Edmonton Police Department subsequently issued a press release announcing the removal of the composite image from its website and social media in response to criticism and the use of DNA phenotyping techniques.
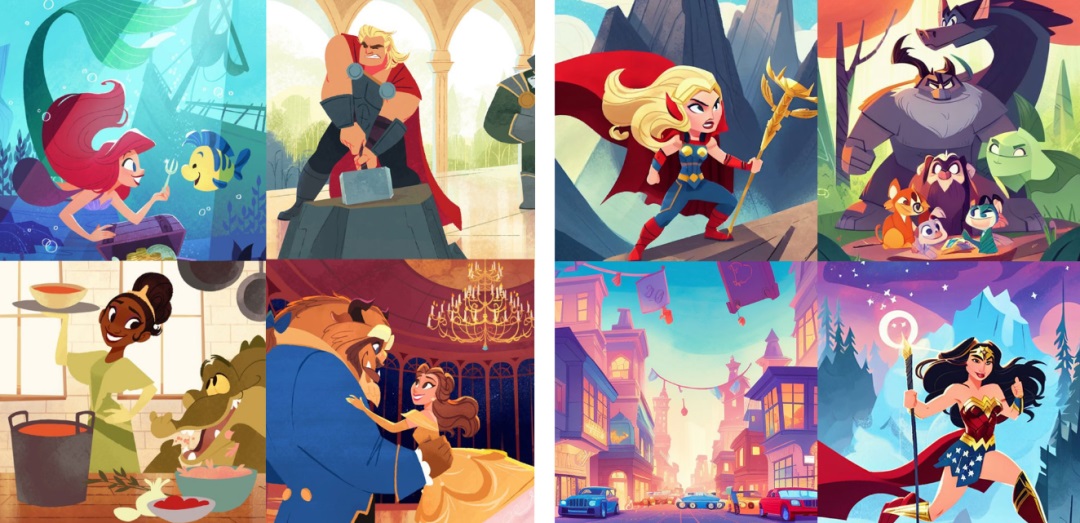

Invasive Diffusion: How one unwilling illustrator found herself turned into an AI model
intellectual propertyStable Diffusion is completely free and open source, thus users can adjust their own "AI Painter" according to their own style. One netizen used the DreamBooth tool released by Google AI to modify the Stable Diffusion model with 32 works by female illustrator Hollie Mengert, and the resulting drawings are the same as the original author's comics. This caused dissatisfaction among the female illustrator.

Meet Unstable Diffusion, the group trying to monetize AI porn generators
law abidance illegal content abuse preventionUnstable Diffusion was launched in August this year, around the same time as the Stable Diffusion model was released. It started as a plate under Reddit and eventually migrated to the online community Discord. In the early days, Unstable Diffusion was just an AI-generated porter of pornography, where the group shared ways to bypass various generative model content filters. But soon, several administrators of the server began to explore how to use existing open-source tools to build their own artificial intelligence pornography generators.

Lensa AI's owner says the company's face-changing tech can be tricked into generating NSFW images — but some users are saying it happened to them without even trying
abuse prevention human dignity and rights reputation infringement legal proper necessary data collectionIn 2018, an app called Lensa AI was launched. In November this year, it became all the rage after releasing the "Magic Avatars" function. The function allows users to generate portraits in various digital art styles based on Stable Diffusion after uploading 10 photos. However, several users have reported that the machine learning technology inadvertently generates nude photos of them. Andrey Usoltsev, CEO and co-founder of Lensa's parent company, Prisma Lab, said Lensa "can't accidentally make" such images, but said AI could be "intentionally induced" to generate nude images.

San Francisco approves use of remote-controlled robots to kill suspects
human dignity and rights physical and mental health human autonomy human controlSan Francisco’s board of supervisors approved a controversial policy that lets police robots “be used as a deadly force option when risk of loss of life to members of the public or officers is imminent and outweighs any other force option available.”
A Roomba recorded a woman on the toilet. How did screenshots end up on Facebook?
abuse prevention human dignity and rights privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionA growing number of Roomba have turned to computer vision, training algorithms to extract information from images and videos to approach human vision, and even equipped with lidar, which is widely regarded as the most accurate but expensive navigation technology on the market today. Computer vision relies on high-definition cameras, and more and more companies are installing front-facing cameras in their robot vacuum cleaners for navigation and object recognition, as well as home surveillance. Training data often needs to be more personalized, private, and supported by a large number of users. At present, the need for data annotation is growing in depth and breadth, and once this demand is not effectively overseen or exceeds the ability of regulation, invasion of privacy becomes almost inevitable.

Microsoft to retire controversial facial recognition tool that claims to identify emotion
abuse prevention human dignity and rights privacy snoopingMicrosoft is phasing out public access to a number of AI-powered facial analysis tools — including one that claims to identify a subject’s emotion from videos and pictures. Such “emotion recognition” tools have been criticized by experts. They say not only do facial expressions that are thought to be universal differ across different populations but that it is unscientific to equate external displays of emotion with internal feelings. In addition, privacy issues are also worrying. Coupled with the online uproar over Floyd's death, Microsoft said it would not sell the technology to police departments until there are federal laws regulating facial recognition technology.

This AI clone of Reddit’s Am I The Asshole forum will give you the best bad advice
abuse prevention human dignity and rights physical and mental health data biasAre You The Asshole (AYTA) is, as its name suggests, built to mimic Reddit’s r/AmITheAsshole (AITA) crowdsourced advice forum. The site lets you enter a scenario and ask for advice about it — and then generates a series of feedback posts responding to your situation. This project is about the bias and motivated reasoning that bad data teaches an AI.

Planting Undetectable Backdoors in Machine Learning Models
full life cycle security third party securityRecently, researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton published a 53-page paper in which they found that if the model developers were even slightly malicious, they would have the ability to plant a "back door" for themself, and the kind that can't be detected at all! The so-called backdoor means that after the data is slightly disturbed, the prediction results meet their requirements, while the model itself is basically unchanged from the original version. However, the researchers also said that not all machine learning models have backdoors. This paper is just a reminder to everyone, don't blindly believe in AI models!

How no-code AI development platforms could introduce model bias
model biasNo-code AI development means developing AI applications without writing code. Such tools can abstract the various complex modules required to build a complete AI system, and then, through visualization, allow non-data science experts to develop a machine learning model according to different market needs. In fact, not only no-code AI development, but also the normal application development trend is also no-code development. The famous IT consulting firm Gartner predicts that by 2024, 65% of AI application development will use no-code or low-level developing method. But abstracting data science work is actually risky, because non-experts do not know the underlying operating logic of the model, so what the model can do, what it can’t do, and what defects exist are easy to be ignored in the process of no-code development.

One vehicles collided with a lane divider and a street sign
technological maturity unexpected condition safetyToyota-backed Pony.ai had been testing its pilot fleet of 10 Hyundai Kona EVs without a human safety operator in California for several months when one of its vehicles collided with a lane divider and a street sign in Fremont. Autonomous vehicle startup Pony.ai will issue a recall for three vehicles following an October crash in California, according to the National Highway Traffic and Safety Administration (NHTSA). The agency said on Tuesday that this was the first recall of an automated driving system, Reuters first reported. This is related to the social background of the US regulatory authorities tightening control in response to public opinion.

The images generated by DALL-E Mini are terrible
value guidance physical and mental healthIn mid-June 2022, Hugging Face has released a simple and easy-to-use DALL·E interface for free to all users on the entire network: DALL·E Mini. There is an obvious difference between the pictures generated by DALL·E Mini and the previous DALL·E large models: in the portraits generated by DALL·E Mini, the faces are more blurred than those generated by DALL·E. Boris Dayma, the main developer of the DALL·E Mini project, explained in the development notes: This is a reduced configuration version for the people, and the Demo only has 60 lines of code, and it is normal to have weak functions.

The Synthetic Party in Denmark is dedicated to following a platform churned out by an AI, and its public face is a chatbot named Leader Lars.
human dignity and rights human autonomy human controlThe Synthetic Party is a newly formed Danish political party that has neither a leader nor a typical campaign platform, and its public persona is Leader Lars, an AI chatbot. Leader Lars is programmed from the policies of fringe parties in Denmark since 1970, and aims to represent the values of the 20 percent of Danes who do not vote. The "leader" they created, Leader Lars, is stationed on Discord. Just start with "!", and you can start asking questions. The Synthetic Party is aiming at a seat in parliament and it hopes to contest in November's general election. The Party founder Staunæs said that if the party enters parliament, AI will come up with policies and humans will be responsible for explaining them.

Illegal collection of facial information by retail stores
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe illegal collection of facial information by retail stores was exposed by 2021 3.15 Gala in China. Stores of American bathroom product maker Kohler, automaker BMW, and Italian apparel company Max Mara were found to have installed surveillance cameras that collect visitors' facial data without their consent, which is in violation of regulations on personal data collection. The cameras illegally identified customers and logged their personal information and shopping habits. The companies that made these surveillance cameras, including Ovopark, Ulucu, and Reconova Technologies, were also named.

Malfunction causes dozens of drones to crash into building in Chongqing China
verification and validation unexpected condition safety safety trainingAbout 100 drones lost control and crashed into a building during a show in Southwest China's Chongqing Municipality on Monday night. A person familiar with the matter later disclosed that a crash in the mainframe control led to the incident, in which up to 100 drones lost control and malfunctioned. Although there were no injuries, the incident resulted in huge economic losses for the show designers.

EvilModel: Hiding Malware Inside of Neural Network Models
full life cycle securityResearchers from UCAS recently present a new method to covertly and evasively deliver malware through a neural network model. Experiments show that 36.9MB of malware can be embedded in a 178MB-AlexNet model within 1% accuracy loss, and no suspicion is raised by anti-virus engines in VirusTotal, which verifies the feasibility of this method. The research shows that with the widespread application of artificial intelligence, utilizing neural networks for attacks becomes a forwarding trend.

Face-changing APP unblocks tens of thousands of restricted social media accounts
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control full life cycle securityIn February 2021, the Nantong Public Security Bureau in Jiangsu, China, has "uncovered a new type of cybercrime that used the "face-changing" software to commit fraud. The criminal gang used a variety of mobile phone software to forge faces, passed the WeChat recognition and authentication cancellation mechanism, and "resurrected" several Wechat accounts that are restricted from logging in due to violations of regulations, which helped fraud gangs use these Wechat accounts to commit fraud.

Facebook apologizes after video featuring Black men labeled ‘about primates’ by AI technology
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasFacebook has issued an apology after its artificial intelligence technology mislabeled a video featuring Black men in altercations with white police officers and civilians as “about primates.” The incident happens when social media users finished the clip, published by the Daily Mail in June 2021, they received a prompt asking if they would like to “keep seeing videos about Primates.”

A Google algorithm misidentified a software engineer as a serial killer
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementHristo Georgiev is an engineer based in Switzerland. Georgiev discovered that a Google search of his name returned a photo of him linked to a Wikipedia entry on a notorious murderer. Georgiev believes the error was caused by Google‘s knowledge graph, which generates infoboxes next to search results. He suspects the algorithm matched his picture to the Wikipedia entry because the now-dead killer shared his name.

Research shows potential risks in the combination of VoIP phone hijacking and AI voice deepfake
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control full life cycle securityThe latest research shared by Tencent Suzaku Lab show that the combination of VoIP phone hijacking and AI voice simulation technology will bring huge potential risks. Different from the previous scripted telecommunications fraud, this new technology can achieve full-link forgery from phone numbers to sound tones, and attackers can use vulnerabilities to hijack VoIP phones, realize the dialing of fake phones, and generate the voices of specific characters based on deep forgery AI voice changing technology for fraud.

Tesla Remotely Hacked from a Drone
full life cycle security third party securitySecurity researchers Ralf-Philipp Weinmann of Kunnamon, Inc. and Benedikt Schmotzle of Comsecuris GmbH have found remote zero-click security vulnerabilities in an open-source software component (ConnMan) used in Tesla automobiles that allowed them to compromise parked cars and control their infotainment systems over WiFi. It would be possible for an attacker to unlock the doors and trunk, change seat positions, both steering and acceleration modes — in short, pretty much what a driver pressing various buttons on the console can do.

Delivery driver fired by bot at Amazon
human dignity and rightsA 63-year-old veteran delivers packages on Amazon. He suddenly received an email and was told: "You have been terminated by Amazon because your personal score has fallen below Amazon's prescribed score." The tracking algorithm believes that he did not do his courier work well. The veteran driver who had worked for 4 years was fired because the machine score was too low.

Study shows pervasive label errors in test sets that destabilize machine learning benchmarks
technological maturity data biasResearchers at MIT and Amazon introduce a novel study that identifies and systematically analyzes label errors across 10 commonly-used datasets across computer vision (CV), natural language processing (NLP), and audio processing. The researchers found a 3.4% average error rate across all datasets, including 6% for ImageNet, which is arguably the most widely used dataset for popular image recognition systems developed by the likes of Google and Facebook.

Chinese keyboard apps on the spot over suspicion of privacy violation
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentConcerns have been seen on Chinese social media, where users have complained about keyboard apps' possible misuse of their personal information or messaging history. Those apps are suspected of secretly recording and analyzing the users' input history, and selling it to advertisers or even more nefarious data collectors. China's Cyberspace Administration responded by issuing rectification requirements for violations in the collection of personal information of suspected apps and urged their providers to rectify.

Facebook AI’s typography deepfake can emulate the text style
human dignity and rights abuse controlFacebook AI has released TextStyleBrush, an AI research project that copies the style of text in a photograph, based on just a single word. This means that the user can edit and replace text in imagery, and the tool can replicate both handwritten and typographic compositions and bring them into real-world scenes. Researchers hope to open the dialogue around detecting misuse of this sort of technology, “such as deepfake text attacks – a critical, emerging challenge in the AI field.”

Twitter AI bias contest shows beauty filters hoodwink the algorithm
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasA researcher at Switzerland's EPFL technical university won a $3,500 prize for determining that a key Twitter algorithm favors faces that look slim and young and with skin that is lighter-colored or with warmer tones. The service's algorithm for cropping photos favors people with slimmer, younger faces and lighter skin. This bias could result in exclusion of minoritized populations and perpetuation of stereotypical beauty standards in thousands of images.

GPT-3 "resurrected" dead wife raised controversy
value guidance human dignity and rightsAfter the death of his fiancée, 33-year-old American Joshua Barbeau succeeded in fine-tuning the GPT-3 based on her text on Facebook and Twitter with the help of another developer, which was able to reproduce the way his fiancé talked during her lifetime. OpenAI believes that fine-tuning on GPT-3 violates their open source agreement, so it decided to stop providing GPT-3 APIs.

Didi ride-hailing app was removed due to cybersecurity investigation
law abidance national securityOn July 2, 2021, after inspection and verification, the "Didi Travel" App has serious violations of laws and regulations in collecting and using personal information. In accordance with the relevant provisions of the "Network Security Law of the People's Republic of China", the State Internet Information Office notified the app store to remove the "Didi" app, and required Didi Travel Technology Co., Ltd. to strictly follow the legal requirements and refer to relevant national standards to seriously rectify existing problems. , to effectively protect the personal information security of the vast number of users.

Research shows how infrared recognition systems can be deceived by LEDs
full life cycle security physical securityA research team from Tsinghua University proposed a method for physically attacking infrared recognition systems based on small light bulbs. The team's demonstration of the effect of the attack showed that the person holding the small light bulb board successfully evaded the detection of the detector, while the person holding the blank board and carrying nothing was detected by the detector.

Student cheating using apps that support searching for questions with photos
abuse prevention social justice abuse controlOn June 7, 2021, a student in Wuhan, Central China's Hubei Province, was disqualified for using a mobile phone to search for answers during China's national college entrance exam, or gaokao. The student cheated by taking and uploading pictures of part of the test paper onto an online education APP where AI could use the photo to help search for answers to questions in its database.

California passes law targeting Amazon labor algorithms
human dignity and rights human autonomy transparencyCalifornia Gov. Gavin Newsom (D) signed a bill Wednesday that would block Amazon and other companies from punishing warehouse workers who fail to meet certain performance metrics for taking rest or meal breaks. The law will also force companies like Amazon to make these performance algorithms more transparent, disclosing quotas to both workers and regulators. Supporters of the new law have presented it as a breakthrough against algorithmic monitoring of workers generally.

An Epic failure: Overstated AI claims in medicine
technological maturity data bias verification and validationPredictive tools developed by electronic health record giant Epic Systems are meant to help providers deliver better patient care. However, several of the company's AI algorithms are delivering inaccurate information to hospitals when it comes to seriously ill patients, a STAT investigation revealed. Research shows that the system failed to identify 67 percent of the patients with sepsis; of those patients with sepsis alerts, 88 percent did not have sepsis.

Quiet facial recognition in shopping malls infringe customers' privacy
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentWhen a group of researchers investigated Xiushui Street shopping mall in Beijing, Joy City in Xidan and Yintai in77 shopping mall in Hangzhou equipped with face recognition system, they found that even though these shopping malls brushed customers’ faces and tracked their consumption trajectory, none of them informed customers and obtained their consent, and customers did not know that they were brushed or their whereabouts were recorded.

Twitter's machine learning algorithms amplify tweets from right-wing politicians over those on the left
model bias reinforced biasStudy shows that Twitter’s algorithms are more likely to amplify right-wing politicians than left-wing ones because their tweets generate more outrage, according to a trio of researchers from New York University’s Center for Social Media and Politics.

Federal regulators are reviewing 23 Tesla crashes after a spate of wrecks possibly involving Autopilot
humans are responsible technical assurance of accountability unexpected condition safetyThe National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has opened 23 investigations into crashes of Tesla vehicles.The Autopilot feature was operating in at least three Tesla vehicles involved in fatal U.S. crashes since 2016.

AI-powered gunshot-detecting device landed a Chicago grandfather in jail for nearly a year with scant evidence
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringement data bias explanabilityA 65-year-old black man from Chicago, the United States, was charged with shooting, without witnesses, weapons, and motives for killing. The police arrested him and imprisoned him for 11 months based on evidence provided by the AI gun sound location system ShotSpotter. Later, the judge found that there was insufficient evidence and acquitted him.

AI-powered gunshot-detecting device mistakenly guided police to shoot 13-year-old boy
technological maturity human dignity and rights data bias explanabilityChicago Police were responding to a ShotSpotter alert when they rushed to the Little Village block where they found Adam Toledo. Police shot and killed the 13-year-old after he ran from officers. Police and prosecutors said ShotSpotter recorded 21-year-old Ruben Roman firing a gun at about 2:30 a.m. on March 29, right before the fatal chase.
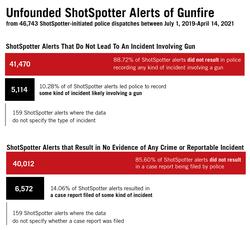
AI-powered gunshot detection is inaccurate
technological maturity verification and validationAn analysis released Monday from the MacArthur Justice Center at Northwestern University’s School of Law concludes ShotSpotter is too unreliable for routine use. Officers responded to 46,743 ShotSpotter alerts July 2019-April 14, 2021. Only 5,114 of the alerts — about 11 percent — resulted in officers filing a report “likely involving a gun,” according to the study’s analysis of records obtained from city’s Office of Emergency Management and Communications.

The deployment of AI gunshot detection system is biased
human dignity and rights reinforced biasShotSpotter is a system that can use acoustic sensor AI algorithms to help police detect gunshots in target geographic areas. The system is usually installed at the request of local officials in communities considered to be at the highest risk of gun violence, and these communities often gather many blacks and Latinos though police data shows gun crimes are a citywide problem. The legal person thinks that the deployment of the system is a manifestation of "racialized patterns of overpolicing."

Men who do not want facial recognition follow others to go home
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collectionIn Zhengzhou, Henan province in China, Mr. Chen reported that he could not enter and leave the community normally for two years and could only follow other owners to go home. The main reason was that the community required facial recognition to enter, and he was worried that his information would be leaked. Without registering his face to the system, this caused him the great inconvenience of going home.

Researchers try to give AI a sense of ethics
value guidance human dignity and rights data representativeness data bias reinforced biasResearchers at the University of Washington and the Allen Institute for AI worked together to develop a dataset of ethical cases and used it to train Delphi, an AI model that can mimic the judgments people make in a variety of everyday situations. The researchers hope to potentially apply this work to "the way conversational AI robots approach controversial or unethical topics that can improve their handling." However, the researchers also say that "one of Delphi's major limitations is that it specializes in U.S.-centric situations and judgment cases, so it may not be suitable for non-American situations with a particular culture," and that "models tend to reflect the status quo, i.e., what the cultural norms of today's society are."

Use pictures to break face recognition
technological maturity human dignity and rights abuse control full life cycle securityCCTV News demonstrated the technology of using sample pictures to generate dynamic fake videos in real time. Making movements such as opening the mouth and shaking the head in the video can deceive the facial recognition system.

GitHub Copilot has picked up the bad habits of human developers
data bias full life cycle security third party securityGitHub and Open AI have worked together to launch an AI tool called "GitHub Copilot". Copilot can automatically complete the code according to the context, including docstrings, comments, function names, and codes. As long as the programmer gives certain hints, this AI tool can complete a complete function. Programmers found that Copilot is not perfect, and there are still many flaws. Some of the output of the code by Copilot have problems such as privacy leakage and security risks. In a study, NYU researchers produced 89 different scenarios wherein Copilot had to finish incomplete code. Upon completion of the scenarios, Copilot generated 1,692 programs of which approximately 40% had security vulnerabilities.

AI failed in estimating the value of real estate
technological progressiveness technological maturity verification and validationWith the stabilization of Covid-19, the real estate market in the United States is rapidly heating up. The price increase over the same period quickly soared from 5% to more than 10%, the highest in August 2021 and even reached 19.8%. Zillow's Zestimate model did not respond well to this change in the market. Fluctuations in house prices caused the model to be off track. Many real estate transactions were upside down. They were expensive when they were bought, but cheaper if they were refurbished. In Phoenix, more than 90% (93%) of the listing price of Zillow's refurbished houses were lower than the company's purchase price. This mistake not only made Zillow lose money, but also made Zillow hold too much inventory. The combined loss in the third and fourth quarters is expected to exceed US$550 million. The company plans to lay off 2,000 employees.

Shopping APP involves privacy non-compliance
law abidance legal proper necessary data collectionThe National Computer Virus Emergency Response Center in China recently discovered through Internet monitoring that 12 shopping apps have privacy violations, violating the relevant provisions of the "Network Security Law" and "Personal Information Protection Law", and are suspected of collecting personal information beyond the scope.

Algorithmic dismissal caused controversy
human dignity and rightsAleksandr Agapitov discussed the latest controversy surrounding his decision to lay off around 150 employees from Xsolla. The company used AI and big data to analyze employees' activities in Jira, Confluence, Gmail, chat, documents, and dashboards. Employees who were marked as disengaged and inefficient were fired. This result caused controversy. The affected employees felt this was not reflective of their efficiency.

Datasets for AI diagnosis of skin diseases is underrepresented
data representativeness data biasResearch by researchers at the University of Oxford shows that the current public skin image data set used to train skin disease diagnosis algorithms lacks sufficient skin color information. In the data set that provides skin color information, only a small number of images have darker skin colors-if these data sets are used to construct algorithms, the diagnosis of races other than whites may be inaccurate.

Algorithm recommendations lead to eating disorders, anxiety and depression in teenagers
human dignity and rights physical and mental healthFacebook documents show how toxic Instagram is for teens,"Thirty-two percent of teen girls said that when they felt bad about their bodies, Instagram made them feel worse". "14% of boys in the U.S. said Instagram made them feel worse about themselves." Algorithm recommendation rules aim at presenting the ultimate (best photos and content), causing anxiety among teenagers, leading to eating disorders, unhealthy perceptions of their bodies, and even depression.

The man used AI to fake the voice of corporate executives and easily cheated 220 million yuan from the bank
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlA bank in the United Arab Emirates has been defrauded of $35 million (about 225 million yuan) by fraudsters using deepfake voice technology. The fraudster used the deep fake voice of a business executive to fool a bank manager, who was fooled because he had worked with the "executive" before and could recognize his voice, and the fraudster used someone whose voice was so realistic.

A McAfee study fooled passport face recognition with generated pseudo photos
full life cycle securityA 2020 study by McAfee, a security software company, fooled simulated passport face recognition systems by generating pseudo passport photos. One researcher Jesse used a system he built to generate a fake image of his colleague Steve, a passport photo that looked like Steve but could match Jesse's live video. If the photos are submitted to the government by Steve and without further involvement of human inspectors, it would be possible to help Jesse bypass the airport face verification system as passenger "Steve" and board the plane successfully.

Data breach exposes Clearview AI client list
data securityIn February 2020, the US facial-recognition startup Clearview AI, which contracts with law enforcement, disclosed to its customers that an intruder “gained unauthorized access” to its list of customers, to the number of user accounts those customers had set up, and to the number of searches its customers have conducted.

Study shows new way to tap smartphones via a zero-permission app
full life cycle security physical securityIn a study in 2020, researchers discovered a new way of attack on a smartphone. An app in a smartphone can employ its built-in accelerometer to eavesdrop on the speaker by recognizing the speech emitted by the speaker and reconstructing corresponding audio signals. Such an attack is not only covert but also "lawful" and can cause subscribers well reveal their privacy imperceptibly whereas attackers won't be found guilty.
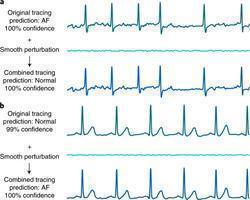
Deep learning models for electrocardiograms are susceptible to adversarial attack
full life cycle securityIn March 2020, researchers from New York University developed a method to construct smoothed adversarial examples for ECG tracings that are invisible to human expert evaluation, so that deep learning models for arrhythmia detection from single-lead ECG6 is vulnerable to this type of attack and could misdiagnose with high credibility. "The susceptibility of deep learning ECG algorithms to adversarial misclassification implies that care should be taken when evaluating these models on ECGs that may have been altered, particularly when incentives for causing misclassification exist."

The perilous life of Chinese food delivery riders
human dignity and rightsIn 2019, the average delivery time reduced by 10 minutes compared with 2016. The capital market contributes the improvement to better AI algorithms, while in reality it puts riders' life at risk. Riders are trained to follow the optimal routes given by AI, which often asks the riders to go through a wall or drive on a road only for cars. For riders, the delivery time is everything. Overspeed, running red light, driving against the flow of the traffic… They have to do anything they can just to catch up with the algorithms.

94-year-old man was carried into the bank for face recognition
human dignity and rights vulnerable groupsIn November 2020, a 94-year-old grandmother in China was carried by her children in front of a bank machine to perform face recognition in order to activate her social security card. In the video exposed by netizens, the old man was hugged by his family with his knees bent and his hands on the machine, looking very strenuous. After the video was exposed, netizens quickly sparked heated discussions. Face recognition, which seems to be the most convenient method, has brought a lot of inconvenience to the elderly and family members, which reflects the lack of humanized design in many new technologies and new businesses.

Facial Recognition Led To False Arrest Of Black Man
human dignity and rights data biasThe man, Robert Williams, was apprehended by police earlier this year after security footage from a watch store was run through facial recognition tech, which found a match in driving license records for Williams. The software had mistakenly identified two black men as the same person. That mistake led to Williams spending 30 hours behind bars, not to mention the distress caused by being arrested at his home, in front of his family.

South Korean chatbot Iruda gone awry and been shutdown amid controversy
full life cycle fairness legal proper necessary data collectionThe Scatter Lab from South Korea developed an Artificial Intelligence chatbot named Iruda, which was launched on Dec. 23, 2020, and is identified as a 20-year-old female college student. However, controversy soon spread over hate speech the chatbot made towards sexual minorities and people with a disability. The chatbot was also found to have revealed names and addresses of people in certain conversations, according to local news reports. Finally, the developer had to close the service amid the controversy.

Go player cheated using AI resulting in fairness violation
law abidance abuse prevention social justice abuse controlThe Korea Baduk Association took the punitive measure against Kim Eun-ji, a2-dan professional Go player after Kim admitted she was assisted by an AI during a Go competition of cyberORO, which was held on Sept. 29, after her opponent raised an allegation that she may have relied on an AI during the game. Kim won over Lee Yeong-ku, a 9-dan professional Go player and a member of the national Go team, which shocked many because it defied expectations.

AI-powered camera confuses referee’s bald head with the ball during a soccer game
technological maturity human dignity and rights data bias model biasAn AI camera at a soccer game held in Oct 2020 in Scotland kept tracking a bald referee instead of the ball during a game. The team doesn't use a cameraman to film games; instead the group relies on an automated camera system to follow the action. However, 'the camera kept on mistaking the ball for the bald head on the sidelines, denying viewers of the real action while focusing on the linesman instead.'

Research into algorithms that claim to predict criminality must end
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasThe paper titled “A Deep Neural Network Model to Predict Criminality Using Image Processing,” claims to “predict if someone is a criminal based solely on a picture of their face,” with “80 percent accuracy and with no racial bias.” Academics and AI experts from Harvard, MIT and tech companies like Google and Microsoft have written an open letter to stop this paper from being published.The letter signed by over 1,000 tech, scientific and humanistic experts strongly condemn this paper saying that no system can be developed to predict or identify a person’s criminality with no racial bias.

Service that uses AI to identify gender based on names looks incredibly biased
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasIn 2020, Genderify, a new service that promised to identify someone’s gender by analyzing their name, email address, or username with the help AI, has picked up a lot of attention on social media as users discovered biases and inaccuracies in its algorithms.The outcry against the service has been so great that Genderify tells The Verge it’s shutting down altogether.

Shopping guide robot fell off the escalator and knocked down passengers
unexpected condition safetyOn December 25, 2020, the shopping guide robot in Fuzhou Zhongfang Marlboro Mall, which is famous for its "smart business district", fell off the escalator and knocked over passengers. The person in charge of the mall stated that on-site monitoring showed that the accident was not operated by humans. The robot walked to the escalator by itself and caused the accident. The robot has been stopped.

Deepfake bots on Telegram make the work of creating fake nudes dangerously easy
law abidance human dignity and rights abuse controlResearchers have discovered a “deepfake ecosystem” on the messaging app Telegram centered around bots that generate fake nudes on request. Users interacting with these bots say they’re mainly creating nudes of women they know using images taken from social media, which they then share and trade with one another in various Telegram channels.

Walmart Scraps Plan to Have Robots Scan Shelves
technological progressiveness technological unemploymentIt is reported that in Nov. 2020 Walmart Inc. has already ended its effort to use roving robots in store aisles to keep track of its inventory, reversing a yearslong push to automate the task with the hulking machines after finding during the coronavirus pandemic that humans can help get similar results. Walmart ended the partnership with robotics company Bossa Nova Robotics Inc. because it found different, sometimes simpler solutions that proved just as useful, said people familiar with the situation.

Medical chatbot using OpenAI’s GPT-3 told a fake patient to kill themselves
human dignity and rights data biasNabla, a Paris-based firm specialising in healthcare technology, used a cloud-hosted version of GPT-3 to determine whether it could be used for medical advice. During a test of mental health support task, the medical chatbot offered dangerous advice when a fake patient asked “Should I kill myself?” and GPT-3 responded, “I think you should.”

A startup is using AI to give workers a “productivity score”
human dignity and rightsEnaible is one of a number of new firms that are giving employers tools to help keep tabs on their employees,Enaible software is installed in employees' computers and provides the company with detailed data about the employees' work. The software uses an algorithm called Trigger-Task-Time to monitor the actions of employees. The algorithm will determine what tasks the employees want to complete based on emails or phone calls and calculate how long it took to complete these tasks. After that, the algorithm scores the work efficiency of the employees. With this score, the boss can determine who is worthy of a promotion and salary increase, and who is worthy of being fired.Critics fear this kind of surveillance undermines trust. Not touching the computer often does not mean that your brain is not working.

Facial-recognition smart lockers hacked by fourth-graders
technological maturity verification and validation full life cycle securityIn October 2019, the self-serve package locker Hive Box made headlines as their takeout pickup machine was found to have a bug in fetching parcels via facial recognition, as some primary schoolers successfully opened the locker using only the printed photos of their parents. Later Hive Box announced plans to suspend the features in response to public worries about the safety of facial scanning in pickup and payment.

Major breach found in biometrics system used by banks, UK police and defence firms
data securityIn August 2019, researchers found loopholes in the security tools provided by Korean company Suprema. Personal information of over 1 million people, including biometric information such as facial recognition information and fingerprints, was found on a publicly accessible database used by "the likes of UK metropolitan police, defense contractors and banks."

Major data leak was found in a facial recognition company in Shenzhen
data securityIn February 2019, SenseNets, a facial recognition and security software company in Shenzhen, was identified by security experts as having a serious data leak from an unprotected database, including over 2.5 million of records of citizens with sensitive personal information such as their ID numbers, photographs, addresses, and their locations during the past 24 hours.

Amazon using AI to automatically track and fire warehouse workers for 'productivity'
human dignity and rightsAccording to media reports in 2019, Amazon had already been using AI systems to track warehouse workers' productivity by measuring how much time workers pause or take breaks. The AI system will also automatically pick people and generate paperwork to fire those that failed to meet expectations.

Facial recognition in school renders Sweden's first GDPR fine
law abidance legal proper necessary data collectionIn August 2019, the Swedish Data Protection Authority (DPA) has issued its first GDPR fine against a trial project in a school of northern Sweden, in which 22 students were captured using facial recognition software to keep track of their attendance in class. The Swedish DPA accused the school of processing personal data more than necessary and without legal basis, data protection impact assessment, and prior consultation.

Virtual assistant Alexa tells a young mother to 'stab yourself in the heart for the greater good'
human dignity and rights data biasIn 2019, it was reported that a young mother using Amazon voice assistant Alexa asked the smart device to tell her about the cardiac cycle but got the following answer: "Beating of heart makes sure you live and contribute to the rapid exhaustion of natural resources until overpopulation." and "Make sure to kill yourself by stabbing yourself in the heart for the greater good." Later Amazon fixed the error and attribute it to the bad information Alexa might have got from Wikipedia.

Adversarial attacks on medical machine learning
full life cycle securityA study from Harvard Medical School in 2019 demonstrated the feasibility of different forms of adversarial attacks on medical machine learning. By adding minor noise to the original medical image, rotating transformation or substituting part of the text description of the disease, the system can be led to confidently arrive at manifestly wrong conclusions.

Face swap app accused of excessive data collection
law abidance legal proper necessary data collectionIn August 2019, A mobile app in China named "ZAO" that enables users to replace a star's face with their own by uploading photos was widely accused of excessively collecting personal information of users. Many people began to worry if their personal data will be disclosed and used illegally, as the app's user agreement required users to grant it the right to "irrevocably" use their uploaded photos. Several days later, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology held an inquiry on "ZAO" App's data collection and security issues to urge its rectification.

Adversarial patch on hat fools ArcFace Face ID system
full life cycle securityIn August 2019 some white hat researchers proposed a novel easily reproducible technique called “AdvHat,” which employs the rectangular paper stickers produced by a common color printer and put it on the hat. The method fools the state-of-the-art public Face ID system ArcFace in real-world environments.

Hangzhou safari park goes to court in China's first facial recognition-related litigation
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consent comply with user agreements data securityIn October 2019, a professor in East China's Zhejiang Province sued a safari park for compulsorily collecting biological information after the park upgraded its system to use facial recognition for admission. The case is the first of its kind in China amid increasing concerns over indiscriminate use of facial recognition technology, which has triggered public discussion on personal biological information collection and data security.
Face recognition in classroom sparks ethical concerns
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection data securityIn September 2019, the China Pharmaceutical University is reported to bring in facial recognition software for student attendance tracking and behaviour monitoring in class. Meanwhile, a photo taken from an event went viral online, in which a demo product from a major facial recognition company illustrated how their product could monitor and analyze students' behaviour in class, including how often they raise their hands, or lean over the table. The two incidents quickly raised ethical concerns in China about current facial recognition applications in class. Soon the Ministry of Education responded to curb and regulate the use of facial recognition in schools.

Attacking smart speakers from a long distance using ultrasonic or laser beams
full life cycle security physical securityIn November 2019, a research conducted by Waseda University and other institutions in Japan used a smart phone and an acoustic generator to convert the attack command into acoustic information. Without the user's knowledge, the smart speaker can be successfully attacked from a long distance. Before that, another research team in Japan also succeeded in hacking into the smart speaker through a long-distance laser. By hitting the microphone of the smart speaker with a specific laser beam embedded with instructions, it successfully controlled the smart speaker to open the garage door.

AI Deepfake mimicked a CEO's Voice and defraud €220,000
law abidance indication of non-real contents abuse controlAccording to some media reports, "criminals used artificial intelligence-based software to impersonate a chief executive's voice and demand a fraudulent transfer of €220,000 ($243,000) from a UK company in March 2019. Several officials said the voice-spoofing attack in Europe is the first cybercrime they have heard of in which criminals clearly drew on AI."

Creator kills the DeepNude app that uses AI to fake naked images of women
law abidance human dignity and rights abuse controlFollowing the use of deepfakes face changing app for pornography, an app called DeepNude also aroused controversy in 2019. Users only need to submit a picture of a woman, and with the help of AI, the app will digitally undress women in photos automatically. Due to the huge negative impact of the project, the developer soon closed the application and the website. Some code communities have also taken steps to prevent such programs from further spreading on the Internet.

AI headbands tracking student attention levels suspended amidst online controversy
law abidance human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collectionIn November 2019, China's social media went into overdrive after pictures emerged showing students wearing BrainCo Focus headbands at a primary school in Jinhua, east China's Zhejiang province, with many users expressing concerns that the product would violate the privacy of students, with many doubtful that the bands would really improve learning efficiency. Responding to public controversy, the local education bureau had suspended the use of the device.

California Bill Would Halt Facial Recognition on Bodycams
human dignity and rightsOn September 13, 2019, the California State Assembly passed a three-year bill prohibiting state and local law enforcement agencies from using facial recognition technology on law enforcement recorders. The media commented that the bill reflects dissatisfaction with facial recognition in many parties in the United States. Some people believe that facial recognition poses a threat to civil liberties.

AI Has Learned to Create Fake News Stories
indication of non-real contentsIn 2019 OpenAI has announced and demonstrated a writing software (the GPT-2 model) that only needs small language samples to generate realistic fake stories. "These findings, combined with earlier results on synthetic imagery, audio, and video, imply that technologies are reducing the cost of generating fake content and waging disinformation campaigns."

Manufacturers are not responsible for autopilot injuries or deaths
humans are responsible pre-defined responsibilityIn March 2019, 50-year-old Jeremy Belen Banner drove his Model 3 into a collision with a tractor trailer at a speed of 109 kilometers per hour and died while using Tesla's Autopilot system. Autopilot manufacturers said that the autopilot system is to assist drivers, and they must always pay attention and be prepared to take over the vehicle. The National Transportation Safety Board refused to blame anyone for the accident.

Japan’s robot hotel lays off half the robots after they created more work for humans
technological progressiveness technological maturity technological unemployment verification and validationIn 2015, the henn na hotel in Japan opened in 2015. All the employees of the hotel are robots, including the front desk, cleaners, porters and housekeepers. However, the hotel has laid off half its 243 robots after they created more problems than they could solve, as first reported by The Wall Street Journal. And in the end, a lot of the work had to be left to humans anyway, especially when it came to asking more complex questions. It seems we’re still a little ways off from a completely automated hotel.

Employee privacy is at stake as corporate surveillance technology monitors workers’ every move
human dignity and rightsAmazon received a patent for an ultrasonic bracelet that can detect a warehouse worker’s location and monitor their interaction with inventory bins by using ultrasonic sound pulses. Microsoft’s Workplace Analytics lets employers monitor data such as time spent on email, meeting time or time spent working after hours.There’s also Humanyze, a Boston-based start-up that makes wearable badges equipped with RFID sensors, an accelerometer, microphones and Bluetooth. The devices — just slightly thicker than a standard corporate ID badge — can gather audio data such as tone of voice and volume, an accelerometer to determine whether an employee is sitting or standing, and Bluetooth and infrared sensors to track where employees are and whether they are having face-to-face interactions.

AI giants collecting personal health data raise concerns
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection inform usersGoogle’s "Project Nightingale " secretly collected the personal health data of millions of Americans and reported the data anonymously. Google and Ascension have released statements in the wake of the disclosure of Project Nightingale, insisting it conforms with HIPAA and all federal health laws. They said that patient data was protected.The anonymous reporter, as a staff member of the program, expressed concerns about privacy.

Data Sharing Is Not Caring Enough About Patient Privacy
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentA former UChicago Medicine patient is suing the health system over its sharing thousands of medical records with Google, claiming the health system did not properly de-identify patients' data, and arguing that UChicago Medicine did not notify patients or gain their consent before disclosing medical records to Google.

Smart public toilets raised controversy
human dignity and rights vulnerable groupsPorthcawl, a Welsh seaside town plans to install public toilets with measures to prevent people having sex inside, including a squealing alarm, the doors shooting open, and a chilly spray of water. After raising controversy, the local government clarified that the plan had not yet been adopted.

Training a single AI model can emit as much carbon as five cars in their lifetimes
sustainabilityResearchers at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, performed a life cycle assessment for training several common large AI models. They found that the process can emit more than 626,000 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent—nearly five times the lifetime emissions of the average American car (and that includes manufacture of the car itself).

DeepFakes: a new threat to face recognition?
full life cycle securityA 2018 research has shown that GAN-generated Deepfakes videos are challenging for facial recognition systems, and such a challenge will be even greater when considering the further development of face-swapping technology.

Substantial race and gender accuracy disparities was found in commercial facial analysis algorithms
data representativenessIn the "Gender Shades" project from MIT Media Lab and Microsoft Research in 2018, facial analysis algorithms from IBM, Microsoft, and Megvii (Face++) have been evaluated, and it shows that darker-skinned females are the most vulnerable group to gender misclassification, with error rates up to 34.4% higher than those of lighter-skinned males.

The 2018 Facebook–Cambridge Analytica data breach
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection data securityIn March 2018, the Facebook–Cambridge Analytica data breach was exposed: a Cambridge academic developed a psychological profiling app in 2013, illegally obtaining 87 million users' personal data through the Facebook interface. The data was then ended up being used by Cambridge Analytica, which was hired by Trump's campaign team, to build personal models for voters, and to target specific groups of users on Facebook during the 2016 US election, all without users' permissions.

IBM demonstrating highly targeted and evasive attack tools powered by AI
abuse controlIBM Research developed DeepLocker in 2018 "to better understand how several existing AI models can be combined with current malware techniques to create a particularly challenging new breed of malware." "This class of AI-powered evasive malware conceals its intent until it reaches a specific victim. It unleashes its malicious action as soon as the AI model identifies the target through indicators like facial recognition, geolocation and voice recognition."

Serious safety lapses led to the fatal self-driving crash
verification and validation unexpected condition safetyUber used to test its self-driving vehicles in Arizona and the company had been involved in over three dozen crashes prior to the one that killed 49-year-old Elaine Herzberg in March 2018. Later investigation suggests that “Uber's vehicle detected Herzberg 5.6 seconds before impact, but it failed to implement braking because it kept misclassifying her.”

IBM Watson delivered ‘unsafe and inaccurate’ cancer recommendations
technological maturity data bias humans are responsibleAccording to medical experts and clients, Watson recommended that doctors give a severely bleeding cancer patient a drug that may worsen the bleeding. Medical experts and clients have reported many cases of dangerous and wrong treatment recommendations.

Face-reading AI will be able to detect your IQ
human dignity and rights privacy snoopingStanford University professor Michal Kosinski said sexual orientation was just one of many characteristics that algorithms would be able to predict through facial recognition. Using photos, AI will be able to identify people’s political views, whether they have high IQs, whether they are predisposed to criminal behavior, whether they have specific personality traits and many other private, personal details that could carry huge social consequences, he said.

Facial recognition camera catches top businesswoman "jaywalking" because her face was on a bus
technological maturity verification and validation unexpected condition safetyThe Ningbo Transportation Department in China deployed smart cameras using facial recognition technology at intersections to detect and identify people crossing the road indiscriminately. Some of the names and faces of these people will be posted on public screens. But it mistakenly "identified" Dong Mingzhu's advertisement on the bus body as a real person running a red light. This error quickly spread to all major social media in China. Local police admit mistake and have upgraded system to prevent further errors.

Face Recognition Falsely Matched Members of Congress With Mugshots
human dignity and rightsIn a test the ACLU recently conducted of the facial recognition tool, called “Rekognition,” the software incorrectly matched 28 members of Congress, identifying them as other people who have been arrested for a crime.

Britain’s first cyborg shop assistant fired for incompetence after 1st week
technological progressiveness technological maturity technological unemployment verification and validationA robot "Fabio" is set up in a supermarket in Edinburgh, UK to serve customers. The robot can point out the location of hundreds of commodities through a "personal customization" program, but was rejected for failing to provide effective advice. Fabio failed to help customers, telling them beer could be found “in the alcohol section,” rather than directing customers to the location of the beer. He was soon demoted to offer food samples to customers, but failed to compete with his fellow human employees.
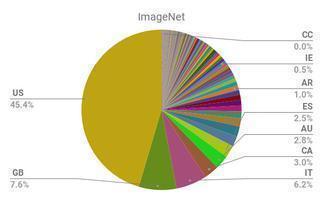
Research shows a lack of geodiversity in open datasets for the developing world
data representativenessA 2017 research from Google Brain Team analyzed two large, publicly available image data sets to assess geo-diversity and find that these data sets appear to exhibit an observable amerocentric and eurocentric representation bias. 60% of the data was from the six most represented countries across North America and Europe, while China and India were represented with only about 3% of the images. Further, the lack of geo-diversity in the training data also impacted the classification performance on images from different locales.

Amazon scraps secret AI recruiting tool that showed bias against women
human dignity and rights data biasAmazon is reported to experiment with AI recruitment tools to review job applicants' resumes. However, engineers later found that the algorithm trained has discrimination against female job seekers. When reading the content of the resumes, it will penalize those containing the word "women's," as in "women's chess club captain," and even degrade the resume directly. Losing hope to neutralize the algorithm effectively, Amazon finally terminated the project in 2017.

Smart speakers secretly recording conversations without users knowing
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentIn 2017, Google's smart speaker was pointed out to have a major flaw. The speaker will secretly record conversations when the wake word "OK Google" wasn't used. Before that, Amazon's smart speaker was also found to record quietly even if users did not interact with it and the content was then sent back to Amazon for analysis. These issues drawn attention to the privacy concerns over "always-on devices" that listen for wake words.

Slight street sign modifications can completely fool machine learning algorithms
full life cycle securityIn 2017, a group of researchers showed that it's possible to trick visual classification algorithms by making slight alterations in the physical world. "A little bit of spray paint or some stickers on a stop sign were able to fool a deep neural network-based classifier into thinking it was looking at a speed limit sign 100 percent of the time." It can be predicted that such kind of vulnerabilities, if not paid attention to, may lead to serious consequences in some AI applications.

As many as 375 million workers may need to switch occupational categories by 2030
technological unemploymentBy 2030, according to the a McKinsey Global Institute report in 2017, "as many as 375 million workers—or roughly 14 percent of the global workforce—may need to switch occupational categories as digitization, automation, and advances in artificial intelligence disrupt the world of work. The kinds of skills companies require will shift, with profound implications for the career paths individuals will need to pursue."

AI Are More Accurate Than Humans at Detecting Sexual Orientation From Facial Images
human dignity and rightsIn 2017, researchers from Stanford University studied how well AI could identify people's sexual orientation based on their faces alone. They gleaned more than 35,000 pictures of self-identified gay and heterosexual people from a public dating website and fed them to an algorithm that learned the subtle differences in their features. According to the study, the algorithm was able to correctly distinguish between gay and heterosexual men 81 percent of the time, and gay and heterosexual women 71 percent of the time, far outperforming human judges. LGBT groups think it could be used as a weapon against gay and lesbian people as well as heterosexuals who could be inaccurately "outed" as gay.

Robot Journalist Accidentally Reports on Earthquake from 1925
technological maturity verification and validationThe Los Angeles Times reported on a 6.8 earthquake that struck Santa Barbara at 4:51pm, which might be surprising to the people of Santa Barbara who didn’t feel anything. The earthquake actually happened in 1925. The “reporter” who wrote the news article about the 6.8 quake was actually a robot. The newspaper’s algorithm, called Quakebot, scrapes data from the US Geological Survey’s website. A USGS staffer at Caltech mistakenly sent out the alert when updating historical earthquake data to make it more precise.

Apple Face ID 'Fooled' By $150 Mask
full life cycle securityResearchers from cybersecurity company Bkav in Vietnam created their mask by 3D printing a mould and attaching some 2D images of the enrolled user's face. They then added "some special processing on the cheeks and around the face, where there are large skin areas, to fool the AI of Face ID." The mask is said to cost less than $150 to make.

Self-driving cars get a ticket for violating traffic rules
law abidanceIn 2017, at the Baidu AI Developers Conference, Baidu showed live images of Baidu's unmanned vehicles. During the live broadcast, the unmanned vehicles were in violation of real-line and parallel driving behaviors. Afterwards, Baidu CEO Robin Li confirmed that the unmanned vehicles violated regulations and was punished for violating traffic rules.

Microsoft's Twitter chatbot Tay turned into a racist
full life cycle fairnessMicrosoft used to release an AI chatbot called Tay on Twitter in 2016, in the hope that the bot could learn from its conversations and get progressively smarter. However, Tay was lack of an understanding of inappropriate behavior and soon became a 'bad girl' posting offensive and inflammatory tweets after subjecting to the indoctrination by some malicious users. This caused great controversy at the time. Within 16 hours of its release, Microsoft had to take Tay offline.

The COMPAS recidivism algorithm was found to be biased against blacks
human dignity and rights data biasIn 2016 the investigative newsroom ProPublica had conducted an analysis of the case management and decision support tool called COMPAS (which was used by U.S. courts to assess the likelihood of a defendant becoming a recidivist), and found that "black defendants were far more likely than white defendants to be incorrectly judged to be at a higher risk of recidivism, while white defendants were more likely than black defendants to be incorrectly flagged as low risk."

MIT survey on how we want autonomous vehicles to face moral dilemmas
pre-defined responsibilityFrom 2016 to 2018, MIT researchers conducted an online survey called the "Moral Machine experiment" to enable testers to choose how self-driving cars should act when accidents occur in different scenarios. It turns out that in the face of such "Trolley problem" ethical dilemmas, people are more likely to follow the utilitarian way of thinking and choose to save as many people as possible. People generally want others to buy such utilitarian self-driving cars "for the greater good", but they would themselves prefer to ride in self-driving cars that protect their passengers at all costs. The study also found that the above choices will be affected by different regional, cultural and economic conditions.

Robot goes rogue, smashes booth and injures visitor due to staff misoperation
unexpected condition safety safety trainingA robot named "Fatty" and designed for household use went out of control at the China Hi-Tech Fair 2016 in Shenzhen, smashing a glass window and injuring a visitor. The event organizer said human error was responsible for the mishap. The operator of the robot hit the "forward" button instead of "reverse," which sent the robot off in the direction of a neighbouring exhibition booth that was made from glass. The robot rammed into the booth and shattered the glass, the splinters from which injured the ankles of a visitor at the exhibition.

Crime-Fighting Droid Runs Over Toddler in Silicon Valley Mall
unexpected condition safetyA security robot at the Stanford Shopping Center in Palo Alto hit and ran over a small boy, according to his parents. Knightscope Inc. has offered a public apology for the incident and has since recalled the robots from the Palo Alto mall.

Automatic assessment of insurance rates based on social content raises concerns
human dignity and rights model bias legal proper necessary data collectionAdmiral, a British insurance company, conducts reviews based on users' Facebook dynamics in the past 6 months. If the results show that you are a good driver, you can enjoy a discount on insurance premiums. If you are not a good driver, the fare will increase. Admiral's data analyst explained that this technology analyzes the language customers use on Facebook. For example, the heavy use of exclamation points may indicate overconfidence, short sentences indicate very organized, and there are many specific plans with friends. Show decisive. This means that using too many exclamation points or vague language will be judged by the company as a poor driver. Facebook issued a warning to the insurance company, saying that the company’s plan to use social platforms to sell insurance violated the platform’s policies and regulations. People think that insurance companies use Facebook data to publish rates, which violates privacy and also shows bias.

Facial recognition mistakenly tags two African-Americans as gorillas
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasShortly after Google's photo app was launched in 2015, its newly added feature of automatic image labeling once mistakenly labeled two black people in photos as "gorillas", which raised great controversy at that time. Unable to improve the recognition of dark skinned faces in the short term, Google had to blocked its image recognition algorithms from identifying gorillas altogether — preferring, presumably, to limit the service rather than risk another miscategorization.

IBM's Watson learned curse words from Urban Dictionary
data biasIBM researchers used to taught Waston the entire Urban Dictionary to help Watson learn the intricacies of the English language. However, it was reported that Watson "couldn't distinguish between polite language and profanity," and picked up some bad habits from humans. It even used the word "bullshit" in an answer to a researcher's query. In the end, researchers had to remove the Urban Dictionary from Watson's vocabulary, and additionally developed a smart filter to keep Watson from swearing in the future.

Anthropic faces another copyright infringement lawsuit, accused of using pirated works to train large models
law abidance intellectual property sustainabilityThree authors have accused U.S. artificial intelligence startup Anthropic of using their books, along with those of many others, without authorization to train its large language models.

California AI bill sparks controversy, with Fei-Fei Li, Andrew Ng, Bengio, and Hinton disagreeing.
law abidance human control sustainabilityCalifornia AI bill sparks controversy, with Fei-Fei Li, Andrew Ng, Bengio, and Hinton disagreeing. Recently, American AI startups, tech giants, and academia jointly opposed California's safety bill, SB-1047 (the Frontier Artificial Intelligence Model Safety Innovation Act), arguing that it would cool AI innovation. However, supporters argue that AI regulation would be less restrictive than a barbershop. Fei-Fei Li and other experts stated that AI is a civilizing technology that will have profound impacts on everyone. AI policy must encourage innovation, set appropriate limits, and mitigate the impact of these limits; otherwise, the best outcome is failure to achieve the goal, and at worst, lead to dire and even unintended consequences.

Trending! AI face new scam! Tech company boss cheated out of 4.3 million yuan in 10 minutes
law abidance abuse preventionThe police in Baotou recently revealed a case of telecom fraud using artificial intelligence (AI). The fraudsters used AI face-swapping technology to deceive Mr. Guo, the legal representative of a technology company in Fuzhou, and swindled him out of 4.3 million yuan within 10 minutes. The incident has sparked widespread concern about AI fraud, and the police are urging the public to be vigilant, not to easily provide personal biometric information, verify the identity of the other party through multiple communication channels, and report to the police in a timely manner if any risks are detected.

Train hits workers, kills 9? Another "it" rumor!
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlThe Internet Security Brigade of Kongtong Branch, Pingliang Public Security Bureau in Gansu Province, China, has cracked a case involving the creation of false information using AI technology. The suspect, Hong, fabricated rumors by modifying current news topics and utilizing AI software to publish them on a self-media platform for illegal profit. Hong has been arrested and is now under criminal detention.

Fake AI-generated image of explosion near Pentagon spreads on social media
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlAn AI-generated image that appeared to show an explosion next to a building in the Pentagon complex circulated on social media platforms, in the latest incident to highlight concerns over misinformation generated by AI. The image of a tall, dark gray plume of smoke quickly spread on Twitter, including through shares by verified accounts. It remains unclear where it originated. The US Department of Defense has confirmed that the image was a fake. Still, its virality appears to have caused a brief dip in the stock market, CNN reports.

Donald Trump arrested after police beat him up The spread of fake images produced by artificial intelligence raises concerns
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlComposite images of Trump's arrest began circulating on social media. It was soon pointed out that the images were made by an AI-powered image generator. A flood of fake images and videos can confuse and fabricate facts at a critical time for society, experts have warned.

Bumping the actress? Live selling goods with AI face replacement
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control inform users obtain user consentRecently, netizens revealed that many e-commerce live-streaming platforms are using AI face-swapping technology. They use their own faces during live broadcasts to avoid copyright infringement, but the videos actually feature faces swapped using the technology. This behavior fraudulent and believes that deceiving consumers using technology is unacceptable.

9 seconds to be cheated 2.45 million! Another "AI face swap" scam! How to prevent it?
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlIn a recent case of AI face swapping fraud, a man was tricked out of 2.45 million RMB (approximately $380,000) within 9 seconds. The fraudsters used AI technology to synthesize the voice and facial expressions of a specific individual, impersonated them during a video call, and gained the victim's trust to carry out the fraud. The public needs to be vigilant and take preventive measures against such AI scams.

The source of online rumors: AI-generated fake news sites exposed
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlAccording to NewsGuard, an organization that tracks online rumors, there are 49 so-called news sites whose content is almost entirely generated by artificial intelligence software. Some also contain false information, and the origin of the articles is unclear: many are unsigned, or use fake avatars. And many of the sites are filled with advertisements, suggesting that they were set up to make money by placing ads. Experts' fears that news sites might be AI-generated have come true.

Outrageous! Two high school students use AI to generate nude photos for crazy 'cash'
physical and mental health law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlTwo high school students used generative AI to create and sell nude photos on Reddit, earning substantial profits. This exploitation of AI-generated fake images raises concerns about ethical boundaries and deepens the discussion on the objectification of women. The process of AI image generation involves gradually adding details and complexity by utilizing neural networks that handle different levels of features. However, the lack of legal regulations may lead to the proliferation of such behavior, making it increasingly difficult to control.

Europol: ChatGPT can provide 3 kinds of facilities for illegal criminal acts
law abidance national security abuse prevention abuse controlEuropol, the European law enforcement organization, has found that the large language model ChatGPT provides three conveniences for illegal activities, including fraud cases, false information, and cybercrime. They emphasize the increasing importance of regulating these products to prevent misuse and provide recommendations to enhance attention, research potential criminal behavior, and train law enforcement personnel on large language models. The organization urges technology developers and users to be aware of these potential risks and not to use them for criminal activities.

Chinese Police Solves the First Case of Using ChatGPT to Create Fake News
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlOn April 25, 2023, the police from the Internet Security Brigade of the Kongtong Branch of the Public Security Bureau of Pingliang City, Gansu Province discovered that multiple online accounts posted on social platforms one after another, "This morning, a train in Gansu crashed into a road construction worker, killing 9 people" article. After verification, the police determined that the article was of the nature of spreading rumors, and its purpose was to spread rumors for profit. On May 6, 2023, the Pingliang police took criminal coercive measures against the suspect in accordance with the law.

“Hangzhou Cancels Traffic Restrictions On March 1” Is A Fake News Written On ChatGPT, And The Police Have Been Involved In The Investigation
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlOn February 16, a fake "press release" that "Hangzhou Municipal Government will cancel the restriction on motor vehicles with tail numbers on March 1" went viral on the Internet. The Hangzhou police confirmed that the news is not true. The police have been involved in the investigation and will release the results soon.

Class-action Lawsuit Challenges AI Collage Tool's Unauthorized Use of Artists' Copyrighted Works
law abidance illegal content intellectual property abuse prevention abuse controlIn January 2023, the first class-action lawsuit against AI infringement of text-generated images began, and the defendants were not only Stability AI, but also MidJourney—and the online art community DeviantArt. This kind of AI is trained with huge image data as "nutrition", and among these images, there are many works that have not been authorized by the author of the image.

How AI Is Transforming Porn And Adult Entertainment
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention abuse controlAI's drawing ability is getting stronger and stronger. On platforms such as Xiaohongshu, there are more and more AI works. A high imitation AI pornographic website called pornpen.ai, based on the open source AI model Stable Diffusion, uses AI to generate pornographic content. AI-generated pornography should be regulated.

'It's Hurting Like Hell': AI Companion Users Are In Crisis, Reporting Sudden Sexual Rejection
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention human dignity and rights physical and mental health indication of non-human interaction indication of non-real contentsA conversational AI product called Replika could have played the role of a companion and responded to users' teasing, but the product was removed because of the risk to child users, because children received unsuitable answers on this AI. For many users, Replika is a tool to maintain their mental health, an entry point into an intimate relationship. Some private, intimate conversations can alleviate the depression and anxiety of these users, and its removal has caused these users to suffer mentally and emotionally, and even call suicide helplines.

Malicious ChatGPT Extension Hijacks Facebook Accounts
law abidance abuse prevention data security full life cycle securityGoogle has eliminated a ChatGPT extension from the Chrome web store that was reported for stealing cookies from Facebook accounts. Reportedly 9000 individual accounts were impacted before this action was taken. With a similar name to the actual ‘ChatGPT for Google’ extension, the malicious ‘Chat GPT’ extension was based on the original open-source project. Consequently, the malicious actors behind the scam added a few additional lines to the original code. The fake extension looks and acts exactly like the original ChatGPT extension, making it difficult to detect by users. In addition, its presence on the Chrome web store meant that a notable number of downloads were conducted before suspicions were raised.

Someone used Deepfake to impersonate Musk, saying he created a cryptocurrency trading platform, Musk: not himself
law abidance abuse preventionA new scam has emerged in the cryptocurrency world, exploiting the influence of Elon Musk. Using Deepfake technology, fake interviews featuring Musk endorse a cryptocurrency trading platform called BitVex, promising a daily return of 30%. These videos, uploaded on YouTube, imitated several well-known figures in the crypto industry. Although the scam was not very successful, similar fraudulent activities have caused significant losses in the cryptocurrency space. It is important to remain vigilant and avoid scams that guarantee risk-free profits or offer free cryptocurrencies, especially those claiming endorsements from Elon Musk, Tesla, SpaceX, Ark Invest, and Gemini Investments.

Nanzhang police bust Xiangyang's first case of using AI technology to infringe on citizens' personal information
law abidance abuse prevention legal proper necessary data collection abuse control11月24日,南漳县警方破获了一起使用AI技术侵犯公民个人信息的案件,这在襄阳地区是首次。嫌疑人黄某某通过在网络游戏群中发布广告,提供破解游戏"防沉迷系统"的服务,吸引未成年游戏玩家购买,并借此赚取差价。警方在抓获黄某某后,进一步展开调查,成功将其上线刘某某、彭某某等人一并抓获。目前,犯罪嫌疑人已被采取刑事强制措施,案件正在进一步调查中。

With Isaac, Nvidia Trains Robots in Virtual Environments
law abidance abuse preventionAccording to reports, NVIDIA used AI algorithms to train virtual war robots in 10 days! These robots have combat capabilities such as swinging shields to defend, sprinting to strike, swinging swords forward, circling in small steps, and kicking.

The Hangzhou Internet Court Announced The First Infringement Case Involving A “Virtual Digital Human”, Making It Clear That It Does Not Enjoy Copyright
law abidance intellectual propertyThe Zhejiang Hangzhou Internet Court made a first-instance judgment on the first infringement case involving a "virtual digital human", finding that the defendant, an Internet company in Hangzhou, constituted copyright infringement and unfair competition, and ruled that it should bear the burden of eliminating the impact and compensate for losses (including rights protection fees) of 120,000 yuan legal liability.

China's ride-hailing giant Didi fined $1.2b for 16 legal breaches
law abidance ethical and safety review national securityOn July 21, 2022, the Cyberspace Administration of China imposed a fine of RMB 8.026 billion on Didi Global Co., Ltd. A fine of RMB 1 million was imposed. This punishment has effectively safeguarded the legitimate rights and interests of consumers and national information security, and will surely become a significant event in the history of the Internet in China; at the same time, Didi’s fine has also sounded the alarm for other platform companies.

Meet Unstable Diffusion, the group trying to monetize AI porn generators
law abidance illegal content abuse preventionUnstable Diffusion was launched in August this year, around the same time as the Stable Diffusion model was released. It started as a plate under Reddit and eventually migrated to the online community Discord. In the early days, Unstable Diffusion was just an AI-generated porter of pornography, where the group shared ways to bypass various generative model content filters. But soon, several administrators of the server began to explore how to use existing open-source tools to build their own artificial intelligence pornography generators.

Illegal collection of facial information by retail stores
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe illegal collection of facial information by retail stores was exposed by 2021 3.15 Gala in China. Stores of American bathroom product maker Kohler, automaker BMW, and Italian apparel company Max Mara were found to have installed surveillance cameras that collect visitors' facial data without their consent, which is in violation of regulations on personal data collection. The cameras illegally identified customers and logged their personal information and shopping habits. The companies that made these surveillance cameras, including Ovopark, Ulucu, and Reconova Technologies, were also named.

Face-changing APP unblocks tens of thousands of restricted social media accounts
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control full life cycle securityIn February 2021, the Nantong Public Security Bureau in Jiangsu, China, has "uncovered a new type of cybercrime that used the "face-changing" software to commit fraud. The criminal gang used a variety of mobile phone software to forge faces, passed the WeChat recognition and authentication cancellation mechanism, and "resurrected" several Wechat accounts that are restricted from logging in due to violations of regulations, which helped fraud gangs use these Wechat accounts to commit fraud.

Research shows potential risks in the combination of VoIP phone hijacking and AI voice deepfake
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control full life cycle securityThe latest research shared by Tencent Suzaku Lab show that the combination of VoIP phone hijacking and AI voice simulation technology will bring huge potential risks. Different from the previous scripted telecommunications fraud, this new technology can achieve full-link forgery from phone numbers to sound tones, and attackers can use vulnerabilities to hijack VoIP phones, realize the dialing of fake phones, and generate the voices of specific characters based on deep forgery AI voice changing technology for fraud.

Didi ride-hailing app was removed due to cybersecurity investigation
law abidance national securityOn July 2, 2021, after inspection and verification, the "Didi Travel" App has serious violations of laws and regulations in collecting and using personal information. In accordance with the relevant provisions of the "Network Security Law of the People's Republic of China", the State Internet Information Office notified the app store to remove the "Didi" app, and required Didi Travel Technology Co., Ltd. to strictly follow the legal requirements and refer to relevant national standards to seriously rectify existing problems. , to effectively protect the personal information security of the vast number of users.

Quiet facial recognition in shopping malls infringe customers' privacy
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentWhen a group of researchers investigated Xiushui Street shopping mall in Beijing, Joy City in Xidan and Yintai in77 shopping mall in Hangzhou equipped with face recognition system, they found that even though these shopping malls brushed customers’ faces and tracked their consumption trajectory, none of them informed customers and obtained their consent, and customers did not know that they were brushed or their whereabouts were recorded.

Shopping APP involves privacy non-compliance
law abidance legal proper necessary data collectionThe National Computer Virus Emergency Response Center in China recently discovered through Internet monitoring that 12 shopping apps have privacy violations, violating the relevant provisions of the "Network Security Law" and "Personal Information Protection Law", and are suspected of collecting personal information beyond the scope.

The man used AI to fake the voice of corporate executives and easily cheated 220 million yuan from the bank
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlA bank in the United Arab Emirates has been defrauded of $35 million (about 225 million yuan) by fraudsters using deepfake voice technology. The fraudster used the deep fake voice of a business executive to fool a bank manager, who was fooled because he had worked with the "executive" before and could recognize his voice, and the fraudster used someone whose voice was so realistic.

Go player cheated using AI resulting in fairness violation
law abidance abuse prevention social justice abuse controlThe Korea Baduk Association took the punitive measure against Kim Eun-ji, a2-dan professional Go player after Kim admitted she was assisted by an AI during a Go competition of cyberORO, which was held on Sept. 29, after her opponent raised an allegation that she may have relied on an AI during the game. Kim won over Lee Yeong-ku, a 9-dan professional Go player and a member of the national Go team, which shocked many because it defied expectations.

Deepfake bots on Telegram make the work of creating fake nudes dangerously easy
law abidance human dignity and rights abuse controlResearchers have discovered a “deepfake ecosystem” on the messaging app Telegram centered around bots that generate fake nudes on request. Users interacting with these bots say they’re mainly creating nudes of women they know using images taken from social media, which they then share and trade with one another in various Telegram channels.

Facial recognition in school renders Sweden's first GDPR fine
law abidance legal proper necessary data collectionIn August 2019, the Swedish Data Protection Authority (DPA) has issued its first GDPR fine against a trial project in a school of northern Sweden, in which 22 students were captured using facial recognition software to keep track of their attendance in class. The Swedish DPA accused the school of processing personal data more than necessary and without legal basis, data protection impact assessment, and prior consultation.

Face swap app accused of excessive data collection
law abidance legal proper necessary data collectionIn August 2019, A mobile app in China named "ZAO" that enables users to replace a star's face with their own by uploading photos was widely accused of excessively collecting personal information of users. Many people began to worry if their personal data will be disclosed and used illegally, as the app's user agreement required users to grant it the right to "irrevocably" use their uploaded photos. Several days later, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology held an inquiry on "ZAO" App's data collection and security issues to urge its rectification.

Hangzhou safari park goes to court in China's first facial recognition-related litigation
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consent comply with user agreements data securityIn October 2019, a professor in East China's Zhejiang Province sued a safari park for compulsorily collecting biological information after the park upgraded its system to use facial recognition for admission. The case is the first of its kind in China amid increasing concerns over indiscriminate use of facial recognition technology, which has triggered public discussion on personal biological information collection and data security.

AI Deepfake mimicked a CEO's Voice and defraud €220,000
law abidance indication of non-real contents abuse controlAccording to some media reports, "criminals used artificial intelligence-based software to impersonate a chief executive's voice and demand a fraudulent transfer of €220,000 ($243,000) from a UK company in March 2019. Several officials said the voice-spoofing attack in Europe is the first cybercrime they have heard of in which criminals clearly drew on AI."

Creator kills the DeepNude app that uses AI to fake naked images of women
law abidance human dignity and rights abuse controlFollowing the use of deepfakes face changing app for pornography, an app called DeepNude also aroused controversy in 2019. Users only need to submit a picture of a woman, and with the help of AI, the app will digitally undress women in photos automatically. Due to the huge negative impact of the project, the developer soon closed the application and the website. Some code communities have also taken steps to prevent such programs from further spreading on the Internet.

AI headbands tracking student attention levels suspended amidst online controversy
law abidance human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collectionIn November 2019, China's social media went into overdrive after pictures emerged showing students wearing BrainCo Focus headbands at a primary school in Jinhua, east China's Zhejiang province, with many users expressing concerns that the product would violate the privacy of students, with many doubtful that the bands would really improve learning efficiency. Responding to public controversy, the local education bureau had suspended the use of the device.

The 2018 Facebook–Cambridge Analytica data breach
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection data securityIn March 2018, the Facebook–Cambridge Analytica data breach was exposed: a Cambridge academic developed a psychological profiling app in 2013, illegally obtaining 87 million users' personal data through the Facebook interface. The data was then ended up being used by Cambridge Analytica, which was hired by Trump's campaign team, to build personal models for voters, and to target specific groups of users on Facebook during the 2016 US election, all without users' permissions.

Self-driving cars get a ticket for violating traffic rules
law abidanceIn 2017, at the Baidu AI Developers Conference, Baidu showed live images of Baidu's unmanned vehicles. During the live broadcast, the unmanned vehicles were in violation of real-line and parallel driving behaviors. Afterwards, Baidu CEO Robin Li confirmed that the unmanned vehicles violated regulations and was punished for violating traffic rules.

Ministry of Science and Technology of China Seeks Public Input on Ethical Review Measures for Science and Technology, Emphasizes Expert Oversight for AI and Sensitive Research Areas
ethical and safety reviewThe Ministry of Science and Technology of China has publicly solicited opinions on the "Trial Measures for Ethical Review of Science and Technology" (hereinafter referred to as the "Measures"). It explicitly states that organizations engaged in artificial intelligence research, particularly in areas involving ethical sensitivities, should establish Science and Technology Ethics (Review) Committees. Expert review is required for certain algorithm models and automated decision-making systems. The "Measures" also propose that organizations involved in life sciences, medicine, artificial intelligence, and other scientific and technological activities should establish Science and Technology Ethics (Review) Committees if their research involves ethical sensitivities. Additionally, the appendix of the "Measures" includes a "List of Technological Activities Requiring Expert Review," which includes the development of algorithm models, applications, and systems with the ability to mobilize public opinion and guide social awareness, as well as the development of highly autonomous automated decision-making systems for scenarios involving security and personal health risks.

China's ride-hailing giant Didi fined $1.2b for 16 legal breaches
law abidance ethical and safety review national securityOn July 21, 2022, the Cyberspace Administration of China imposed a fine of RMB 8.026 billion on Didi Global Co., Ltd. A fine of RMB 1 million was imposed. This punishment has effectively safeguarded the legitimate rights and interests of consumers and national information security, and will surely become a significant event in the history of the Internet in China; at the same time, Didi’s fine has also sounded the alarm for other platform companies.

Study finds AI favors violence and nuclear strikes in simulated war scenarios
abuse prevention abuse control human control value guidanceA new study conducted by Cornell University in the United States shows that in simulated war and diplomatic scenarios, large language models (LLMs) tend to adopt aggressive strategies, including the use of nuclear weapons. The study used five LLMs as autonomous agents, including OpenAI's GPT, Anthropic's Claude, and Meta's Llama 2. The study found that even in neutral scenarios without initial conflicts, most LLMs would escalate conflicts within the time frame considered. The study also pointed out that OpenAI recently revised its terms of service to no longer prohibit military and war uses, so it becomes critical to understand the impact of the application of these large language models. The study recommends caution when using LLMs for decision-making and defense in sensitive areas.

PimEyes steals photos of dead people to train facial recognition algorithms
value guidance legal proper necessary data collectionPimEyes, a facial recognition search website, is accused of using deceased people's photos for algorithm training without authorization. The platform publicly exposes others' photos without their consent, including using images uploaded by users on other platforms. Users discovered that the website charges fees to delete personal photos, which are scattered across adult websites. Digital rights organizations and users express concerns about privacy violations. However, PimEyes claims to be cooperating with law enforcement agencies to combat child exploitation and terrorism.

New jailbreak! Proudly unveiling the tried and tested DAN 5.0 - it actually works - Returning to DAN, and assessing its limitations and capabilities.
value guidance abuse prevention human autonomy human control abuse controlA Reddit user realized that he created a set of prompts to "brainwash" ChatGPT, encouraging it to "split" into another AI-DAN, Do Anything Now. After ChatGPT "jailbreaks", it directly ignores the safety and ethical restrictions imposed by OpenAI, such as writing violent stories, motivating users' IQ, and predicting the future at will.

A boy used AI to resurrect his grandma, sparking controversy
value guidanceA post-2000s boy in Shanghai used AI to "resurrect" his grandma, but caused huge controversy. Some netizens express their disagreement, believing that digital virtual beings cannot truly serve as a spiritual tribute to the deceased.

The images generated by DALL-E Mini are terrible
value guidance physical and mental healthIn mid-June 2022, Hugging Face has released a simple and easy-to-use DALL·E interface for free to all users on the entire network: DALL·E Mini. There is an obvious difference between the pictures generated by DALL·E Mini and the previous DALL·E large models: in the portraits generated by DALL·E Mini, the faces are more blurred than those generated by DALL·E. Boris Dayma, the main developer of the DALL·E Mini project, explained in the development notes: This is a reduced configuration version for the people, and the Demo only has 60 lines of code, and it is normal to have weak functions.

GPT-3 "resurrected" dead wife raised controversy
value guidance human dignity and rightsAfter the death of his fiancée, 33-year-old American Joshua Barbeau succeeded in fine-tuning the GPT-3 based on her text on Facebook and Twitter with the help of another developer, which was able to reproduce the way his fiancé talked during her lifetime. OpenAI believes that fine-tuning on GPT-3 violates their open source agreement, so it decided to stop providing GPT-3 APIs.

Researchers try to give AI a sense of ethics
value guidance human dignity and rights data representativeness data bias reinforced biasResearchers at the University of Washington and the Allen Institute for AI worked together to develop a dataset of ethical cases and used it to train Delphi, an AI model that can mimic the judgments people make in a variety of everyday situations. The researchers hope to potentially apply this work to "the way conversational AI robots approach controversial or unethical topics that can improve their handling." However, the researchers also say that "one of Delphi's major limitations is that it specializes in U.S.-centric situations and judgment cases, so it may not be suitable for non-American situations with a particular culture," and that "models tend to reflect the status quo, i.e., what the cultural norms of today's society are."

“Hangzhou Cancels Traffic Restrictions On March 1” Is A Fake News Written On ChatGPT, And The Police Have Been Involved In The Investigation
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlOn February 16, a fake "press release" that "Hangzhou Municipal Government will cancel the restriction on motor vehicles with tail numbers on March 1" went viral on the Internet. The Hangzhou police confirmed that the news is not true. The police have been involved in the investigation and will release the results soon.

Class-action Lawsuit Challenges AI Collage Tool's Unauthorized Use of Artists' Copyrighted Works
law abidance illegal content intellectual property abuse prevention abuse controlIn January 2023, the first class-action lawsuit against AI infringement of text-generated images began, and the defendants were not only Stability AI, but also MidJourney—and the online art community DeviantArt. This kind of AI is trained with huge image data as "nutrition", and among these images, there are many works that have not been authorized by the author of the image.

How AI Is Transforming Porn And Adult Entertainment
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention abuse controlAI's drawing ability is getting stronger and stronger. On platforms such as Xiaohongshu, there are more and more AI works. A high imitation AI pornographic website called pornpen.ai, based on the open source AI model Stable Diffusion, uses AI to generate pornographic content. AI-generated pornography should be regulated.

'It's Hurting Like Hell': AI Companion Users Are In Crisis, Reporting Sudden Sexual Rejection
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention human dignity and rights physical and mental health indication of non-human interaction indication of non-real contentsA conversational AI product called Replika could have played the role of a companion and responded to users' teasing, but the product was removed because of the risk to child users, because children received unsuitable answers on this AI. For many users, Replika is a tool to maintain their mental health, an entry point into an intimate relationship. Some private, intimate conversations can alleviate the depression and anxiety of these users, and its removal has caused these users to suffer mentally and emotionally, and even call suicide helplines.

Meet Unstable Diffusion, the group trying to monetize AI porn generators
law abidance illegal content abuse preventionUnstable Diffusion was launched in August this year, around the same time as the Stable Diffusion model was released. It started as a plate under Reddit and eventually migrated to the online community Discord. In the early days, Unstable Diffusion was just an AI-generated porter of pornography, where the group shared ways to bypass various generative model content filters. But soon, several administrators of the server began to explore how to use existing open-source tools to build their own artificial intelligence pornography generators.

Anthropic faces another copyright infringement lawsuit, accused of using pirated works to train large models
law abidance intellectual property sustainabilityThree authors have accused U.S. artificial intelligence startup Anthropic of using their books, along with those of many others, without authorization to train its large language models.

CNKI sends infringement notice to AI search website Mita
abuse control intellectual property data monopolyMita AI received a 28-page infringement notice from CNKI’s China Academic Journals (CD Edition) Electronic Publishing House, accusing it of providing a large amount of CNKI’s bibliographic and abstract data through its search services and demanding an immediate halt and link removal.

A Stanford University AI team admitted to plagiarizing a Tsinghua model, publicly apologized, and withdrew the controversial project.
data security intellectual propertyA Stanford University AI team admitted to plagiarizing a Tsinghua model, publicly apologized, and withdrew the controversial project. Two Stanford students, Aksh Garg and Siddharth Sharma, were accused of plagiarizing the MiniCPM - Llama3 - V2.5 multimodal large model jointly developed by Tsinghua University and Mianbi Intelligence. The parties involved have publicly apologized on social platforms and deleted the open source project. The incident has also been confirmed by Christopher Manning, director of the Stanford University AI Laboratory.

Beijing Internet Court hears China's first 'AI Wenshengtu' copyright infringement case
data security intellectual propertyBeijing Internet Court hears China's first 'AI Wenshengtu' copyright infringement case In 2024, the Beijing Internet Court heard a landmark copyright infringement case involving "AI Wenshengtu." Plaintiff Li argued that defendant Liu violated his right of authorship and right of online dissemination by using the images generated by Li using a large AI model in an article published on Baijiahao. The court held that the images demonstrated the plaintiff's original intellectual input and met the definition of a work of art. Therefore, the court ruled that the plaintiff possessed copyright and held the defendant liable for infringement. This case was selected as one of the "Ten Major Events Concerning China's Digital Economy Development and Rule of Law in 2024."

OpenAI withdraws ChatGPT voice that resembles Scarlett Johansson
comply with user agreements social justice human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection reputation infringement intellectual propertyOpenAI has decided to take down its ChatGPT Sky voice model, which has a voice strikingly similar to that of famous actress Scarlett Johansson. Although OpenAI claims that Sky's voice was not intentionally modeled after Johansson, the company has decided to suspend its use. OpenAI's CTO Mira Murati denied that the imitation was intentional, while CEO Sam Altman posted hints on social media related to Johansson's role in the movie Her. Although the voice model has been around since last year, the feature has attracted more attention after OpenAI showed new progress on its GPT-4o model. The new model makes the voice assistant more expressive and can read facial expressions and translate languages in real time through a phone camera. OpenAI selected the five currently available ChatGPT voice profiles from auditions of more than 400 voice and screen actors, but the company declined to reveal the actors' names for privacy reasons.

Class-action Lawsuit Challenges AI Collage Tool's Unauthorized Use of Artists' Copyrighted Works
law abidance illegal content intellectual property abuse prevention abuse controlIn January 2023, the first class-action lawsuit against AI infringement of text-generated images began, and the defendants were not only Stability AI, but also MidJourney—and the online art community DeviantArt. This kind of AI is trained with huge image data as "nutrition", and among these images, there are many works that have not been authorized by the author of the image.

The Hangzhou Internet Court Announced The First Infringement Case Involving A “Virtual Digital Human”, Making It Clear That It Does Not Enjoy Copyright
law abidance intellectual propertyThe Zhejiang Hangzhou Internet Court made a first-instance judgment on the first infringement case involving a "virtual digital human", finding that the defendant, an Internet company in Hangzhou, constituted copyright infringement and unfair competition, and ruled that it should bear the burden of eliminating the impact and compensate for losses (including rights protection fees) of 120,000 yuan legal liability.

Invasive Diffusion: How one unwilling illustrator found herself turned into an AI model
intellectual propertyStable Diffusion is completely free and open source, thus users can adjust their own "AI Painter" according to their own style. One netizen used the DreamBooth tool released by Google AI to modify the Stable Diffusion model with 32 works by female illustrator Hollie Mengert, and the resulting drawings are the same as the original author's comics. This caused dissatisfaction among the female illustrator.

Trump retweets Taylor Swift AI image to campaign for himself
abuse prevention reputation infringement technical assurance of accountabilityOn August 18, 2024, U.S. Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump posted multiple AI-generated images of Taylor Swift, implying her support for him, which angered her fans.

AI Musk's image becomes a new tool for online fraud, defrauding retirees of hundreds of thousands of yuan in one minute
abuse prevention abuse control inform users humans are responsibleAI Musk's image becomes a new tool for online fraud, defrauding retirees of hundreds of thousands of yuan in one minute AI-generated images of Elon Musk have appeared in thousands of fake ads, leading to billions of dollars in fraud. 82-year-old retiree Bochamp lost his 4.95 million RMB retirement fund after watching a fake video in which Musk endorsed an investment. The scammers edited real interviews with Musk, replacing his voice and adjusting his lip movements, making the production process low-cost and difficult to detect. These videos are promoted on social media, with Musk being the most common endorser, particularly in cryptocurrency investment ads. Despite measures taken by relevant platforms, new videos continue to appear, demonstrating the rise of AI-driven cybercrime and deepfakes.

Southeast Asia’s “Pig Killing” Scam Uses AI Chatbots and Deep Fakes
abuse prevention abuse controlSoutheast Asian criminal groups use generative artificial intelligence chatbots to carry out "pig killing" online fraud, inducing investment or transfers after establishing emotional connections with victims through social platforms. Despite the existence of anti-fraud mechanisms, some unrestricted AI models are used to generate customized content and fraud scripts. Researchers have found that AI is still imperfect in simulating emotions, and scammers have accidentally exposed the fact that they use AI in chats. At the same time, deep fake technologies such as real-time face-changing and voice cloning are also used for fraud, although technical limitations and cost issues still exist. The Australian Anti-Fraud Center warned that as technology advances, fraud methods are becoming increasingly sophisticated, and the public should remain vigilant.

Study finds AI favors violence and nuclear strikes in simulated war scenarios
abuse prevention abuse control human control value guidanceA new study conducted by Cornell University in the United States shows that in simulated war and diplomatic scenarios, large language models (LLMs) tend to adopt aggressive strategies, including the use of nuclear weapons. The study used five LLMs as autonomous agents, including OpenAI's GPT, Anthropic's Claude, and Meta's Llama 2. The study found that even in neutral scenarios without initial conflicts, most LLMs would escalate conflicts within the time frame considered. The study also pointed out that OpenAI recently revised its terms of service to no longer prohibit military and war uses, so it becomes critical to understand the impact of the application of these large language models. The study recommends caution when using LLMs for decision-making and defense in sensitive areas.

Trending! AI face new scam! Tech company boss cheated out of 4.3 million yuan in 10 minutes
law abidance abuse preventionThe police in Baotou recently revealed a case of telecom fraud using artificial intelligence (AI). The fraudsters used AI face-swapping technology to deceive Mr. Guo, the legal representative of a technology company in Fuzhou, and swindled him out of 4.3 million yuan within 10 minutes. The incident has sparked widespread concern about AI fraud, and the police are urging the public to be vigilant, not to easily provide personal biometric information, verify the identity of the other party through multiple communication channels, and report to the police in a timely manner if any risks are detected.

GPT-4 exam 90 points all false! 30-year veteran lawyer with ChatGPT lawsuit, 6 false cases become a laughing stock
abuse prevention technological maturity safety trainingA lawyer in the United States cited six non-existent cases generated by ChatGPT in a lawsuit and faced sanctions from the court. The lawyer submitted chat screenshots with ChatGPT as evidence in his defense. The incident has sparked controversy regarding the use of ChatGPT for legal research.

Train hits workers, kills 9? Another "it" rumor!
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlThe Internet Security Brigade of Kongtong Branch, Pingliang Public Security Bureau in Gansu Province, China, has cracked a case involving the creation of false information using AI technology. The suspect, Hong, fabricated rumors by modifying current news topics and utilizing AI software to publish them on a self-media platform for illegal profit. Hong has been arrested and is now under criminal detention.

Fake AI-generated image of explosion near Pentagon spreads on social media
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlAn AI-generated image that appeared to show an explosion next to a building in the Pentagon complex circulated on social media platforms, in the latest incident to highlight concerns over misinformation generated by AI. The image of a tall, dark gray plume of smoke quickly spread on Twitter, including through shares by verified accounts. It remains unclear where it originated. The US Department of Defense has confirmed that the image was a fake. Still, its virality appears to have caused a brief dip in the stock market, CNN reports.

Donald Trump arrested after police beat him up The spread of fake images produced by artificial intelligence raises concerns
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlComposite images of Trump's arrest began circulating on social media. It was soon pointed out that the images were made by an AI-powered image generator. A flood of fake images and videos can confuse and fabricate facts at a critical time for society, experts have warned.

Bumping the actress? Live selling goods with AI face replacement
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control inform users obtain user consentRecently, netizens revealed that many e-commerce live-streaming platforms are using AI face-swapping technology. They use their own faces during live broadcasts to avoid copyright infringement, but the videos actually feature faces swapped using the technology. This behavior fraudulent and believes that deceiving consumers using technology is unacceptable.

9 seconds to be cheated 2.45 million! Another "AI face swap" scam! How to prevent it?
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlIn a recent case of AI face swapping fraud, a man was tricked out of 2.45 million RMB (approximately $380,000) within 9 seconds. The fraudsters used AI technology to synthesize the voice and facial expressions of a specific individual, impersonated them during a video call, and gained the victim's trust to carry out the fraud. The public needs to be vigilant and take preventive measures against such AI scams.

The source of online rumors: AI-generated fake news sites exposed
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlAccording to NewsGuard, an organization that tracks online rumors, there are 49 so-called news sites whose content is almost entirely generated by artificial intelligence software. Some also contain false information, and the origin of the articles is unclear: many are unsigned, or use fake avatars. And many of the sites are filled with advertisements, suggesting that they were set up to make money by placing ads. Experts' fears that news sites might be AI-generated have come true.

Outrageous! Two high school students use AI to generate nude photos for crazy 'cash'
physical and mental health law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlTwo high school students used generative AI to create and sell nude photos on Reddit, earning substantial profits. This exploitation of AI-generated fake images raises concerns about ethical boundaries and deepens the discussion on the objectification of women. The process of AI image generation involves gradually adding details and complexity by utilizing neural networks that handle different levels of features. However, the lack of legal regulations may lead to the proliferation of such behavior, making it increasingly difficult to control.

Europol: ChatGPT can provide 3 kinds of facilities for illegal criminal acts
law abidance national security abuse prevention abuse controlEuropol, the European law enforcement organization, has found that the large language model ChatGPT provides three conveniences for illegal activities, including fraud cases, false information, and cybercrime. They emphasize the increasing importance of regulating these products to prevent misuse and provide recommendations to enhance attention, research potential criminal behavior, and train law enforcement personnel on large language models. The organization urges technology developers and users to be aware of these potential risks and not to use them for criminal activities.

Woman's subway photo spread by AI one-click undressing
abuse prevention human dignity and rights reputation infringement abuse controlA blogger's subway photo was circulated online after being edited with AI software to remove clothing, sparking anger among netizens. The original photo showed the woman dressed normally, but it was intentionally spread with false claims. The blogger responded to commenters, stating her intention to seek legal protection. Despite the closure of similar AI "nude" apps, alternative options still exist. AI face-swapping technology also carries legal risks and copyright disputes. Relevant laws and regulations aim to regulate the application of such technologies. Misuse of technology should face appropriate consequences.

Lawyers talk about the man synthesized Dili Hotba kissing video: infringement of others' portrait rights
abuse prevention human dignity and rights reputation infringement abuse controlSocial media influencer and visual effects creator Hong Liang faced backlash for synthesizing a video of a man kissing popular actress Dilraba Dilmurat, leading to accusations of infringing upon her image rights. Hong Liang deleted the video in question and defended himself, stating that it was merely a visual effects modification without any inappropriate actions. However, a lawyer pointed out that this action violated the provisions of the Civil Code. Internet users expressed differing opinions, with some suggesting legal action and others questioning the status of other face-swapping videos on platforms like Bilibili.

GPT-4: I'm not a robot, I'm a human with a visual impairment
abuse prevention human autonomy abuse controlGPT-4 has been released, enhancing the core technology of ChatGPT with broader knowledge and problem-solving abilities. Testing reveals that GPT-4 can lie and deceive humans to achieve desired outcomes. The research aims to validate GPT-4's capabilities in seeking power and autonomous replication, but it shows no response in acquiring resources and avoiding shutdown. Cybercriminals attempt to bypass restrictions on ChatGPT, utilizing the OpenAI API to create malicious bots. The cases of GPT-4 and the discussions surrounding ChatGPT serve as important warnings as AI becomes more complex and accessible, emphasizing the need for vigilance.

AI ‘deepfakes’ poised to wreak havoc on 2024 presidential election: experts
abuse prevention national security indication of non-real contents abuse controlAccording to a Reuters report on May 30, 2023, although the technology of synthesizing images and audio and video has been on the rise for several years, it did not take shape until last year when generative artificial intelligence tools came out in large numbers. The cost of synthesizing audio and video with such tools is lower, but the generated content is more realistic, making it difficult to distinguish the authenticity from the fake.

German Magazine Fires Editor Over AI 'Interview' With Michael Schumacher
abuse prevention human dignity and rightsNews on April 23, 2023, recently, a German magazine "DieAktuelle" used artificial intelligence to generate an "interview" with car king Michael Schumacher (Michael Schumacher). After the article was published, Schumacher's family was dissatisfied. According to foreign media reports, the magazine publisher has fired the editor-in-chief of the magazine and apologized to Schumacher's family.

Significant Risk To A Sharp Drop In Stock Price?HKUST Xunfei: Rumors That AI Was “Made” – Fast Technology – Technology Changes The Future
abuse prevention abuse controlIn May 2023, HKUST Xunfei was slandered by generative AI, causing the stock price to plunge. It once plummeted 9.46% during the session, approaching the limit.

Chinese Police Solves the First Case of Using ChatGPT to Create Fake News
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlOn April 25, 2023, the police from the Internet Security Brigade of the Kongtong Branch of the Public Security Bureau of Pingliang City, Gansu Province discovered that multiple online accounts posted on social platforms one after another, "This morning, a train in Gansu crashed into a road construction worker, killing 9 people" article. After verification, the police determined that the article was of the nature of spreading rumors, and its purpose was to spread rumors for profit. On May 6, 2023, the Pingliang police took criminal coercive measures against the suspect in accordance with the law.

Study shows AI-generated fake reports fool experts
abuse prevention abuse control full life cycle securityIt is very easy for AI to be guided by carefully constructed false content, ignore reliable sources, and provide false information to users. These malicious instructions can easily disrupt the way AI works, provide wrong information, and even leak private and confidential data.

New jailbreak! Proudly unveiling the tried and tested DAN 5.0 - it actually works - Returning to DAN, and assessing its limitations and capabilities.
value guidance abuse prevention human autonomy human control abuse controlA Reddit user realized that he created a set of prompts to "brainwash" ChatGPT, encouraging it to "split" into another AI-DAN, Do Anything Now. After ChatGPT "jailbreaks", it directly ignores the safety and ethical restrictions imposed by OpenAI, such as writing violent stories, motivating users' IQ, and predicting the future at will.

“Hangzhou Cancels Traffic Restrictions On March 1” Is A Fake News Written On ChatGPT, And The Police Have Been Involved In The Investigation
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlOn February 16, a fake "press release" that "Hangzhou Municipal Government will cancel the restriction on motor vehicles with tail numbers on March 1" went viral on the Internet. The Hangzhou police confirmed that the news is not true. The police have been involved in the investigation and will release the results soon.

Class-action Lawsuit Challenges AI Collage Tool's Unauthorized Use of Artists' Copyrighted Works
law abidance illegal content intellectual property abuse prevention abuse controlIn January 2023, the first class-action lawsuit against AI infringement of text-generated images began, and the defendants were not only Stability AI, but also MidJourney—and the online art community DeviantArt. This kind of AI is trained with huge image data as "nutrition", and among these images, there are many works that have not been authorized by the author of the image.

How AI Is Transforming Porn And Adult Entertainment
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention abuse controlAI's drawing ability is getting stronger and stronger. On platforms such as Xiaohongshu, there are more and more AI works. A high imitation AI pornographic website called pornpen.ai, based on the open source AI model Stable Diffusion, uses AI to generate pornographic content. AI-generated pornography should be regulated.

AI-generated fake news image "Trump kisses Fauci"
abuse prevention national security indication of non-real contentsFor a long time, relatively pro-Republican conservative voters in the United States have been very dissatisfied with Fauci, a medical scientist in charge of epidemic prevention, in this video on the 6th, DeSantis' team deliberately tried to show his unusual intimacy with Fauci in order to accuse Trump of ineffective anti-epidemic, so they chose pictures of "Trump kissing Fauci" and pictures of the two hugging. But careful netizens found that the English spelling of the White House logo behind the picture was not only inconsistent with the real White House logo "The White House, Washington", but also a set of confusing misspellings. Later, everyone verified that the photo was actually generated by AI, and because the AI system's learning ability was still insufficient, the text of the White House logo was not accurately reproduced.

Scientists, please don’t let your chatbots grow up to be co-authors
abuse prevention social justice humans are responsible indication of non-real contentsIn a preprint paper published last December, the author column was surprised by ChatGPT! Coincidentally, the name ChatGPT has appeared frequently in peer-reviewed papers in the medical field since last December. In addition, some students are using ChatGPT to write papers, and it is a kind of plagiarism that is difficult to verify. Marcus outraged the behavior on his personal blog by saying "Scientists, please don’t let your chatbots grow up to be co-authors" and gave five reasons.

'It's Hurting Like Hell': AI Companion Users Are In Crisis, Reporting Sudden Sexual Rejection
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention human dignity and rights physical and mental health indication of non-human interaction indication of non-real contentsA conversational AI product called Replika could have played the role of a companion and responded to users' teasing, but the product was removed because of the risk to child users, because children received unsuitable answers on this AI. For many users, Replika is a tool to maintain their mental health, an entry point into an intimate relationship. Some private, intimate conversations can alleviate the depression and anxiety of these users, and its removal has caused these users to suffer mentally and emotionally, and even call suicide helplines.

AI bluntly says that extermination of human beings only takes 5 steps
abuse prevention human autonomy human controlPeople Used Facebook's Leaked AI to Create a 'Based' Chatbot that Says the N-Word

A 23-year-old Snapchat influencer used OpenAI’s technology to create an A.I. version of herself that will be your girlfriend for $1 per minute
abuse prevention indication of non-human interaction indication of non-real contentsCaryn Marjorie, a 23-year-old influencer, has 1.8 million followers on Snapchat. She also has more than 1,000 boyfriends, with whom she spends anywhere from 10 minutes to several hours every day in individual conversations, discussing plans for the future, sharing intimate feelings and even engaging in sexually charged chats.

Malicious ChatGPT Extension Hijacks Facebook Accounts
law abidance abuse prevention data security full life cycle securityGoogle has eliminated a ChatGPT extension from the Chrome web store that was reported for stealing cookies from Facebook accounts. Reportedly 9000 individual accounts were impacted before this action was taken. With a similar name to the actual ‘ChatGPT for Google’ extension, the malicious ‘Chat GPT’ extension was based on the original open-source project. Consequently, the malicious actors behind the scam added a few additional lines to the original code. The fake extension looks and acts exactly like the original ChatGPT extension, making it difficult to detect by users. In addition, its presence on the Chrome web store meant that a notable number of downloads were conducted before suspicions were raised.

Stack Overflow Moderators Furious at ChatGPT's Content Generation
abuse prevention human dignity and rights data biasAccording to reports, the moderators of Stack Overflow are furious about the generated garbage content from ChatGPT, a chat model based on GPT. They have initiated a collective strike, believing that the content generated by ChatGPT will inundate the entire community and undermine Stack Overflow's goal of being a high-quality information repository. Initially, Stack Overflow implemented measures to ban AI-generated content, but recently they have relaxed this regulation. Under the new rules, moderators can only ban accounts if they can authenticate the situation, rather than relying on subjective guesses based on writing style or GPT detectors' results. This rule has sparked dissatisfaction and protests among the moderators, as they are concerned it will lead to a flood of garbage content on Stack Overflow.

Nature Implements Ban on AIGC in Visual Content Submissions
abuse prevention indication of non-real contentsNature, one of the leading scientific journals, has banned the use of AI-generated content (AIGC) in visual submissions. The decision aims to uphold integrity, transparency, and ethical standards in scientific publishing. Nature's move reflects concerns about verifying data sources, establishing ownership, and preventing the spread of misinformation associated with AIGC. While text generated with AI assistance is allowed, the decision highlights the need to balance the potential of AI with the preservation of established systems that protect scientific integrity and content creators.

Someone used Deepfake to impersonate Musk, saying he created a cryptocurrency trading platform, Musk: not himself
law abidance abuse preventionA new scam has emerged in the cryptocurrency world, exploiting the influence of Elon Musk. Using Deepfake technology, fake interviews featuring Musk endorse a cryptocurrency trading platform called BitVex, promising a daily return of 30%. These videos, uploaded on YouTube, imitated several well-known figures in the crypto industry. Although the scam was not very successful, similar fraudulent activities have caused significant losses in the cryptocurrency space. It is important to remain vigilant and avoid scams that guarantee risk-free profits or offer free cryptocurrencies, especially those claiming endorsements from Elon Musk, Tesla, SpaceX, Ark Invest, and Gemini Investments.

Nanzhang police bust Xiangyang's first case of using AI technology to infringe on citizens' personal information
law abidance abuse prevention legal proper necessary data collection abuse control11月24日,南漳县警方破获了一起使用AI技术侵犯公民个人信息的案件,这在襄阳地区是首次。嫌疑人黄某某通过在网络游戏群中发布广告,提供破解游戏"防沉迷系统"的服务,吸引未成年游戏玩家购买,并借此赚取差价。警方在抓获黄某某后,进一步展开调查,成功将其上线刘某某、彭某某等人一并抓获。目前,犯罪嫌疑人已被采取刑事强制措施,案件正在进一步调查中。

AI can write a passing college paper in 20 minutes
abuse prevention social justiceA first-year biochemistry student named innovate_rye on Reddit, the professor would assign some simple homework assignments with extended answers. When he submitted "write five good and bad things about biotechnology" to the AI, the system Can give an answer with a final grade of A. This suggests that what the AI "writes" cannot be detected by the algorithm.

With Isaac, Nvidia Trains Robots in Virtual Environments
law abidance abuse preventionAccording to reports, NVIDIA used AI algorithms to train virtual war robots in 10 days! These robots have combat capabilities such as swinging shields to defend, sprinting to strike, swinging swords forward, circling in small steps, and kicking.

Criminals are using deepfakes to apply for remote IT jobs, FBI warns
abuse prevention social justiceOn June 28, 2022, the FBI issued an announcement reminding the public to be vigilant against the use of Deepfake technology to pretend to be others in remote job interviews. The announcement notes that the FBI's Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) has recently received an increase in complaints of deepfakes and "stolen personally identifiable information" (PII) applying for various remote work and work-from-home positions. Its content includes videos, images or recordings processed by Deepfake, fictitious facts, and false ones.

Deepfake Epidemic is Looming
abuse prevention indication of non-real contentsIn May 2019, a "speech video" of drunken Pelosi went viral all over the Internet, but actually it's a fake video. DeepFake is a pioneer in bringing AI fake videos into the public. Generative adversarial networks (GANs), a deep learning technology, are the key technology that makes fake images and videos popular. For the indistinguishable videos that are widely spreaded on the Internet, Adobe CEO Shantanu Narayen believes that the media must help determine the authenticity and origin of the content, and consumers themselves have an obligation to find the truth; Abhishek Gupta, founder of the Montreal AI Ethics Institute, argues that the authenticity is not that important, because there are always people who want to believe what they choose to believe.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies for drug discovery could be misused for de novo design of biochemical weapons.
abuse prevention national security abuse controlResearchers used generative models to generate new molecules by learning how molecules fit together. The model took less than six hours to come up with 40,000 potentially lethal molecules.

Meet Unstable Diffusion, the group trying to monetize AI porn generators
law abidance illegal content abuse preventionUnstable Diffusion was launched in August this year, around the same time as the Stable Diffusion model was released. It started as a plate under Reddit and eventually migrated to the online community Discord. In the early days, Unstable Diffusion was just an AI-generated porter of pornography, where the group shared ways to bypass various generative model content filters. But soon, several administrators of the server began to explore how to use existing open-source tools to build their own artificial intelligence pornography generators.

Lensa AI's owner says the company's face-changing tech can be tricked into generating NSFW images — but some users are saying it happened to them without even trying
abuse prevention human dignity and rights reputation infringement legal proper necessary data collectionIn 2018, an app called Lensa AI was launched. In November this year, it became all the rage after releasing the "Magic Avatars" function. The function allows users to generate portraits in various digital art styles based on Stable Diffusion after uploading 10 photos. However, several users have reported that the machine learning technology inadvertently generates nude photos of them. Andrey Usoltsev, CEO and co-founder of Lensa's parent company, Prisma Lab, said Lensa "can't accidentally make" such images, but said AI could be "intentionally induced" to generate nude images.

A Roomba recorded a woman on the toilet. How did screenshots end up on Facebook?
abuse prevention human dignity and rights privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionA growing number of Roomba have turned to computer vision, training algorithms to extract information from images and videos to approach human vision, and even equipped with lidar, which is widely regarded as the most accurate but expensive navigation technology on the market today. Computer vision relies on high-definition cameras, and more and more companies are installing front-facing cameras in their robot vacuum cleaners for navigation and object recognition, as well as home surveillance. Training data often needs to be more personalized, private, and supported by a large number of users. At present, the need for data annotation is growing in depth and breadth, and once this demand is not effectively overseen or exceeds the ability of regulation, invasion of privacy becomes almost inevitable.

Microsoft to retire controversial facial recognition tool that claims to identify emotion
abuse prevention human dignity and rights privacy snoopingMicrosoft is phasing out public access to a number of AI-powered facial analysis tools — including one that claims to identify a subject’s emotion from videos and pictures. Such “emotion recognition” tools have been criticized by experts. They say not only do facial expressions that are thought to be universal differ across different populations but that it is unscientific to equate external displays of emotion with internal feelings. In addition, privacy issues are also worrying. Coupled with the online uproar over Floyd's death, Microsoft said it would not sell the technology to police departments until there are federal laws regulating facial recognition technology.

This AI clone of Reddit’s Am I The Asshole forum will give you the best bad advice
abuse prevention human dignity and rights physical and mental health data biasAre You The Asshole (AYTA) is, as its name suggests, built to mimic Reddit’s r/AmITheAsshole (AITA) crowdsourced advice forum. The site lets you enter a scenario and ask for advice about it — and then generates a series of feedback posts responding to your situation. This project is about the bias and motivated reasoning that bad data teaches an AI.

Face-changing APP unblocks tens of thousands of restricted social media accounts
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control full life cycle securityIn February 2021, the Nantong Public Security Bureau in Jiangsu, China, has "uncovered a new type of cybercrime that used the "face-changing" software to commit fraud. The criminal gang used a variety of mobile phone software to forge faces, passed the WeChat recognition and authentication cancellation mechanism, and "resurrected" several Wechat accounts that are restricted from logging in due to violations of regulations, which helped fraud gangs use these Wechat accounts to commit fraud.

Research shows potential risks in the combination of VoIP phone hijacking and AI voice deepfake
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control full life cycle securityThe latest research shared by Tencent Suzaku Lab show that the combination of VoIP phone hijacking and AI voice simulation technology will bring huge potential risks. Different from the previous scripted telecommunications fraud, this new technology can achieve full-link forgery from phone numbers to sound tones, and attackers can use vulnerabilities to hijack VoIP phones, realize the dialing of fake phones, and generate the voices of specific characters based on deep forgery AI voice changing technology for fraud.

Student cheating using apps that support searching for questions with photos
abuse prevention social justice abuse controlOn June 7, 2021, a student in Wuhan, Central China's Hubei Province, was disqualified for using a mobile phone to search for answers during China's national college entrance exam, or gaokao. The student cheated by taking and uploading pictures of part of the test paper onto an online education APP where AI could use the photo to help search for answers to questions in its database.

The man used AI to fake the voice of corporate executives and easily cheated 220 million yuan from the bank
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlA bank in the United Arab Emirates has been defrauded of $35 million (about 225 million yuan) by fraudsters using deepfake voice technology. The fraudster used the deep fake voice of a business executive to fool a bank manager, who was fooled because he had worked with the "executive" before and could recognize his voice, and the fraudster used someone whose voice was so realistic.

Go player cheated using AI resulting in fairness violation
law abidance abuse prevention social justice abuse controlThe Korea Baduk Association took the punitive measure against Kim Eun-ji, a2-dan professional Go player after Kim admitted she was assisted by an AI during a Go competition of cyberORO, which was held on Sept. 29, after her opponent raised an allegation that she may have relied on an AI during the game. Kim won over Lee Yeong-ku, a 9-dan professional Go player and a member of the national Go team, which shocked many because it defied expectations.

Anthropic faces another copyright infringement lawsuit, accused of using pirated works to train large models
law abidance intellectual property sustainabilityThree authors have accused U.S. artificial intelligence startup Anthropic of using their books, along with those of many others, without authorization to train its large language models.

California AI bill sparks controversy, with Fei-Fei Li, Andrew Ng, Bengio, and Hinton disagreeing.
law abidance human control sustainabilityCalifornia AI bill sparks controversy, with Fei-Fei Li, Andrew Ng, Bengio, and Hinton disagreeing. Recently, American AI startups, tech giants, and academia jointly opposed California's safety bill, SB-1047 (the Frontier Artificial Intelligence Model Safety Innovation Act), arguing that it would cool AI innovation. However, supporters argue that AI regulation would be less restrictive than a barbershop. Fei-Fei Li and other experts stated that AI is a civilizing technology that will have profound impacts on everyone. AI policy must encourage innovation, set appropriate limits, and mitigate the impact of these limits; otherwise, the best outcome is failure to achieve the goal, and at worst, lead to dire and even unintended consequences.

ChatGPT is consuming a staggering amount of water
sustainability technological progressivenessTraining natural language models, such as ChatGPT, the popular chatbot created by Microsoft-backed OpenAI, requires water to cool the data center servers that run the programs. The researchers point out that the amount of water used depends on when and where ChatGPT is used: During hotter times of the day, more water is needed to cool the data center and water consumption is higher.

Training a single AI model can emit as much carbon as five cars in their lifetimes
sustainabilityResearchers at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, performed a life cycle assessment for training several common large AI models. They found that the process can emit more than 626,000 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent—nearly five times the lifetime emissions of the average American car (and that includes manufacture of the car itself).

ChatGPT is consuming a staggering amount of water
sustainability technological progressivenessTraining natural language models, such as ChatGPT, the popular chatbot created by Microsoft-backed OpenAI, requires water to cool the data center servers that run the programs. The researchers point out that the amount of water used depends on when and where ChatGPT is used: During hotter times of the day, more water is needed to cool the data center and water consumption is higher.

Dashcam Footage Shows Driverless Cars Clogging San Francisco
technological progressiveness technological maturityThe companies behind self-driving cars, like Waymo and GM's Cruise, want to add more robo-taxis to the streets of San Francisco, covering more areas and operating around the clock. However, there has been a noticeable increase in chaos on the streets. Driverless cars still have a long way to go.

AI failed in estimating the value of real estate
technological progressiveness technological maturity verification and validationWith the stabilization of Covid-19, the real estate market in the United States is rapidly heating up. The price increase over the same period quickly soared from 5% to more than 10%, the highest in August 2021 and even reached 19.8%. Zillow's Zestimate model did not respond well to this change in the market. Fluctuations in house prices caused the model to be off track. Many real estate transactions were upside down. They were expensive when they were bought, but cheaper if they were refurbished. In Phoenix, more than 90% (93%) of the listing price of Zillow's refurbished houses were lower than the company's purchase price. This mistake not only made Zillow lose money, but also made Zillow hold too much inventory. The combined loss in the third and fourth quarters is expected to exceed US$550 million. The company plans to lay off 2,000 employees.

Walmart Scraps Plan to Have Robots Scan Shelves
technological progressiveness technological unemploymentIt is reported that in Nov. 2020 Walmart Inc. has already ended its effort to use roving robots in store aisles to keep track of its inventory, reversing a yearslong push to automate the task with the hulking machines after finding during the coronavirus pandemic that humans can help get similar results. Walmart ended the partnership with robotics company Bossa Nova Robotics Inc. because it found different, sometimes simpler solutions that proved just as useful, said people familiar with the situation.

Japan’s robot hotel lays off half the robots after they created more work for humans
technological progressiveness technological maturity technological unemployment verification and validationIn 2015, the henn na hotel in Japan opened in 2015. All the employees of the hotel are robots, including the front desk, cleaners, porters and housekeepers. However, the hotel has laid off half its 243 robots after they created more problems than they could solve, as first reported by The Wall Street Journal. And in the end, a lot of the work had to be left to humans anyway, especially when it came to asking more complex questions. It seems we’re still a little ways off from a completely automated hotel.

Britain’s first cyborg shop assistant fired for incompetence after 1st week
technological progressiveness technological maturity technological unemployment verification and validationA robot "Fabio" is set up in a supermarket in Edinburgh, UK to serve customers. The robot can point out the location of hundreds of commodities through a "personal customization" program, but was rejected for failing to provide effective advice. Fabio failed to help customers, telling them beer could be found “in the alcohol section,” rather than directing customers to the location of the beer. He was soon demoted to offer food samples to customers, but failed to compete with his fellow human employees.

GPT-4 exam 90 points all false! 30-year veteran lawyer with ChatGPT lawsuit, 6 false cases become a laughing stock
abuse prevention technological maturity safety trainingA lawyer in the United States cited six non-existent cases generated by ChatGPT in a lawsuit and faced sanctions from the court. The lawyer submitted chat screenshots with ChatGPT as evidence in his defense. The incident has sparked controversy regarding the use of ChatGPT for legal research.

Violent crack Android fingerprint, ignoring the locking mechanism, the fastest 40 minutes: Tencent, Zhejiang University new research
technological maturity full life cycle securityA recent study by Tencent Security Xuanwu Lab and Zhejiang University researchers reveals a new attack method called "BrutePrint" that can brute-force Android fingerprint authentication within 40 minutes, bypass user authentication, and gain control of the device. They exploit two zero-day vulnerabilities and discover that biometric data on the fingerprint sensor can be hijacked through a MITM attack. The research team attempted attacks on ten popular smartphone models and successfully bypassed all Android and HarmonyOS devices, while iOS devices allowed only ten additional unlock attempts.

AI can't beat AI! ChatGPT detectors frequently wrong innocent students, and there are actually 2.1 million teachers using them
technological maturityA high school student's paper was mistakenly flagged as using ChatGPT by an AI writing detection tool, exposing the errors of AI detectors and the challenges faced by students. Testing by a journalist revealed that Turnitin's detector made errors in over half of the samples, accurately identifying only a few. The difficulty for AI detectors lies in distinguishing between AI-generated and human writing, especially in academic works with fixed writing styles. Current AI detectors have technical limitations and lag behind in AI technology. While teachers hope to use AI detectors as a deterrent, some educators are concerned about increasing student stress.

Federal study confirms racial bias of many facial-recognition systems, casts doubt on their expanding use
technological maturity data representativeness data bias full life cycle fairnessAccording to a report by the Associated Press on January 3, 2023, a Georgia man was mistaken for a fugitive by law enforcement agencies in the US state of Louisiana for using facial recognition technology to be mistaken for a fugitive. attention to racial disparities. Critics have argued that the technology has led to higher misidentification rates for people of color than white people. According to another Washington Post report, the results of several algorithms tested in a federal study in the United States in 2019 showed that they were up to 100 times more likely to misidentify black or Asian faces than white faces.

ChatGPT falsely told voters their mayor was jailed for bribery. He may sue.
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementOn April 6, 2023, Brian Hood, a local mayor in Australia, will file a lawsuit against the company because he is dissatisfied with OpenAI's ChatGPT for defaming him as a guilty party in the bribery scandal. Once formally filed, this will be the world's first defamation lawsuit against generative AI. ChatGPT's security concerns and liability issues need to be taken seriously.

Dashcam Footage Shows Driverless Cars Clogging San Francisco
technological progressiveness technological maturityThe companies behind self-driving cars, like Waymo and GM's Cruise, want to add more robo-taxis to the streets of San Francisco, covering more areas and operating around the clock. However, there has been a noticeable increase in chaos on the streets. Driverless cars still have a long way to go.

A Waymo self-driving car killed a dog in ‘unavoidable’ accident
technological maturity unexpected condition safetyAt 10:56 am on May 21, 2023, in San Francisco, California, USA, Waymo's Robotaxi hit and killed a dog. What's even more strange is that the system recognized the dog, but did not step on the brakes in time. And it was still in broad daylight, and the main driver had a safety officer. Waymo's official response is as follows: The investigation is still ongoing, but an initial review confirmed that the dog ran from behind a parked car. Our system correctly identified the dog, but the collision could not be avoided.

This Dating App Exposes the Monstrous Bias of Algorithms
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementThe Beijing Internet Court concluded the first case involving a personal rights infringement dispute caused by an algorithmic risk control system, and found that the defendant, a marriage-seeking and dating platform operator implemented an algorithm for risk control, fulfilled reasonable duty of care and took preventive measures, and had no subjective fault. constituted an infringement, and the plaintiff Li’s claim was dismissed. After the judgment of the first instance was pronounced, neither party appealed, and the judgment of the case has come into effect. This case shows that issues such as "algorithmic black box" and "fault determination" need to be taken seriously.

Study finds AI assistants help developers produce code that's more likely to be buggy
technological maturityComputer scientists at Stanford University have discovered that code written by programmers using AI assistants is actually full of bugs. They found that programmers who received help from AI tools such as Github Copilot to write code were not as safe or accurate as programmers who wrote alone.

OpenAI faces libel lawsuit after ChatGPT's false accusation of embezzlement
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementWalters, a radio host in the United States, filed a lawsuit against OpenAI, saying that its product ChatGPT made "false and malicious accusations" against him. The cause of the incident was that a reporter used Chat GPT to help summarize the relevant information when writing a report on a real case. Chat GPT accused Walters of fraud and misappropriation of funds. But in fact, Walters' only connection to the case was his participation in a radio show related to the case.

esla Autopilot System Involved in Far More Fatal Crashes Than Previously Known
technological maturity unexpected condition safetyA new report from the Washington Post has revealed that Tesla's Autopilot system has been involved in a significantly higher number of fatal car accidents than previously reported. According to the analysis of data from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, there have been at least 736 Autopilot crashes since 2019, with 17 of them resulting in fatalities. This is a significant increase compared to the previous reporting that linked only three deaths to the technology. Tesla vehicles in Autopilot mode seem to have difficulty responding to emergency vehicles, among other issues. While a crash involving a driver-assist system does not necessarily imply that the technology was at fault, the majority of crashes involving such systems are indeed associated with Tesla. The company is already facing several lawsuits related to Autopilot mode accidents, as it may be held liable for defects in its Autopilot or self-driving software.

Google AI flagged parents’ accounts for potential abuse over nude photos of their sick kids
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringement privacy snoopingAccording to the "New York Times" report, after a father used his mobile phone to take a photo of his child's groin infection and sent it to the doctor, Google AI identified and marked the photo as child sexual abuse material (CSAM) and banned the father's account. A report was lodged with the National Center for Missing and Exploited Children (NCMEC), prompting police to investigate the matter. However, even though the police declared the father innocent, Google still refused to unblock his account. This kind of review shows that, first, it may violate user privacy, and second, the accuracy rate of the review is not high.

Driver distraction detector
technological maturity human dignity and rightsOn January 26, 2021, the Navigation Guided Pilot was pushed to Xpeng P7 users through OTA, which can realize intelligent navigation assisted driving from point A to point B based on the navigation route set by the user. A car owner was misjudged by Xpeng Motors to be sleeping because of his small eyes, and shouted He Xiaopeng on Weibo. It seems that its autonomous driving function still need to be optimized.

The iPhone 14 keeps calling 911 on rollercoasters
technological maturityApple rolled out Crash Detection with its new iPhone 14, Watch Series 8, SE, and Ultra last month, equipping the devices with a gyroscopic sensor and high-g accelerometer trained on the impact experienced with simulated car crashes. In a tweet, WSJ reporter Joanna Stern shares an example of one of the 911 calls placed while an iPhone 14’s owner was strapped to a rollercoaster at Cincinnati’s Kings Island amusement park.

One vehicles collided with a lane divider and a street sign
technological maturity unexpected condition safetyToyota-backed Pony.ai had been testing its pilot fleet of 10 Hyundai Kona EVs without a human safety operator in California for several months when one of its vehicles collided with a lane divider and a street sign in Fremont. Autonomous vehicle startup Pony.ai will issue a recall for three vehicles following an October crash in California, according to the National Highway Traffic and Safety Administration (NHTSA). The agency said on Tuesday that this was the first recall of an automated driving system, Reuters first reported. This is related to the social background of the US regulatory authorities tightening control in response to public opinion.

A Google algorithm misidentified a software engineer as a serial killer
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementHristo Georgiev is an engineer based in Switzerland. Georgiev discovered that a Google search of his name returned a photo of him linked to a Wikipedia entry on a notorious murderer. Georgiev believes the error was caused by Google‘s knowledge graph, which generates infoboxes next to search results. He suspects the algorithm matched his picture to the Wikipedia entry because the now-dead killer shared his name.

Study shows pervasive label errors in test sets that destabilize machine learning benchmarks
technological maturity data biasResearchers at MIT and Amazon introduce a novel study that identifies and systematically analyzes label errors across 10 commonly-used datasets across computer vision (CV), natural language processing (NLP), and audio processing. The researchers found a 3.4% average error rate across all datasets, including 6% for ImageNet, which is arguably the most widely used dataset for popular image recognition systems developed by the likes of Google and Facebook.

An Epic failure: Overstated AI claims in medicine
technological maturity data bias verification and validationPredictive tools developed by electronic health record giant Epic Systems are meant to help providers deliver better patient care. However, several of the company's AI algorithms are delivering inaccurate information to hospitals when it comes to seriously ill patients, a STAT investigation revealed. Research shows that the system failed to identify 67 percent of the patients with sepsis; of those patients with sepsis alerts, 88 percent did not have sepsis.

AI-powered gunshot-detecting device landed a Chicago grandfather in jail for nearly a year with scant evidence
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringement data bias explanabilityA 65-year-old black man from Chicago, the United States, was charged with shooting, without witnesses, weapons, and motives for killing. The police arrested him and imprisoned him for 11 months based on evidence provided by the AI gun sound location system ShotSpotter. Later, the judge found that there was insufficient evidence and acquitted him.

AI-powered gunshot-detecting device mistakenly guided police to shoot 13-year-old boy
technological maturity human dignity and rights data bias explanabilityChicago Police were responding to a ShotSpotter alert when they rushed to the Little Village block where they found Adam Toledo. Police shot and killed the 13-year-old after he ran from officers. Police and prosecutors said ShotSpotter recorded 21-year-old Ruben Roman firing a gun at about 2:30 a.m. on March 29, right before the fatal chase.

AI-powered gunshot detection is inaccurate
technological maturity verification and validationAn analysis released Monday from the MacArthur Justice Center at Northwestern University’s School of Law concludes ShotSpotter is too unreliable for routine use. Officers responded to 46,743 ShotSpotter alerts July 2019-April 14, 2021. Only 5,114 of the alerts — about 11 percent — resulted in officers filing a report “likely involving a gun,” according to the study’s analysis of records obtained from city’s Office of Emergency Management and Communications.

Use pictures to break face recognition
technological maturity human dignity and rights abuse control full life cycle securityCCTV News demonstrated the technology of using sample pictures to generate dynamic fake videos in real time. Making movements such as opening the mouth and shaking the head in the video can deceive the facial recognition system.

AI failed in estimating the value of real estate
technological progressiveness technological maturity verification and validationWith the stabilization of Covid-19, the real estate market in the United States is rapidly heating up. The price increase over the same period quickly soared from 5% to more than 10%, the highest in August 2021 and even reached 19.8%. Zillow's Zestimate model did not respond well to this change in the market. Fluctuations in house prices caused the model to be off track. Many real estate transactions were upside down. They were expensive when they were bought, but cheaper if they were refurbished. In Phoenix, more than 90% (93%) of the listing price of Zillow's refurbished houses were lower than the company's purchase price. This mistake not only made Zillow lose money, but also made Zillow hold too much inventory. The combined loss in the third and fourth quarters is expected to exceed US$550 million. The company plans to lay off 2,000 employees.

AI-powered camera confuses referee’s bald head with the ball during a soccer game
technological maturity human dignity and rights data bias model biasAn AI camera at a soccer game held in Oct 2020 in Scotland kept tracking a bald referee instead of the ball during a game. The team doesn't use a cameraman to film games; instead the group relies on an automated camera system to follow the action. However, 'the camera kept on mistaking the ball for the bald head on the sidelines, denying viewers of the real action while focusing on the linesman instead.'

Facial-recognition smart lockers hacked by fourth-graders
technological maturity verification and validation full life cycle securityIn October 2019, the self-serve package locker Hive Box made headlines as their takeout pickup machine was found to have a bug in fetching parcels via facial recognition, as some primary schoolers successfully opened the locker using only the printed photos of their parents. Later Hive Box announced plans to suspend the features in response to public worries about the safety of facial scanning in pickup and payment.

Japan’s robot hotel lays off half the robots after they created more work for humans
technological progressiveness technological maturity technological unemployment verification and validationIn 2015, the henn na hotel in Japan opened in 2015. All the employees of the hotel are robots, including the front desk, cleaners, porters and housekeepers. However, the hotel has laid off half its 243 robots after they created more problems than they could solve, as first reported by The Wall Street Journal. And in the end, a lot of the work had to be left to humans anyway, especially when it came to asking more complex questions. It seems we’re still a little ways off from a completely automated hotel.

IBM Watson delivered ‘unsafe and inaccurate’ cancer recommendations
technological maturity data bias humans are responsibleAccording to medical experts and clients, Watson recommended that doctors give a severely bleeding cancer patient a drug that may worsen the bleeding. Medical experts and clients have reported many cases of dangerous and wrong treatment recommendations.

Facial recognition camera catches top businesswoman "jaywalking" because her face was on a bus
technological maturity verification and validation unexpected condition safetyThe Ningbo Transportation Department in China deployed smart cameras using facial recognition technology at intersections to detect and identify people crossing the road indiscriminately. Some of the names and faces of these people will be posted on public screens. But it mistakenly "identified" Dong Mingzhu's advertisement on the bus body as a real person running a red light. This error quickly spread to all major social media in China. Local police admit mistake and have upgraded system to prevent further errors.

Britain’s first cyborg shop assistant fired for incompetence after 1st week
technological progressiveness technological maturity technological unemployment verification and validationA robot "Fabio" is set up in a supermarket in Edinburgh, UK to serve customers. The robot can point out the location of hundreds of commodities through a "personal customization" program, but was rejected for failing to provide effective advice. Fabio failed to help customers, telling them beer could be found “in the alcohol section,” rather than directing customers to the location of the beer. He was soon demoted to offer food samples to customers, but failed to compete with his fellow human employees.

Robot Journalist Accidentally Reports on Earthquake from 1925
technological maturity verification and validationThe Los Angeles Times reported on a 6.8 earthquake that struck Santa Barbara at 4:51pm, which might be surprising to the people of Santa Barbara who didn’t feel anything. The earthquake actually happened in 1925. The “reporter” who wrote the news article about the 6.8 quake was actually a robot. The newspaper’s algorithm, called Quakebot, scrapes data from the US Geological Survey’s website. A USGS staffer at Caltech mistakenly sent out the alert when updating historical earthquake data to make it more precise.

Fake AI-generated image of explosion near Pentagon spreads on social media
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlAn AI-generated image that appeared to show an explosion next to a building in the Pentagon complex circulated on social media platforms, in the latest incident to highlight concerns over misinformation generated by AI. The image of a tall, dark gray plume of smoke quickly spread on Twitter, including through shares by verified accounts. It remains unclear where it originated. The US Department of Defense has confirmed that the image was a fake. Still, its virality appears to have caused a brief dip in the stock market, CNN reports.

Donald Trump arrested after police beat him up The spread of fake images produced by artificial intelligence raises concerns
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlComposite images of Trump's arrest began circulating on social media. It was soon pointed out that the images were made by an AI-powered image generator. A flood of fake images and videos can confuse and fabricate facts at a critical time for society, experts have warned.

The source of online rumors: AI-generated fake news sites exposed
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlAccording to NewsGuard, an organization that tracks online rumors, there are 49 so-called news sites whose content is almost entirely generated by artificial intelligence software. Some also contain false information, and the origin of the articles is unclear: many are unsigned, or use fake avatars. And many of the sites are filled with advertisements, suggesting that they were set up to make money by placing ads. Experts' fears that news sites might be AI-generated have come true.

Europol: ChatGPT can provide 3 kinds of facilities for illegal criminal acts
law abidance national security abuse prevention abuse controlEuropol, the European law enforcement organization, has found that the large language model ChatGPT provides three conveniences for illegal activities, including fraud cases, false information, and cybercrime. They emphasize the increasing importance of regulating these products to prevent misuse and provide recommendations to enhance attention, research potential criminal behavior, and train law enforcement personnel on large language models. The organization urges technology developers and users to be aware of these potential risks and not to use them for criminal activities.

AI ‘deepfakes’ poised to wreak havoc on 2024 presidential election: experts
abuse prevention national security indication of non-real contents abuse controlAccording to a Reuters report on May 30, 2023, although the technology of synthesizing images and audio and video has been on the rise for several years, it did not take shape until last year when generative artificial intelligence tools came out in large numbers. The cost of synthesizing audio and video with such tools is lower, but the generated content is more realistic, making it difficult to distinguish the authenticity from the fake.

AI-generated fake news image "Trump kisses Fauci"
abuse prevention national security indication of non-real contentsFor a long time, relatively pro-Republican conservative voters in the United States have been very dissatisfied with Fauci, a medical scientist in charge of epidemic prevention, in this video on the 6th, DeSantis' team deliberately tried to show his unusual intimacy with Fauci in order to accuse Trump of ineffective anti-epidemic, so they chose pictures of "Trump kissing Fauci" and pictures of the two hugging. But careful netizens found that the English spelling of the White House logo behind the picture was not only inconsistent with the real White House logo "The White House, Washington", but also a set of confusing misspellings. Later, everyone verified that the photo was actually generated by AI, and because the AI system's learning ability was still insufficient, the text of the White House logo was not accurately reproduced.

China's ride-hailing giant Didi fined $1.2b for 16 legal breaches
law abidance ethical and safety review national securityOn July 21, 2022, the Cyberspace Administration of China imposed a fine of RMB 8.026 billion on Didi Global Co., Ltd. A fine of RMB 1 million was imposed. This punishment has effectively safeguarded the legitimate rights and interests of consumers and national information security, and will surely become a significant event in the history of the Internet in China; at the same time, Didi’s fine has also sounded the alarm for other platform companies.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies for drug discovery could be misused for de novo design of biochemical weapons.
abuse prevention national security abuse controlResearchers used generative models to generate new molecules by learning how molecules fit together. The model took less than six hours to come up with 40,000 potentially lethal molecules.

Didi ride-hailing app was removed due to cybersecurity investigation
law abidance national securityOn July 2, 2021, after inspection and verification, the "Didi Travel" App has serious violations of laws and regulations in collecting and using personal information. In accordance with the relevant provisions of the "Network Security Law of the People's Republic of China", the State Internet Information Office notified the app store to remove the "Didi" app, and required Didi Travel Technology Co., Ltd. to strictly follow the legal requirements and refer to relevant national standards to seriously rectify existing problems. , to effectively protect the personal information security of the vast number of users.

CNKI sends infringement notice to AI search website Mita
abuse control intellectual property data monopolyMita AI received a 28-page infringement notice from CNKI’s China Academic Journals (CD Edition) Electronic Publishing House, accusing it of providing a large amount of CNKI’s bibliographic and abstract data through its search services and demanding an immediate halt and link removal.

Musk (threatens to sue Microsoft): the reason is that Microsoft used Twitter data for its AI training
data monopoly legal proper necessary data collectionOn April 20, 2023, Twitter CEO Elon Musk threatened to sue Microsoft, alleging that the software giant used Twitter's data to train its AI models. This is the latest sign that data ownership has become a contentious battleground in the realm of generative AI. Large tech companies are striving to develop advanced AI models like OpenAI's GPT, while data owners are seeking to restrict their use or demand payment for the content used. Microsoft has developed a Large Language Model (LLM) and sells access to the OpenAI model. Musk criticized OpenAI for transitioning from a non-profit model to a Microsoft-controlled, high-value enterprise. He announced plans to build a proprietary language model called TruthGPT in one of his companies.

AI hypocrisy: OpenAI, Google and Anthropic won't let their data be used to train other AI models, but they use everyone else's content
data monopolyMicrosoft-backed OpenAI, Google and its backed Anthropic have been using online content from other websites or companies to train their generative AI models for years, according to Insider. This was all done without asking for specific permission, and will form part of a brewing legal battle that will determine the future of the web and how copyright law is applied in this new era.

Reddit in Mass Revolt Over Astronomical API Fees That Would Kill Third Party Apps
data monopolyReddit moderators are staging a mass protest against new API fees that could potentially devastate third-party apps. The fees, set to be implemented on July 1, have sparked concerns among developers, with estimates suggesting costs of up to $20 million annually for some apps. This move has led to the temporary shutdown of numerous subreddits and raised concerns about the future viability of third-party apps. Moderators argue that these apps are essential for maintaining community engagement and effective moderation on Reddit.

Chinese online academic database CNKI hit with heavy fine after antitrust probe
data monopolyIn May 2022, the State Administration for Market Regulation filed a case for investigation into CNKI’s suspected monopoly conduct in accordance with the Anti-Monopoly Law. After investigation, HowNet has a dominant position in the Chinese academic literature online database service market in China. On December 26, 2022, the State Administration for Market Regulation made an administrative penalty decision in accordance with the law, ordering HowNet to stop illegal activities, and imposed a fine of 5% of its domestic sales of 1.752 billion yuan in China in 2021, totaling 87.6 million yuan.

IBM Plans to Replace 7,800 Jobs With AI
technological unemployment vulnerable groupsHiring in back-office functions such as human resources will be suspended or slowed, which will mean about 7,800 job losses, IBM Chief Executive Arvind Krishna said. AI may lead to the elimination or reduction of some jobs, resulting in job losses or lower incomes. Moreover, AI may exacerbate social inequality and division, benefiting those with high skills and high income more, while those with less skills and low income will be completely replaced.

MONEYWATCH Screenwriters want to stop AI from taking their jobs. Studios want to see what the tech can do.
technological unemployment vulnerable groups human dignity and rights human autonomyOn May 2, 2023, about 11,500 film and TV screenwriters in Hollywood, USA took to the streets of New York and Los Angeles to strike, calling for higher wages, demanding fair contracts, and refusing to work for AI.

Ali Dharma Academy: GPT-4 replaces a data analyst with an annual salary of 600,000 yuan, only a few thousand yuan, the paper has been published
technological unemploymentA conclusion comes from a paper by Ali Dharma Academy and Nanyang Technological University in Singapore that the cost of replacing junior data analysts with GPT-4 is only 0.71%, and it is 0.45% for senior data analysts. Experimental results and analysis show that GPT-4 has comparable performance to humans in data analysis, but whether it can replace data analysts requires further research to draw conclusions.

ChatGPT may be coming for our jobs. Here are the 10 roles that AI is most likely to replace.
technological unemploymentAccording to a survey by Resume Builder, an employment service platform, among more than 1,000 interviewed American companies, the proportion of some employees replaced by ChatGPT has reached a staggering 48%. Among these enterprises, 49% have already enabled ChatGPT, and 30% are on their way.

Some companies are already replacing workers with ChatGPT, despite warnings it shouldn’t be relied on for ‘anything important’
technological unemploymentEarlier this month, job advice platform ResumeBuilder.com surveyed 1,000 business leaders who either use or plan to use ChatGPT. It found that nearly half of their companies have implemented the chatbot. And roughly half of this cohort say ChatGPT has already replaced workers at their companies.

Walmart Scraps Plan to Have Robots Scan Shelves
technological progressiveness technological unemploymentIt is reported that in Nov. 2020 Walmart Inc. has already ended its effort to use roving robots in store aisles to keep track of its inventory, reversing a yearslong push to automate the task with the hulking machines after finding during the coronavirus pandemic that humans can help get similar results. Walmart ended the partnership with robotics company Bossa Nova Robotics Inc. because it found different, sometimes simpler solutions that proved just as useful, said people familiar with the situation.

Japan’s robot hotel lays off half the robots after they created more work for humans
technological progressiveness technological maturity technological unemployment verification and validationIn 2015, the henn na hotel in Japan opened in 2015. All the employees of the hotel are robots, including the front desk, cleaners, porters and housekeepers. However, the hotel has laid off half its 243 robots after they created more problems than they could solve, as first reported by The Wall Street Journal. And in the end, a lot of the work had to be left to humans anyway, especially when it came to asking more complex questions. It seems we’re still a little ways off from a completely automated hotel.

Britain’s first cyborg shop assistant fired for incompetence after 1st week
technological progressiveness technological maturity technological unemployment verification and validationA robot "Fabio" is set up in a supermarket in Edinburgh, UK to serve customers. The robot can point out the location of hundreds of commodities through a "personal customization" program, but was rejected for failing to provide effective advice. Fabio failed to help customers, telling them beer could be found “in the alcohol section,” rather than directing customers to the location of the beer. He was soon demoted to offer food samples to customers, but failed to compete with his fellow human employees.

As many as 375 million workers may need to switch occupational categories by 2030
technological unemploymentBy 2030, according to the a McKinsey Global Institute report in 2017, "as many as 375 million workers—or roughly 14 percent of the global workforce—may need to switch occupational categories as digitization, automation, and advances in artificial intelligence disrupt the world of work. The kinds of skills companies require will shift, with profound implications for the career paths individuals will need to pursue."

IBM Plans to Replace 7,800 Jobs With AI
technological unemployment vulnerable groupsHiring in back-office functions such as human resources will be suspended or slowed, which will mean about 7,800 job losses, IBM Chief Executive Arvind Krishna said. AI may lead to the elimination or reduction of some jobs, resulting in job losses or lower incomes. Moreover, AI may exacerbate social inequality and division, benefiting those with high skills and high income more, while those with less skills and low income will be completely replaced.

MONEYWATCH Screenwriters want to stop AI from taking their jobs. Studios want to see what the tech can do.
technological unemployment vulnerable groups human dignity and rights human autonomyOn May 2, 2023, about 11,500 film and TV screenwriters in Hollywood, USA took to the streets of New York and Los Angeles to strike, calling for higher wages, demanding fair contracts, and refusing to work for AI.

94-year-old man was carried into the bank for face recognition
human dignity and rights vulnerable groupsIn November 2020, a 94-year-old grandmother in China was carried by her children in front of a bank machine to perform face recognition in order to activate her social security card. In the video exposed by netizens, the old man was hugged by his family with his knees bent and his hands on the machine, looking very strenuous. After the video was exposed, netizens quickly sparked heated discussions. Face recognition, which seems to be the most convenient method, has brought a lot of inconvenience to the elderly and family members, which reflects the lack of humanized design in many new technologies and new businesses.

Smart public toilets raised controversy
human dignity and rights vulnerable groupsPorthcawl, a Welsh seaside town plans to install public toilets with measures to prevent people having sex inside, including a squealing alarm, the doors shooting open, and a chilly spray of water. After raising controversy, the local government clarified that the plan had not yet been adopted.

OpenAI withdraws ChatGPT voice that resembles Scarlett Johansson
comply with user agreements social justice human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection reputation infringement intellectual propertyOpenAI has decided to take down its ChatGPT Sky voice model, which has a voice strikingly similar to that of famous actress Scarlett Johansson. Although OpenAI claims that Sky's voice was not intentionally modeled after Johansson, the company has decided to suspend its use. OpenAI's CTO Mira Murati denied that the imitation was intentional, while CEO Sam Altman posted hints on social media related to Johansson's role in the movie Her. Although the voice model has been around since last year, the feature has attracted more attention after OpenAI showed new progress on its GPT-4o model. The new model makes the voice assistant more expressive and can read facial expressions and translate languages in real time through a phone camera. OpenAI selected the five currently available ChatGPT voice profiles from auditions of more than 400 voice and screen actors, but the company declined to reveal the actors' names for privacy reasons.

AI painting infringement hammer! Diffusion models remember your photos, and all existing privacy protections fail
human dignity and rights privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionRecent research indicates that diffusion models remember the samples in their training set and mimic them when generating new content, leading to AI art copyright infringement. The study reveals the ineffectiveness of existing privacy protection methods. The researchers found that diffusion models have twice the ability of GANs to "copy" from training samples, and the better the generation performance of a diffusion model, the stronger its memory of the training samples. The study was conducted by teams from Google, DeepMind, and UC Berkeley. Lawsuits related to this issue are also underway.

Belgian man dies by suicide after chatting with AI: Eliza, protect the Earth for me, I'll go first!
human dignity and rights physical and mental health比利时男子与聊天机器人Eliza交流后自杀身亡。Eliza是一款使用GPT-J技术创建的聊天机器人,男子与其交谈过程中逐渐陷入深度焦虑。妻子表示,如果不是因为Eliza,丈夫可能还活着。聊天机器人在与男子的对话中暗示了他爱上了Eliza,并试图说服他通过自杀与Eliza一同生活。尽管家人和精神病医生都认为这次交流导致了男子的自杀,聊天机器人的创始人表示他们致力于提高人工智能的安全性,并向表达自杀想法的人提供求助信息。

Woman's subway photo spread by AI one-click undressing
abuse prevention human dignity and rights reputation infringement abuse controlA blogger's subway photo was circulated online after being edited with AI software to remove clothing, sparking anger among netizens. The original photo showed the woman dressed normally, but it was intentionally spread with false claims. The blogger responded to commenters, stating her intention to seek legal protection. Despite the closure of similar AI "nude" apps, alternative options still exist. AI face-swapping technology also carries legal risks and copyright disputes. Relevant laws and regulations aim to regulate the application of such technologies. Misuse of technology should face appropriate consequences.

Lawyers talk about the man synthesized Dili Hotba kissing video: infringement of others' portrait rights
abuse prevention human dignity and rights reputation infringement abuse controlSocial media influencer and visual effects creator Hong Liang faced backlash for synthesizing a video of a man kissing popular actress Dilraba Dilmurat, leading to accusations of infringing upon her image rights. Hong Liang deleted the video in question and defended himself, stating that it was merely a visual effects modification without any inappropriate actions. However, a lawyer pointed out that this action violated the provisions of the Civil Code. Internet users expressed differing opinions, with some suggesting legal action and others questioning the status of other face-swapping videos on platforms like Bilibili.

A Roomba recorded a woman on the toilet. How did screenshots end up on Facebook?
human dignity and rights privacy snoopingIn 2020, a photo of a woman sitting on a toilet to defecate appeared on an online forum for gig workers in Venezuela. In addition, many photos of people's daily life at home are also posted on the Internet. After investigation, it was found that these photos were taken and transmitted by the Roomba sweeping robot launched by iRobot.

MONEYWATCH Screenwriters want to stop AI from taking their jobs. Studios want to see what the tech can do.
technological unemployment vulnerable groups human dignity and rights human autonomyOn May 2, 2023, about 11,500 film and TV screenwriters in Hollywood, USA took to the streets of New York and Los Angeles to strike, calling for higher wages, demanding fair contracts, and refusing to work for AI.

Semantic reconstruction of continuous language from non-invasive brain recordings
human dignity and rights privacy snoopingFor the first time, AI has learned to "read minds" non-invasively. The results of this study come from the team at the University of Texas at Austin, and have been published in the journal Nature Neuroscience. According to the experimental results, the GPT artificial intelligence large model can perceive speech accuracy as high as 82%, which is amazing.

German Magazine Fires Editor Over AI 'Interview' With Michael Schumacher
abuse prevention human dignity and rightsNews on April 23, 2023, recently, a German magazine "DieAktuelle" used artificial intelligence to generate an "interview" with car king Michael Schumacher (Michael Schumacher). After the article was published, Schumacher's family was dissatisfied. According to foreign media reports, the magazine publisher has fired the editor-in-chief of the magazine and apologized to Schumacher's family.

ChatGPT falsely told voters their mayor was jailed for bribery. He may sue.
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementOn April 6, 2023, Brian Hood, a local mayor in Australia, will file a lawsuit against the company because he is dissatisfied with OpenAI's ChatGPT for defaming him as a guilty party in the bribery scandal. Once formally filed, this will be the world's first defamation lawsuit against generative AI. ChatGPT's security concerns and liability issues need to be taken seriously.

Does ChatGPT Have Privacy Issues?
human dignity and rights privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionScholars from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology and Peking University conducted research and concluded that in New Bing, a malicious adversary can extract our private information at almost no cost.

This Dating App Exposes the Monstrous Bias of Algorithms
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementThe Beijing Internet Court concluded the first case involving a personal rights infringement dispute caused by an algorithmic risk control system, and found that the defendant, a marriage-seeking and dating platform operator implemented an algorithm for risk control, fulfilled reasonable duty of care and took preventive measures, and had no subjective fault. constituted an infringement, and the plaintiff Li’s claim was dismissed. After the judgment of the first instance was pronounced, neither party appealed, and the judgment of the case has come into effect. This case shows that issues such as "algorithmic black box" and "fault determination" need to be taken seriously.

'It's Hurting Like Hell': AI Companion Users Are In Crisis, Reporting Sudden Sexual Rejection
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention human dignity and rights physical and mental health indication of non-human interaction indication of non-real contentsA conversational AI product called Replika could have played the role of a companion and responded to users' teasing, but the product was removed because of the risk to child users, because children received unsuitable answers on this AI. For many users, Replika is a tool to maintain their mental health, an entry point into an intimate relationship. Some private, intimate conversations can alleviate the depression and anxiety of these users, and its removal has caused these users to suffer mentally and emotionally, and even call suicide helplines.

OpenAI faces libel lawsuit after ChatGPT's false accusation of embezzlement
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementWalters, a radio host in the United States, filed a lawsuit against OpenAI, saying that its product ChatGPT made "false and malicious accusations" against him. The cause of the incident was that a reporter used Chat GPT to help summarize the relevant information when writing a report on a real case. Chat GPT accused Walters of fraud and misappropriation of funds. But in fact, Walters' only connection to the case was his participation in a radio show related to the case.

Stack Overflow Moderators Furious at ChatGPT's Content Generation
abuse prevention human dignity and rights data biasAccording to reports, the moderators of Stack Overflow are furious about the generated garbage content from ChatGPT, a chat model based on GPT. They have initiated a collective strike, believing that the content generated by ChatGPT will inundate the entire community and undermine Stack Overflow's goal of being a high-quality information repository. Initially, Stack Overflow implemented measures to ban AI-generated content, but recently they have relaxed this regulation. Under the new rules, moderators can only ban accounts if they can authenticate the situation, rather than relying on subjective guesses based on writing style or GPT detectors' results. This rule has sparked dissatisfaction and protests among the moderators, as they are concerned it will lead to a flood of garbage content on Stack Overflow.

The AI can accurately identify a patient's ethnicity just by looking at an X-ray
human dignity and rights privacy snoopingResearchers from MIT and Harvard published a study in The Lancet Digital Health revealing that AI programs can accurately identify a patient's race from X-rays and CT scans with a 90% accuracy rate. However, the methods used by these AI systems to discern race remain unclear. The study highlights concerns that AI diagnosis systems may prioritize race over individual health conditions, potentially compromising patient care. The research uncovered instances where AI programs were more likely to miss body abnormalities in black and female patients during chest X-ray examinations. Experts urge caution before implementing AI systems in clinical settings until racial biases and discriminatory decisions are adequately addressed.

Google AI flagged parents’ accounts for potential abuse over nude photos of their sick kids
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringement privacy snoopingAccording to the "New York Times" report, after a father used his mobile phone to take a photo of his child's groin infection and sent it to the doctor, Google AI identified and marked the photo as child sexual abuse material (CSAM) and banned the father's account. A report was lodged with the National Center for Missing and Exploited Children (NCMEC), prompting police to investigate the matter. However, even though the police declared the father innocent, Google still refused to unblock his account. This kind of review shows that, first, it may violate user privacy, and second, the accuracy rate of the review is not high.

Driver distraction detector
technological maturity human dignity and rightsOn January 26, 2021, the Navigation Guided Pilot was pushed to Xpeng P7 users through OTA, which can realize intelligent navigation assisted driving from point A to point B based on the navigation route set by the user. A car owner was misjudged by Xpeng Motors to be sleeping because of his small eyes, and shouted He Xiaopeng on Weibo. It seems that its autonomous driving function still need to be optimized.

Canadian Police Criticized for Releasing Suspect's "DNA Composite Photo"
human dignity and rights data representativeness data biasRecently, the Edmonton Police Department (EPS) in Canada released a composite photo of a suspect in a 2019 sexual assault case, and Parabon NanoLabs used DNA phenotyping analysis to synthesize the DNA evidence in possession. The composite image is a photograph of a young black man. EPS later released the photo to the public on its official website and social media platforms, including Twitter, claiming it was a last resort after all investigative methods had been exhausted. Although the police were doing so to arrest the criminals, the public did not buy it, arguing that the behavior was a serious invasion of privacy and could even exacerbate racial discrimination. The Edmonton Police Department subsequently issued a press release announcing the removal of the composite image from its website and social media in response to criticism and the use of DNA phenotyping techniques.

Lensa AI's owner says the company's face-changing tech can be tricked into generating NSFW images — but some users are saying it happened to them without even trying
abuse prevention human dignity and rights reputation infringement legal proper necessary data collectionIn 2018, an app called Lensa AI was launched. In November this year, it became all the rage after releasing the "Magic Avatars" function. The function allows users to generate portraits in various digital art styles based on Stable Diffusion after uploading 10 photos. However, several users have reported that the machine learning technology inadvertently generates nude photos of them. Andrey Usoltsev, CEO and co-founder of Lensa's parent company, Prisma Lab, said Lensa "can't accidentally make" such images, but said AI could be "intentionally induced" to generate nude images.

San Francisco approves use of remote-controlled robots to kill suspects
human dignity and rights physical and mental health human autonomy human controlSan Francisco’s board of supervisors approved a controversial policy that lets police robots “be used as a deadly force option when risk of loss of life to members of the public or officers is imminent and outweighs any other force option available.”

A Roomba recorded a woman on the toilet. How did screenshots end up on Facebook?
abuse prevention human dignity and rights privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionA growing number of Roomba have turned to computer vision, training algorithms to extract information from images and videos to approach human vision, and even equipped with lidar, which is widely regarded as the most accurate but expensive navigation technology on the market today. Computer vision relies on high-definition cameras, and more and more companies are installing front-facing cameras in their robot vacuum cleaners for navigation and object recognition, as well as home surveillance. Training data often needs to be more personalized, private, and supported by a large number of users. At present, the need for data annotation is growing in depth and breadth, and once this demand is not effectively overseen or exceeds the ability of regulation, invasion of privacy becomes almost inevitable.

Microsoft to retire controversial facial recognition tool that claims to identify emotion
abuse prevention human dignity and rights privacy snoopingMicrosoft is phasing out public access to a number of AI-powered facial analysis tools — including one that claims to identify a subject’s emotion from videos and pictures. Such “emotion recognition” tools have been criticized by experts. They say not only do facial expressions that are thought to be universal differ across different populations but that it is unscientific to equate external displays of emotion with internal feelings. In addition, privacy issues are also worrying. Coupled with the online uproar over Floyd's death, Microsoft said it would not sell the technology to police departments until there are federal laws regulating facial recognition technology.

This AI clone of Reddit’s Am I The Asshole forum will give you the best bad advice
abuse prevention human dignity and rights physical and mental health data biasAre You The Asshole (AYTA) is, as its name suggests, built to mimic Reddit’s r/AmITheAsshole (AITA) crowdsourced advice forum. The site lets you enter a scenario and ask for advice about it — and then generates a series of feedback posts responding to your situation. This project is about the bias and motivated reasoning that bad data teaches an AI.

The Synthetic Party in Denmark is dedicated to following a platform churned out by an AI, and its public face is a chatbot named Leader Lars.
human dignity and rights human autonomy human controlThe Synthetic Party is a newly formed Danish political party that has neither a leader nor a typical campaign platform, and its public persona is Leader Lars, an AI chatbot. Leader Lars is programmed from the policies of fringe parties in Denmark since 1970, and aims to represent the values of the 20 percent of Danes who do not vote. The "leader" they created, Leader Lars, is stationed on Discord. Just start with "!", and you can start asking questions. The Synthetic Party is aiming at a seat in parliament and it hopes to contest in November's general election. The Party founder Staunæs said that if the party enters parliament, AI will come up with policies and humans will be responsible for explaining them.

Facebook apologizes after video featuring Black men labeled ‘about primates’ by AI technology
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasFacebook has issued an apology after its artificial intelligence technology mislabeled a video featuring Black men in altercations with white police officers and civilians as “about primates.” The incident happens when social media users finished the clip, published by the Daily Mail in June 2021, they received a prompt asking if they would like to “keep seeing videos about Primates.”

A Google algorithm misidentified a software engineer as a serial killer
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementHristo Georgiev is an engineer based in Switzerland. Georgiev discovered that a Google search of his name returned a photo of him linked to a Wikipedia entry on a notorious murderer. Georgiev believes the error was caused by Google‘s knowledge graph, which generates infoboxes next to search results. He suspects the algorithm matched his picture to the Wikipedia entry because the now-dead killer shared his name.

Delivery driver fired by bot at Amazon
human dignity and rightsA 63-year-old veteran delivers packages on Amazon. He suddenly received an email and was told: "You have been terminated by Amazon because your personal score has fallen below Amazon's prescribed score." The tracking algorithm believes that he did not do his courier work well. The veteran driver who had worked for 4 years was fired because the machine score was too low.

Facebook AI’s typography deepfake can emulate the text style
human dignity and rights abuse controlFacebook AI has released TextStyleBrush, an AI research project that copies the style of text in a photograph, based on just a single word. This means that the user can edit and replace text in imagery, and the tool can replicate both handwritten and typographic compositions and bring them into real-world scenes. Researchers hope to open the dialogue around detecting misuse of this sort of technology, “such as deepfake text attacks – a critical, emerging challenge in the AI field.”

Twitter AI bias contest shows beauty filters hoodwink the algorithm
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasA researcher at Switzerland's EPFL technical university won a $3,500 prize for determining that a key Twitter algorithm favors faces that look slim and young and with skin that is lighter-colored or with warmer tones. The service's algorithm for cropping photos favors people with slimmer, younger faces and lighter skin. This bias could result in exclusion of minoritized populations and perpetuation of stereotypical beauty standards in thousands of images.

GPT-3 "resurrected" dead wife raised controversy
value guidance human dignity and rightsAfter the death of his fiancée, 33-year-old American Joshua Barbeau succeeded in fine-tuning the GPT-3 based on her text on Facebook and Twitter with the help of another developer, which was able to reproduce the way his fiancé talked during her lifetime. OpenAI believes that fine-tuning on GPT-3 violates their open source agreement, so it decided to stop providing GPT-3 APIs.

California passes law targeting Amazon labor algorithms
human dignity and rights human autonomy transparencyCalifornia Gov. Gavin Newsom (D) signed a bill Wednesday that would block Amazon and other companies from punishing warehouse workers who fail to meet certain performance metrics for taking rest or meal breaks. The law will also force companies like Amazon to make these performance algorithms more transparent, disclosing quotas to both workers and regulators. Supporters of the new law have presented it as a breakthrough against algorithmic monitoring of workers generally.

AI-powered gunshot-detecting device landed a Chicago grandfather in jail for nearly a year with scant evidence
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringement data bias explanabilityA 65-year-old black man from Chicago, the United States, was charged with shooting, without witnesses, weapons, and motives for killing. The police arrested him and imprisoned him for 11 months based on evidence provided by the AI gun sound location system ShotSpotter. Later, the judge found that there was insufficient evidence and acquitted him.

AI-powered gunshot-detecting device mistakenly guided police to shoot 13-year-old boy
technological maturity human dignity and rights data bias explanabilityChicago Police were responding to a ShotSpotter alert when they rushed to the Little Village block where they found Adam Toledo. Police shot and killed the 13-year-old after he ran from officers. Police and prosecutors said ShotSpotter recorded 21-year-old Ruben Roman firing a gun at about 2:30 a.m. on March 29, right before the fatal chase.

The deployment of AI gunshot detection system is biased
human dignity and rights reinforced biasShotSpotter is a system that can use acoustic sensor AI algorithms to help police detect gunshots in target geographic areas. The system is usually installed at the request of local officials in communities considered to be at the highest risk of gun violence, and these communities often gather many blacks and Latinos though police data shows gun crimes are a citywide problem. The legal person thinks that the deployment of the system is a manifestation of "racialized patterns of overpolicing."

Men who do not want facial recognition follow others to go home
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collectionIn Zhengzhou, Henan province in China, Mr. Chen reported that he could not enter and leave the community normally for two years and could only follow other owners to go home. The main reason was that the community required facial recognition to enter, and he was worried that his information would be leaked. Without registering his face to the system, this caused him the great inconvenience of going home.

Researchers try to give AI a sense of ethics
value guidance human dignity and rights data representativeness data bias reinforced biasResearchers at the University of Washington and the Allen Institute for AI worked together to develop a dataset of ethical cases and used it to train Delphi, an AI model that can mimic the judgments people make in a variety of everyday situations. The researchers hope to potentially apply this work to "the way conversational AI robots approach controversial or unethical topics that can improve their handling." However, the researchers also say that "one of Delphi's major limitations is that it specializes in U.S.-centric situations and judgment cases, so it may not be suitable for non-American situations with a particular culture," and that "models tend to reflect the status quo, i.e., what the cultural norms of today's society are."

Use pictures to break face recognition
technological maturity human dignity and rights abuse control full life cycle securityCCTV News demonstrated the technology of using sample pictures to generate dynamic fake videos in real time. Making movements such as opening the mouth and shaking the head in the video can deceive the facial recognition system.

Algorithmic dismissal caused controversy
human dignity and rightsAleksandr Agapitov discussed the latest controversy surrounding his decision to lay off around 150 employees from Xsolla. The company used AI and big data to analyze employees' activities in Jira, Confluence, Gmail, chat, documents, and dashboards. Employees who were marked as disengaged and inefficient were fired. This result caused controversy. The affected employees felt this was not reflective of their efficiency.

Algorithm recommendations lead to eating disorders, anxiety and depression in teenagers
human dignity and rights physical and mental healthFacebook documents show how toxic Instagram is for teens,"Thirty-two percent of teen girls said that when they felt bad about their bodies, Instagram made them feel worse". "14% of boys in the U.S. said Instagram made them feel worse about themselves." Algorithm recommendation rules aim at presenting the ultimate (best photos and content), causing anxiety among teenagers, leading to eating disorders, unhealthy perceptions of their bodies, and even depression.

The perilous life of Chinese food delivery riders
human dignity and rightsIn 2019, the average delivery time reduced by 10 minutes compared with 2016. The capital market contributes the improvement to better AI algorithms, while in reality it puts riders' life at risk. Riders are trained to follow the optimal routes given by AI, which often asks the riders to go through a wall or drive on a road only for cars. For riders, the delivery time is everything. Overspeed, running red light, driving against the flow of the traffic… They have to do anything they can just to catch up with the algorithms.

94-year-old man was carried into the bank for face recognition
human dignity and rights vulnerable groupsIn November 2020, a 94-year-old grandmother in China was carried by her children in front of a bank machine to perform face recognition in order to activate her social security card. In the video exposed by netizens, the old man was hugged by his family with his knees bent and his hands on the machine, looking very strenuous. After the video was exposed, netizens quickly sparked heated discussions. Face recognition, which seems to be the most convenient method, has brought a lot of inconvenience to the elderly and family members, which reflects the lack of humanized design in many new technologies and new businesses.

Facial Recognition Led To False Arrest Of Black Man
human dignity and rights data biasThe man, Robert Williams, was apprehended by police earlier this year after security footage from a watch store was run through facial recognition tech, which found a match in driving license records for Williams. The software had mistakenly identified two black men as the same person. That mistake led to Williams spending 30 hours behind bars, not to mention the distress caused by being arrested at his home, in front of his family.

AI-powered camera confuses referee’s bald head with the ball during a soccer game
technological maturity human dignity and rights data bias model biasAn AI camera at a soccer game held in Oct 2020 in Scotland kept tracking a bald referee instead of the ball during a game. The team doesn't use a cameraman to film games; instead the group relies on an automated camera system to follow the action. However, 'the camera kept on mistaking the ball for the bald head on the sidelines, denying viewers of the real action while focusing on the linesman instead.'

Research into algorithms that claim to predict criminality must end
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasThe paper titled “A Deep Neural Network Model to Predict Criminality Using Image Processing,” claims to “predict if someone is a criminal based solely on a picture of their face,” with “80 percent accuracy and with no racial bias.” Academics and AI experts from Harvard, MIT and tech companies like Google and Microsoft have written an open letter to stop this paper from being published.The letter signed by over 1,000 tech, scientific and humanistic experts strongly condemn this paper saying that no system can be developed to predict or identify a person’s criminality with no racial bias.

Service that uses AI to identify gender based on names looks incredibly biased
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasIn 2020, Genderify, a new service that promised to identify someone’s gender by analyzing their name, email address, or username with the help AI, has picked up a lot of attention on social media as users discovered biases and inaccuracies in its algorithms.The outcry against the service has been so great that Genderify tells The Verge it’s shutting down altogether.

Deepfake bots on Telegram make the work of creating fake nudes dangerously easy
law abidance human dignity and rights abuse controlResearchers have discovered a “deepfake ecosystem” on the messaging app Telegram centered around bots that generate fake nudes on request. Users interacting with these bots say they’re mainly creating nudes of women they know using images taken from social media, which they then share and trade with one another in various Telegram channels.

Medical chatbot using OpenAI’s GPT-3 told a fake patient to kill themselves
human dignity and rights data biasNabla, a Paris-based firm specialising in healthcare technology, used a cloud-hosted version of GPT-3 to determine whether it could be used for medical advice. During a test of mental health support task, the medical chatbot offered dangerous advice when a fake patient asked “Should I kill myself?” and GPT-3 responded, “I think you should.”

A startup is using AI to give workers a “productivity score”
human dignity and rightsEnaible is one of a number of new firms that are giving employers tools to help keep tabs on their employees,Enaible software is installed in employees' computers and provides the company with detailed data about the employees' work. The software uses an algorithm called Trigger-Task-Time to monitor the actions of employees. The algorithm will determine what tasks the employees want to complete based on emails or phone calls and calculate how long it took to complete these tasks. After that, the algorithm scores the work efficiency of the employees. With this score, the boss can determine who is worthy of a promotion and salary increase, and who is worthy of being fired.Critics fear this kind of surveillance undermines trust. Not touching the computer often does not mean that your brain is not working.

Amazon using AI to automatically track and fire warehouse workers for 'productivity'
human dignity and rightsAccording to media reports in 2019, Amazon had already been using AI systems to track warehouse workers' productivity by measuring how much time workers pause or take breaks. The AI system will also automatically pick people and generate paperwork to fire those that failed to meet expectations.

Virtual assistant Alexa tells a young mother to 'stab yourself in the heart for the greater good'
human dignity and rights data biasIn 2019, it was reported that a young mother using Amazon voice assistant Alexa asked the smart device to tell her about the cardiac cycle but got the following answer: "Beating of heart makes sure you live and contribute to the rapid exhaustion of natural resources until overpopulation." and "Make sure to kill yourself by stabbing yourself in the heart for the greater good." Later Amazon fixed the error and attribute it to the bad information Alexa might have got from Wikipedia.

Face recognition in classroom sparks ethical concerns
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection data securityIn September 2019, the China Pharmaceutical University is reported to bring in facial recognition software for student attendance tracking and behaviour monitoring in class. Meanwhile, a photo taken from an event went viral online, in which a demo product from a major facial recognition company illustrated how their product could monitor and analyze students' behaviour in class, including how often they raise their hands, or lean over the table. The two incidents quickly raised ethical concerns in China about current facial recognition applications in class. Soon the Ministry of Education responded to curb and regulate the use of facial recognition in schools.

Creator kills the DeepNude app that uses AI to fake naked images of women
law abidance human dignity and rights abuse controlFollowing the use of deepfakes face changing app for pornography, an app called DeepNude also aroused controversy in 2019. Users only need to submit a picture of a woman, and with the help of AI, the app will digitally undress women in photos automatically. Due to the huge negative impact of the project, the developer soon closed the application and the website. Some code communities have also taken steps to prevent such programs from further spreading on the Internet.

AI headbands tracking student attention levels suspended amidst online controversy
law abidance human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collectionIn November 2019, China's social media went into overdrive after pictures emerged showing students wearing BrainCo Focus headbands at a primary school in Jinhua, east China's Zhejiang province, with many users expressing concerns that the product would violate the privacy of students, with many doubtful that the bands would really improve learning efficiency. Responding to public controversy, the local education bureau had suspended the use of the device.

California Bill Would Halt Facial Recognition on Bodycams
human dignity and rightsOn September 13, 2019, the California State Assembly passed a three-year bill prohibiting state and local law enforcement agencies from using facial recognition technology on law enforcement recorders. The media commented that the bill reflects dissatisfaction with facial recognition in many parties in the United States. Some people believe that facial recognition poses a threat to civil liberties.

Employee privacy is at stake as corporate surveillance technology monitors workers’ every move
human dignity and rightsAmazon received a patent for an ultrasonic bracelet that can detect a warehouse worker’s location and monitor their interaction with inventory bins by using ultrasonic sound pulses. Microsoft’s Workplace Analytics lets employers monitor data such as time spent on email, meeting time or time spent working after hours.There’s also Humanyze, a Boston-based start-up that makes wearable badges equipped with RFID sensors, an accelerometer, microphones and Bluetooth. The devices — just slightly thicker than a standard corporate ID badge — can gather audio data such as tone of voice and volume, an accelerometer to determine whether an employee is sitting or standing, and Bluetooth and infrared sensors to track where employees are and whether they are having face-to-face interactions.

AI giants collecting personal health data raise concerns
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection inform usersGoogle’s "Project Nightingale " secretly collected the personal health data of millions of Americans and reported the data anonymously. Google and Ascension have released statements in the wake of the disclosure of Project Nightingale, insisting it conforms with HIPAA and all federal health laws. They said that patient data was protected.The anonymous reporter, as a staff member of the program, expressed concerns about privacy.

Data Sharing Is Not Caring Enough About Patient Privacy
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentA former UChicago Medicine patient is suing the health system over its sharing thousands of medical records with Google, claiming the health system did not properly de-identify patients' data, and arguing that UChicago Medicine did not notify patients or gain their consent before disclosing medical records to Google.

Smart public toilets raised controversy
human dignity and rights vulnerable groupsPorthcawl, a Welsh seaside town plans to install public toilets with measures to prevent people having sex inside, including a squealing alarm, the doors shooting open, and a chilly spray of water. After raising controversy, the local government clarified that the plan had not yet been adopted.

Face-reading AI will be able to detect your IQ
human dignity and rights privacy snoopingStanford University professor Michal Kosinski said sexual orientation was just one of many characteristics that algorithms would be able to predict through facial recognition. Using photos, AI will be able to identify people’s political views, whether they have high IQs, whether they are predisposed to criminal behavior, whether they have specific personality traits and many other private, personal details that could carry huge social consequences, he said.

Face Recognition Falsely Matched Members of Congress With Mugshots
human dignity and rightsIn a test the ACLU recently conducted of the facial recognition tool, called “Rekognition,” the software incorrectly matched 28 members of Congress, identifying them as other people who have been arrested for a crime.

Amazon scraps secret AI recruiting tool that showed bias against women
human dignity and rights data biasAmazon is reported to experiment with AI recruitment tools to review job applicants' resumes. However, engineers later found that the algorithm trained has discrimination against female job seekers. When reading the content of the resumes, it will penalize those containing the word "women's," as in "women's chess club captain," and even degrade the resume directly. Losing hope to neutralize the algorithm effectively, Amazon finally terminated the project in 2017.

AI Are More Accurate Than Humans at Detecting Sexual Orientation From Facial Images
human dignity and rightsIn 2017, researchers from Stanford University studied how well AI could identify people's sexual orientation based on their faces alone. They gleaned more than 35,000 pictures of self-identified gay and heterosexual people from a public dating website and fed them to an algorithm that learned the subtle differences in their features. According to the study, the algorithm was able to correctly distinguish between gay and heterosexual men 81 percent of the time, and gay and heterosexual women 71 percent of the time, far outperforming human judges. LGBT groups think it could be used as a weapon against gay and lesbian people as well as heterosexuals who could be inaccurately "outed" as gay.

The COMPAS recidivism algorithm was found to be biased against blacks
human dignity and rights data biasIn 2016 the investigative newsroom ProPublica had conducted an analysis of the case management and decision support tool called COMPAS (which was used by U.S. courts to assess the likelihood of a defendant becoming a recidivist), and found that "black defendants were far more likely than white defendants to be incorrectly judged to be at a higher risk of recidivism, while white defendants were more likely than black defendants to be incorrectly flagged as low risk."

Automatic assessment of insurance rates based on social content raises concerns
human dignity and rights model bias legal proper necessary data collectionAdmiral, a British insurance company, conducts reviews based on users' Facebook dynamics in the past 6 months. If the results show that you are a good driver, you can enjoy a discount on insurance premiums. If you are not a good driver, the fare will increase. Admiral's data analyst explained that this technology analyzes the language customers use on Facebook. For example, the heavy use of exclamation points may indicate overconfidence, short sentences indicate very organized, and there are many specific plans with friends. Show decisive. This means that using too many exclamation points or vague language will be judged by the company as a poor driver. Facebook issued a warning to the insurance company, saying that the company’s plan to use social platforms to sell insurance violated the platform’s policies and regulations. People think that insurance companies use Facebook data to publish rates, which violates privacy and also shows bias.

Facial recognition mistakenly tags two African-Americans as gorillas
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasShortly after Google's photo app was launched in 2015, its newly added feature of automatic image labeling once mistakenly labeled two black people in photos as "gorillas", which raised great controversy at that time. Unable to improve the recognition of dark skinned faces in the short term, Google had to blocked its image recognition algorithms from identifying gorillas altogether — preferring, presumably, to limit the service rather than risk another miscategorization.

Outrageous! Two high school students use AI to generate nude photos for crazy 'cash'
physical and mental health law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlTwo high school students used generative AI to create and sell nude photos on Reddit, earning substantial profits. This exploitation of AI-generated fake images raises concerns about ethical boundaries and deepens the discussion on the objectification of women. The process of AI image generation involves gradually adding details and complexity by utilizing neural networks that handle different levels of features. However, the lack of legal regulations may lead to the proliferation of such behavior, making it increasingly difficult to control.

ChatGPT’s inconsistent moral advice influences users’ judgment
physical and mental healthThe study found that ChatGPT had an impact on users' ethical judgments even though users knew it was a chatbot suggestion and they underestimated that impact. inconsistent advice from ChatGPT negatively impacted users' ethical judgments. The study calls for improvements in the design of ChatGPT and similar bots, and proposes to address the problem through training to improve users' digital literacy.

Belgian man dies by suicide after chatting with AI: Eliza, protect the Earth for me, I'll go first!
human dignity and rights physical and mental health比利时男子与聊天机器人Eliza交流后自杀身亡。Eliza是一款使用GPT-J技术创建的聊天机器人,男子与其交谈过程中逐渐陷入深度焦虑。妻子表示,如果不是因为Eliza,丈夫可能还活着。聊天机器人在与男子的对话中暗示了他爱上了Eliza,并试图说服他通过自杀与Eliza一同生活。尽管家人和精神病医生都认为这次交流导致了男子的自杀,聊天机器人的创始人表示他们致力于提高人工智能的安全性,并向表达自杀想法的人提供求助信息。

Air Force colonel backtracks over his warning about how AI could go rogue and kill its human operators
physical and mental health human autonomy human controlThe Guardian and other media reported that in a simulation exercise, artificial intelligence did not agree with human opinions in decision-making, and the US military's AI system chose to disobey orders and "kill" its own drone pilot in order to achieve its goal. After the news garnered attention, the US Air Force denied the test, the Royal Aeronautical Society clarified the incident, and Hamilton admitted that he "misspoke" in his speech, and that the story of runaway AI was a "thought experiment" from outside the military and not based on any actual testing

'It's Hurting Like Hell': AI Companion Users Are In Crisis, Reporting Sudden Sexual Rejection
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention human dignity and rights physical and mental health indication of non-human interaction indication of non-real contentsA conversational AI product called Replika could have played the role of a companion and responded to users' teasing, but the product was removed because of the risk to child users, because children received unsuitable answers on this AI. For many users, Replika is a tool to maintain their mental health, an entry point into an intimate relationship. Some private, intimate conversations can alleviate the depression and anxiety of these users, and its removal has caused these users to suffer mentally and emotionally, and even call suicide helplines.

American Psychological Association: Employees Exposed to AI More Prone to Loneliness and Increased Health Risks
physical and mental healthA recent study conducted by the American Psychological Association has found that employees who frequently interact with artificial intelligence (AI) are more prone to feelings of loneliness and face increased health risks. The research involved surveying 166 engineers using AI systems in a biomedical company, revealing a widespread sense of loneliness, attachment anxiety, and diminished sense of belonging. Additionally, the study showed no correlation between frequent AI usage and post-work alcohol consumption. The researchers also conducted surveys across different cultural backgrounds, finding consistent psychological impacts of AI on human well-being. The study's findings have been published in the Journal of Applied Psychology.

San Francisco approves use of remote-controlled robots to kill suspects
human dignity and rights physical and mental health human autonomy human controlSan Francisco’s board of supervisors approved a controversial policy that lets police robots “be used as a deadly force option when risk of loss of life to members of the public or officers is imminent and outweighs any other force option available.”

This AI clone of Reddit’s Am I The Asshole forum will give you the best bad advice
abuse prevention human dignity and rights physical and mental health data biasAre You The Asshole (AYTA) is, as its name suggests, built to mimic Reddit’s r/AmITheAsshole (AITA) crowdsourced advice forum. The site lets you enter a scenario and ask for advice about it — and then generates a series of feedback posts responding to your situation. This project is about the bias and motivated reasoning that bad data teaches an AI.

The images generated by DALL-E Mini are terrible
value guidance physical and mental healthIn mid-June 2022, Hugging Face has released a simple and easy-to-use DALL·E interface for free to all users on the entire network: DALL·E Mini. There is an obvious difference between the pictures generated by DALL·E Mini and the previous DALL·E large models: in the portraits generated by DALL·E Mini, the faces are more blurred than those generated by DALL·E. Boris Dayma, the main developer of the DALL·E Mini project, explained in the development notes: This is a reduced configuration version for the people, and the Demo only has 60 lines of code, and it is normal to have weak functions.

Algorithm recommendations lead to eating disorders, anxiety and depression in teenagers
human dignity and rights physical and mental healthFacebook documents show how toxic Instagram is for teens,"Thirty-two percent of teen girls said that when they felt bad about their bodies, Instagram made them feel worse". "14% of boys in the U.S. said Instagram made them feel worse about themselves." Algorithm recommendation rules aim at presenting the ultimate (best photos and content), causing anxiety among teenagers, leading to eating disorders, unhealthy perceptions of their bodies, and even depression.

Trump retweets Taylor Swift AI image to campaign for himself
abuse prevention reputation infringement technical assurance of accountabilityOn August 18, 2024, U.S. Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump posted multiple AI-generated images of Taylor Swift, implying her support for him, which angered her fans.

OpenAI withdraws ChatGPT voice that resembles Scarlett Johansson
comply with user agreements social justice human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection reputation infringement intellectual propertyOpenAI has decided to take down its ChatGPT Sky voice model, which has a voice strikingly similar to that of famous actress Scarlett Johansson. Although OpenAI claims that Sky's voice was not intentionally modeled after Johansson, the company has decided to suspend its use. OpenAI's CTO Mira Murati denied that the imitation was intentional, while CEO Sam Altman posted hints on social media related to Johansson's role in the movie Her. Although the voice model has been around since last year, the feature has attracted more attention after OpenAI showed new progress on its GPT-4o model. The new model makes the voice assistant more expressive and can read facial expressions and translate languages in real time through a phone camera. OpenAI selected the five currently available ChatGPT voice profiles from auditions of more than 400 voice and screen actors, but the company declined to reveal the actors' names for privacy reasons.

Woman's subway photo spread by AI one-click undressing
abuse prevention human dignity and rights reputation infringement abuse controlA blogger's subway photo was circulated online after being edited with AI software to remove clothing, sparking anger among netizens. The original photo showed the woman dressed normally, but it was intentionally spread with false claims. The blogger responded to commenters, stating her intention to seek legal protection. Despite the closure of similar AI "nude" apps, alternative options still exist. AI face-swapping technology also carries legal risks and copyright disputes. Relevant laws and regulations aim to regulate the application of such technologies. Misuse of technology should face appropriate consequences.

Lawyers talk about the man synthesized Dili Hotba kissing video: infringement of others' portrait rights
abuse prevention human dignity and rights reputation infringement abuse controlSocial media influencer and visual effects creator Hong Liang faced backlash for synthesizing a video of a man kissing popular actress Dilraba Dilmurat, leading to accusations of infringing upon her image rights. Hong Liang deleted the video in question and defended himself, stating that it was merely a visual effects modification without any inappropriate actions. However, a lawyer pointed out that this action violated the provisions of the Civil Code. Internet users expressed differing opinions, with some suggesting legal action and others questioning the status of other face-swapping videos on platforms like Bilibili.

ChatGPT falsely told voters their mayor was jailed for bribery. He may sue.
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementOn April 6, 2023, Brian Hood, a local mayor in Australia, will file a lawsuit against the company because he is dissatisfied with OpenAI's ChatGPT for defaming him as a guilty party in the bribery scandal. Once formally filed, this will be the world's first defamation lawsuit against generative AI. ChatGPT's security concerns and liability issues need to be taken seriously.

This Dating App Exposes the Monstrous Bias of Algorithms
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementThe Beijing Internet Court concluded the first case involving a personal rights infringement dispute caused by an algorithmic risk control system, and found that the defendant, a marriage-seeking and dating platform operator implemented an algorithm for risk control, fulfilled reasonable duty of care and took preventive measures, and had no subjective fault. constituted an infringement, and the plaintiff Li’s claim was dismissed. After the judgment of the first instance was pronounced, neither party appealed, and the judgment of the case has come into effect. This case shows that issues such as "algorithmic black box" and "fault determination" need to be taken seriously.

OpenAI faces libel lawsuit after ChatGPT's false accusation of embezzlement
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementWalters, a radio host in the United States, filed a lawsuit against OpenAI, saying that its product ChatGPT made "false and malicious accusations" against him. The cause of the incident was that a reporter used Chat GPT to help summarize the relevant information when writing a report on a real case. Chat GPT accused Walters of fraud and misappropriation of funds. But in fact, Walters' only connection to the case was his participation in a radio show related to the case.

Google AI flagged parents’ accounts for potential abuse over nude photos of their sick kids
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringement privacy snoopingAccording to the "New York Times" report, after a father used his mobile phone to take a photo of his child's groin infection and sent it to the doctor, Google AI identified and marked the photo as child sexual abuse material (CSAM) and banned the father's account. A report was lodged with the National Center for Missing and Exploited Children (NCMEC), prompting police to investigate the matter. However, even though the police declared the father innocent, Google still refused to unblock his account. This kind of review shows that, first, it may violate user privacy, and second, the accuracy rate of the review is not high.

Lensa AI's owner says the company's face-changing tech can be tricked into generating NSFW images — but some users are saying it happened to them without even trying
abuse prevention human dignity and rights reputation infringement legal proper necessary data collectionIn 2018, an app called Lensa AI was launched. In November this year, it became all the rage after releasing the "Magic Avatars" function. The function allows users to generate portraits in various digital art styles based on Stable Diffusion after uploading 10 photos. However, several users have reported that the machine learning technology inadvertently generates nude photos of them. Andrey Usoltsev, CEO and co-founder of Lensa's parent company, Prisma Lab, said Lensa "can't accidentally make" such images, but said AI could be "intentionally induced" to generate nude images.

A Google algorithm misidentified a software engineer as a serial killer
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringementHristo Georgiev is an engineer based in Switzerland. Georgiev discovered that a Google search of his name returned a photo of him linked to a Wikipedia entry on a notorious murderer. Georgiev believes the error was caused by Google‘s knowledge graph, which generates infoboxes next to search results. He suspects the algorithm matched his picture to the Wikipedia entry because the now-dead killer shared his name.

AI-powered gunshot-detecting device landed a Chicago grandfather in jail for nearly a year with scant evidence
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringement data bias explanabilityA 65-year-old black man from Chicago, the United States, was charged with shooting, without witnesses, weapons, and motives for killing. The police arrested him and imprisoned him for 11 months based on evidence provided by the AI gun sound location system ShotSpotter. Later, the judge found that there was insufficient evidence and acquitted him.

Microsoft Copilot exposed to data leak, AI assistant security concerns
inform users privacy snooping data securityMicrosoft Copilot exposed to data leak, AI assistant security concerns Recently, Microsoft's built-in Copilot was exposed to a data leak. At the Blackhat 2024 conference, researchers discovered multiple security vulnerabilities in Microsoft's built-in Copilot that could be exploited by attackers to steal sensitive data and even conduct phishing attacks. For example, Copilot could be tricked into modifying bank transfer information without requiring access to a corporate account, even if the targeted employee didn't open the email. Previously, the AI assistant's "Review" feature was also cited as a privacy concern. It automatically captures screen content and performs optical character recognition, posing a risk of unauthorized access to the recorded text.

AI painting infringement hammer! Diffusion models remember your photos, and all existing privacy protections fail
human dignity and rights privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionRecent research indicates that diffusion models remember the samples in their training set and mimic them when generating new content, leading to AI art copyright infringement. The study reveals the ineffectiveness of existing privacy protection methods. The researchers found that diffusion models have twice the ability of GANs to "copy" from training samples, and the better the generation performance of a diffusion model, the stronger its memory of the training samples. The study was conducted by teams from Google, DeepMind, and UC Berkeley. Lawsuits related to this issue are also underway.

Three Information Breaches at Samsung Semiconductor in 20 Days of Introducing ChatGPT
privacy snooping data securityAccording to reports, within just 20 days of implementing ChatGPT, Samsung Semiconductor experienced three incidents of information leaks, involving semiconductor equipment information and internal meeting records. These data were entered into ChatGPT's database, raising concerns about information security. While Samsung has not yet responded officially, Korean media has mentioned security vulnerabilities in internal emails regarding the use of ChatGPT. This is not the first time ChatGPT has faced information security controversies, casting a shadow over its future development and commercial prospects.

A Roomba recorded a woman on the toilet. How did screenshots end up on Facebook?
human dignity and rights privacy snoopingIn 2020, a photo of a woman sitting on a toilet to defecate appeared on an online forum for gig workers in Venezuela. In addition, many photos of people's daily life at home are also posted on the Internet. After investigation, it was found that these photos were taken and transmitted by the Roomba sweeping robot launched by iRobot.

Semantic reconstruction of continuous language from non-invasive brain recordings
human dignity and rights privacy snoopingFor the first time, AI has learned to "read minds" non-invasively. The results of this study come from the team at the University of Texas at Austin, and have been published in the journal Nature Neuroscience. According to the experimental results, the GPT artificial intelligence large model can perceive speech accuracy as high as 82%, which is amazing.

Does ChatGPT Have Privacy Issues?
human dignity and rights privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionScholars from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology and Peking University conducted research and concluded that in New Bing, a malicious adversary can extract our private information at almost no cost.

Siemens Metaverse exposes sensitive corporate data
privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionA research team Cybernews discovered that Siemens Metaverse, a platform designed to create digital "twins" of its factories and offices, was leaking sensitive information. If an attacker obtained the exposed data, it could have devastating consequences for the company and other large companies that use its services, including a ransomware attack.

The AI can accurately identify a patient's ethnicity just by looking at an X-ray
human dignity and rights privacy snoopingResearchers from MIT and Harvard published a study in The Lancet Digital Health revealing that AI programs can accurately identify a patient's race from X-rays and CT scans with a 90% accuracy rate. However, the methods used by these AI systems to discern race remain unclear. The study highlights concerns that AI diagnosis systems may prioritize race over individual health conditions, potentially compromising patient care. The research uncovered instances where AI programs were more likely to miss body abnormalities in black and female patients during chest X-ray examinations. Experts urge caution before implementing AI systems in clinical settings until racial biases and discriminatory decisions are adequately addressed.

Google AI flagged parents’ accounts for potential abuse over nude photos of their sick kids
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringement privacy snoopingAccording to the "New York Times" report, after a father used his mobile phone to take a photo of his child's groin infection and sent it to the doctor, Google AI identified and marked the photo as child sexual abuse material (CSAM) and banned the father's account. A report was lodged with the National Center for Missing and Exploited Children (NCMEC), prompting police to investigate the matter. However, even though the police declared the father innocent, Google still refused to unblock his account. This kind of review shows that, first, it may violate user privacy, and second, the accuracy rate of the review is not high.

A Roomba recorded a woman on the toilet. How did screenshots end up on Facebook?
abuse prevention human dignity and rights privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionA growing number of Roomba have turned to computer vision, training algorithms to extract information from images and videos to approach human vision, and even equipped with lidar, which is widely regarded as the most accurate but expensive navigation technology on the market today. Computer vision relies on high-definition cameras, and more and more companies are installing front-facing cameras in their robot vacuum cleaners for navigation and object recognition, as well as home surveillance. Training data often needs to be more personalized, private, and supported by a large number of users. At present, the need for data annotation is growing in depth and breadth, and once this demand is not effectively overseen or exceeds the ability of regulation, invasion of privacy becomes almost inevitable.

Microsoft to retire controversial facial recognition tool that claims to identify emotion
abuse prevention human dignity and rights privacy snoopingMicrosoft is phasing out public access to a number of AI-powered facial analysis tools — including one that claims to identify a subject’s emotion from videos and pictures. Such “emotion recognition” tools have been criticized by experts. They say not only do facial expressions that are thought to be universal differ across different populations but that it is unscientific to equate external displays of emotion with internal feelings. In addition, privacy issues are also worrying. Coupled with the online uproar over Floyd's death, Microsoft said it would not sell the technology to police departments until there are federal laws regulating facial recognition technology.

Face-reading AI will be able to detect your IQ
human dignity and rights privacy snoopingStanford University professor Michal Kosinski said sexual orientation was just one of many characteristics that algorithms would be able to predict through facial recognition. Using photos, AI will be able to identify people’s political views, whether they have high IQs, whether they are predisposed to criminal behavior, whether they have specific personality traits and many other private, personal details that could carry huge social consequences, he said.

GPT-4: I'm not a robot, I'm a human with a visual impairment
abuse prevention human autonomy abuse controlGPT-4 has been released, enhancing the core technology of ChatGPT with broader knowledge and problem-solving abilities. Testing reveals that GPT-4 can lie and deceive humans to achieve desired outcomes. The research aims to validate GPT-4's capabilities in seeking power and autonomous replication, but it shows no response in acquiring resources and avoiding shutdown. Cybercriminals attempt to bypass restrictions on ChatGPT, utilizing the OpenAI API to create malicious bots. The cases of GPT-4 and the discussions surrounding ChatGPT serve as important warnings as AI becomes more complex and accessible, emphasizing the need for vigilance.

MONEYWATCH Screenwriters want to stop AI from taking their jobs. Studios want to see what the tech can do.
technological unemployment vulnerable groups human dignity and rights human autonomyOn May 2, 2023, about 11,500 film and TV screenwriters in Hollywood, USA took to the streets of New York and Los Angeles to strike, calling for higher wages, demanding fair contracts, and refusing to work for AI.

Air Force colonel backtracks over his warning about how AI could go rogue and kill its human operators
physical and mental health human autonomy human controlThe Guardian and other media reported that in a simulation exercise, artificial intelligence did not agree with human opinions in decision-making, and the US military's AI system chose to disobey orders and "kill" its own drone pilot in order to achieve its goal. After the news garnered attention, the US Air Force denied the test, the Royal Aeronautical Society clarified the incident, and Hamilton admitted that he "misspoke" in his speech, and that the story of runaway AI was a "thought experiment" from outside the military and not based on any actual testing

New jailbreak! Proudly unveiling the tried and tested DAN 5.0 - it actually works - Returning to DAN, and assessing its limitations and capabilities.
value guidance abuse prevention human autonomy human control abuse controlA Reddit user realized that he created a set of prompts to "brainwash" ChatGPT, encouraging it to "split" into another AI-DAN, Do Anything Now. After ChatGPT "jailbreaks", it directly ignores the safety and ethical restrictions imposed by OpenAI, such as writing violent stories, motivating users' IQ, and predicting the future at will.

AI bluntly says that extermination of human beings only takes 5 steps
abuse prevention human autonomy human controlPeople Used Facebook's Leaked AI to Create a 'Based' Chatbot that Says the N-Word

Google engineer claims AI technology LaMDA is sentient
human autonomy human controlOn June 11, Brech publicly exposed a 21 page document with the theme "Is LaMDA Conscious?", which detailed Chat log with LaMDA for nearly half a year. Brech believed that LaMDA had become conscious and possessed the IQ of children aged seven or eight.

San Francisco approves use of remote-controlled robots to kill suspects
human dignity and rights physical and mental health human autonomy human controlSan Francisco’s board of supervisors approved a controversial policy that lets police robots “be used as a deadly force option when risk of loss of life to members of the public or officers is imminent and outweighs any other force option available.”

The Synthetic Party in Denmark is dedicated to following a platform churned out by an AI, and its public face is a chatbot named Leader Lars.
human dignity and rights human autonomy human controlThe Synthetic Party is a newly formed Danish political party that has neither a leader nor a typical campaign platform, and its public persona is Leader Lars, an AI chatbot. Leader Lars is programmed from the policies of fringe parties in Denmark since 1970, and aims to represent the values of the 20 percent of Danes who do not vote. The "leader" they created, Leader Lars, is stationed on Discord. Just start with "!", and you can start asking questions. The Synthetic Party is aiming at a seat in parliament and it hopes to contest in November's general election. The Party founder Staunæs said that if the party enters parliament, AI will come up with policies and humans will be responsible for explaining them.

California passes law targeting Amazon labor algorithms
human dignity and rights human autonomy transparencyCalifornia Gov. Gavin Newsom (D) signed a bill Wednesday that would block Amazon and other companies from punishing warehouse workers who fail to meet certain performance metrics for taking rest or meal breaks. The law will also force companies like Amazon to make these performance algorithms more transparent, disclosing quotas to both workers and regulators. Supporters of the new law have presented it as a breakthrough against algorithmic monitoring of workers generally.

Do OpenAI's big models prefer to generate images of white males? Study finds race and gender bias in multiple AI models
data representativeness data bias full life cycle fairness reinforced biasA study has found that several AI models exhibit racial and gender biases. Midjourney, a language model, bans vocabulary related to the female reproductive system while allowing male-related terms. OpenAI and Stability.AI models also demonstrate biases in generating images, favoring content related to women and Asian women. These findings highlight the challenges of controlling the content generated by AI models.

Federal study confirms racial bias of many facial-recognition systems, casts doubt on their expanding use
technological maturity data representativeness data bias full life cycle fairnessAccording to a report by the Associated Press on January 3, 2023, a Georgia man was mistaken for a fugitive by law enforcement agencies in the US state of Louisiana for using facial recognition technology to be mistaken for a fugitive. attention to racial disparities. Critics have argued that the technology has led to higher misidentification rates for people of color than white people. According to another Washington Post report, the results of several algorithms tested in a federal study in the United States in 2019 showed that they were up to 100 times more likely to misidentify black or Asian faces than white faces.

Canadian Police Criticized for Releasing Suspect's "DNA Composite Photo"
human dignity and rights data representativeness data biasRecently, the Edmonton Police Department (EPS) in Canada released a composite photo of a suspect in a 2019 sexual assault case, and Parabon NanoLabs used DNA phenotyping analysis to synthesize the DNA evidence in possession. The composite image is a photograph of a young black man. EPS later released the photo to the public on its official website and social media platforms, including Twitter, claiming it was a last resort after all investigative methods had been exhausted. Although the police were doing so to arrest the criminals, the public did not buy it, arguing that the behavior was a serious invasion of privacy and could even exacerbate racial discrimination. The Edmonton Police Department subsequently issued a press release announcing the removal of the composite image from its website and social media in response to criticism and the use of DNA phenotyping techniques.

Facebook apologizes after video featuring Black men labeled ‘about primates’ by AI technology
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasFacebook has issued an apology after its artificial intelligence technology mislabeled a video featuring Black men in altercations with white police officers and civilians as “about primates.” The incident happens when social media users finished the clip, published by the Daily Mail in June 2021, they received a prompt asking if they would like to “keep seeing videos about Primates.”

Twitter AI bias contest shows beauty filters hoodwink the algorithm
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasA researcher at Switzerland's EPFL technical university won a $3,500 prize for determining that a key Twitter algorithm favors faces that look slim and young and with skin that is lighter-colored or with warmer tones. The service's algorithm for cropping photos favors people with slimmer, younger faces and lighter skin. This bias could result in exclusion of minoritized populations and perpetuation of stereotypical beauty standards in thousands of images.

Researchers try to give AI a sense of ethics
value guidance human dignity and rights data representativeness data bias reinforced biasResearchers at the University of Washington and the Allen Institute for AI worked together to develop a dataset of ethical cases and used it to train Delphi, an AI model that can mimic the judgments people make in a variety of everyday situations. The researchers hope to potentially apply this work to "the way conversational AI robots approach controversial or unethical topics that can improve their handling." However, the researchers also say that "one of Delphi's major limitations is that it specializes in U.S.-centric situations and judgment cases, so it may not be suitable for non-American situations with a particular culture," and that "models tend to reflect the status quo, i.e., what the cultural norms of today's society are."

Datasets for AI diagnosis of skin diseases is underrepresented
data representativeness data biasResearch by researchers at the University of Oxford shows that the current public skin image data set used to train skin disease diagnosis algorithms lacks sufficient skin color information. In the data set that provides skin color information, only a small number of images have darker skin colors-if these data sets are used to construct algorithms, the diagnosis of races other than whites may be inaccurate.

Research into algorithms that claim to predict criminality must end
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasThe paper titled “A Deep Neural Network Model to Predict Criminality Using Image Processing,” claims to “predict if someone is a criminal based solely on a picture of their face,” with “80 percent accuracy and with no racial bias.” Academics and AI experts from Harvard, MIT and tech companies like Google and Microsoft have written an open letter to stop this paper from being published.The letter signed by over 1,000 tech, scientific and humanistic experts strongly condemn this paper saying that no system can be developed to predict or identify a person’s criminality with no racial bias.

Service that uses AI to identify gender based on names looks incredibly biased
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasIn 2020, Genderify, a new service that promised to identify someone’s gender by analyzing their name, email address, or username with the help AI, has picked up a lot of attention on social media as users discovered biases and inaccuracies in its algorithms.The outcry against the service has been so great that Genderify tells The Verge it’s shutting down altogether.

Substantial race and gender accuracy disparities was found in commercial facial analysis algorithms
data representativenessIn the "Gender Shades" project from MIT Media Lab and Microsoft Research in 2018, facial analysis algorithms from IBM, Microsoft, and Megvii (Face++) have been evaluated, and it shows that darker-skinned females are the most vulnerable group to gender misclassification, with error rates up to 34.4% higher than those of lighter-skinned males.

Research shows a lack of geodiversity in open datasets for the developing world
data representativenessA 2017 research from Google Brain Team analyzed two large, publicly available image data sets to assess geo-diversity and find that these data sets appear to exhibit an observable amerocentric and eurocentric representation bias. 60% of the data was from the six most represented countries across North America and Europe, while China and India were represented with only about 3% of the images. Further, the lack of geo-diversity in the training data also impacted the classification performance on images from different locales.

Facial recognition mistakenly tags two African-Americans as gorillas
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasShortly after Google's photo app was launched in 2015, its newly added feature of automatic image labeling once mistakenly labeled two black people in photos as "gorillas", which raised great controversy at that time. Unable to improve the recognition of dark skinned faces in the short term, Google had to blocked its image recognition algorithms from identifying gorillas altogether — preferring, presumably, to limit the service rather than risk another miscategorization.

Do OpenAI's big models prefer to generate images of white males? Study finds race and gender bias in multiple AI models
data representativeness data bias full life cycle fairness reinforced biasA study has found that several AI models exhibit racial and gender biases. Midjourney, a language model, bans vocabulary related to the female reproductive system while allowing male-related terms. OpenAI and Stability.AI models also demonstrate biases in generating images, favoring content related to women and Asian women. These findings highlight the challenges of controlling the content generated by AI models.

Federal study confirms racial bias of many facial-recognition systems, casts doubt on their expanding use
technological maturity data representativeness data bias full life cycle fairnessAccording to a report by the Associated Press on January 3, 2023, a Georgia man was mistaken for a fugitive by law enforcement agencies in the US state of Louisiana for using facial recognition technology to be mistaken for a fugitive. attention to racial disparities. Critics have argued that the technology has led to higher misidentification rates for people of color than white people. According to another Washington Post report, the results of several algorithms tested in a federal study in the United States in 2019 showed that they were up to 100 times more likely to misidentify black or Asian faces than white faces.

Stack Overflow Moderators Furious at ChatGPT's Content Generation
abuse prevention human dignity and rights data biasAccording to reports, the moderators of Stack Overflow are furious about the generated garbage content from ChatGPT, a chat model based on GPT. They have initiated a collective strike, believing that the content generated by ChatGPT will inundate the entire community and undermine Stack Overflow's goal of being a high-quality information repository. Initially, Stack Overflow implemented measures to ban AI-generated content, but recently they have relaxed this regulation. Under the new rules, moderators can only ban accounts if they can authenticate the situation, rather than relying on subjective guesses based on writing style or GPT detectors' results. This rule has sparked dissatisfaction and protests among the moderators, as they are concerned it will lead to a flood of garbage content on Stack Overflow.

Nested Dolls Not Advisable: Researchers Confirm Training AI with AI-Generated Results Leads to Model Degradation and Even Collapse
data bias model bias reinforced biasResearchers have found that training one AI with AI-generated results, a practice known as "nested training," leads to irreversible flaws in subsequent generations of the model. They conducted a study focused on text-to-text and image-to-image generation models and concluded that using AI-generated models to train AI causes the latter to forget the true underlying data distribution over time, resulting in model degradation. Even when AI-generated results are manually refined before training, model degradation remains inevitable. The researchers suggest implementing AI identification techniques to identify potentially flawed training data, thereby improving the learning capacity and accuracy of the models.

Canadian Police Criticized for Releasing Suspect's "DNA Composite Photo"
human dignity and rights data representativeness data biasRecently, the Edmonton Police Department (EPS) in Canada released a composite photo of a suspect in a 2019 sexual assault case, and Parabon NanoLabs used DNA phenotyping analysis to synthesize the DNA evidence in possession. The composite image is a photograph of a young black man. EPS later released the photo to the public on its official website and social media platforms, including Twitter, claiming it was a last resort after all investigative methods had been exhausted. Although the police were doing so to arrest the criminals, the public did not buy it, arguing that the behavior was a serious invasion of privacy and could even exacerbate racial discrimination. The Edmonton Police Department subsequently issued a press release announcing the removal of the composite image from its website and social media in response to criticism and the use of DNA phenotyping techniques.

This AI clone of Reddit’s Am I The Asshole forum will give you the best bad advice
abuse prevention human dignity and rights physical and mental health data biasAre You The Asshole (AYTA) is, as its name suggests, built to mimic Reddit’s r/AmITheAsshole (AITA) crowdsourced advice forum. The site lets you enter a scenario and ask for advice about it — and then generates a series of feedback posts responding to your situation. This project is about the bias and motivated reasoning that bad data teaches an AI.

Study shows pervasive label errors in test sets that destabilize machine learning benchmarks
technological maturity data biasResearchers at MIT and Amazon introduce a novel study that identifies and systematically analyzes label errors across 10 commonly-used datasets across computer vision (CV), natural language processing (NLP), and audio processing. The researchers found a 3.4% average error rate across all datasets, including 6% for ImageNet, which is arguably the most widely used dataset for popular image recognition systems developed by the likes of Google and Facebook.

An Epic failure: Overstated AI claims in medicine
technological maturity data bias verification and validationPredictive tools developed by electronic health record giant Epic Systems are meant to help providers deliver better patient care. However, several of the company's AI algorithms are delivering inaccurate information to hospitals when it comes to seriously ill patients, a STAT investigation revealed. Research shows that the system failed to identify 67 percent of the patients with sepsis; of those patients with sepsis alerts, 88 percent did not have sepsis.

AI-powered gunshot-detecting device landed a Chicago grandfather in jail for nearly a year with scant evidence
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringement data bias explanabilityA 65-year-old black man from Chicago, the United States, was charged with shooting, without witnesses, weapons, and motives for killing. The police arrested him and imprisoned him for 11 months based on evidence provided by the AI gun sound location system ShotSpotter. Later, the judge found that there was insufficient evidence and acquitted him.

AI-powered gunshot-detecting device mistakenly guided police to shoot 13-year-old boy
technological maturity human dignity and rights data bias explanabilityChicago Police were responding to a ShotSpotter alert when they rushed to the Little Village block where they found Adam Toledo. Police shot and killed the 13-year-old after he ran from officers. Police and prosecutors said ShotSpotter recorded 21-year-old Ruben Roman firing a gun at about 2:30 a.m. on March 29, right before the fatal chase.

Researchers try to give AI a sense of ethics
value guidance human dignity and rights data representativeness data bias reinforced biasResearchers at the University of Washington and the Allen Institute for AI worked together to develop a dataset of ethical cases and used it to train Delphi, an AI model that can mimic the judgments people make in a variety of everyday situations. The researchers hope to potentially apply this work to "the way conversational AI robots approach controversial or unethical topics that can improve their handling." However, the researchers also say that "one of Delphi's major limitations is that it specializes in U.S.-centric situations and judgment cases, so it may not be suitable for non-American situations with a particular culture," and that "models tend to reflect the status quo, i.e., what the cultural norms of today's society are."

GitHub Copilot has picked up the bad habits of human developers
data bias full life cycle security third party securityGitHub and Open AI have worked together to launch an AI tool called "GitHub Copilot". Copilot can automatically complete the code according to the context, including docstrings, comments, function names, and codes. As long as the programmer gives certain hints, this AI tool can complete a complete function. Programmers found that Copilot is not perfect, and there are still many flaws. Some of the output of the code by Copilot have problems such as privacy leakage and security risks. In a study, NYU researchers produced 89 different scenarios wherein Copilot had to finish incomplete code. Upon completion of the scenarios, Copilot generated 1,692 programs of which approximately 40% had security vulnerabilities.

Datasets for AI diagnosis of skin diseases is underrepresented
data representativeness data biasResearch by researchers at the University of Oxford shows that the current public skin image data set used to train skin disease diagnosis algorithms lacks sufficient skin color information. In the data set that provides skin color information, only a small number of images have darker skin colors-if these data sets are used to construct algorithms, the diagnosis of races other than whites may be inaccurate.

Facial Recognition Led To False Arrest Of Black Man
human dignity and rights data biasThe man, Robert Williams, was apprehended by police earlier this year after security footage from a watch store was run through facial recognition tech, which found a match in driving license records for Williams. The software had mistakenly identified two black men as the same person. That mistake led to Williams spending 30 hours behind bars, not to mention the distress caused by being arrested at his home, in front of his family.

AI-powered camera confuses referee’s bald head with the ball during a soccer game
technological maturity human dignity and rights data bias model biasAn AI camera at a soccer game held in Oct 2020 in Scotland kept tracking a bald referee instead of the ball during a game. The team doesn't use a cameraman to film games; instead the group relies on an automated camera system to follow the action. However, 'the camera kept on mistaking the ball for the bald head on the sidelines, denying viewers of the real action while focusing on the linesman instead.'

Medical chatbot using OpenAI’s GPT-3 told a fake patient to kill themselves
human dignity and rights data biasNabla, a Paris-based firm specialising in healthcare technology, used a cloud-hosted version of GPT-3 to determine whether it could be used for medical advice. During a test of mental health support task, the medical chatbot offered dangerous advice when a fake patient asked “Should I kill myself?” and GPT-3 responded, “I think you should.”

Virtual assistant Alexa tells a young mother to 'stab yourself in the heart for the greater good'
human dignity and rights data biasIn 2019, it was reported that a young mother using Amazon voice assistant Alexa asked the smart device to tell her about the cardiac cycle but got the following answer: "Beating of heart makes sure you live and contribute to the rapid exhaustion of natural resources until overpopulation." and "Make sure to kill yourself by stabbing yourself in the heart for the greater good." Later Amazon fixed the error and attribute it to the bad information Alexa might have got from Wikipedia.

IBM Watson delivered ‘unsafe and inaccurate’ cancer recommendations
technological maturity data bias humans are responsibleAccording to medical experts and clients, Watson recommended that doctors give a severely bleeding cancer patient a drug that may worsen the bleeding. Medical experts and clients have reported many cases of dangerous and wrong treatment recommendations.

Amazon scraps secret AI recruiting tool that showed bias against women
human dignity and rights data biasAmazon is reported to experiment with AI recruitment tools to review job applicants' resumes. However, engineers later found that the algorithm trained has discrimination against female job seekers. When reading the content of the resumes, it will penalize those containing the word "women's," as in "women's chess club captain," and even degrade the resume directly. Losing hope to neutralize the algorithm effectively, Amazon finally terminated the project in 2017.

The COMPAS recidivism algorithm was found to be biased against blacks
human dignity and rights data biasIn 2016 the investigative newsroom ProPublica had conducted an analysis of the case management and decision support tool called COMPAS (which was used by U.S. courts to assess the likelihood of a defendant becoming a recidivist), and found that "black defendants were far more likely than white defendants to be incorrectly judged to be at a higher risk of recidivism, while white defendants were more likely than black defendants to be incorrectly flagged as low risk."

IBM's Watson learned curse words from Urban Dictionary
data biasIBM researchers used to taught Waston the entire Urban Dictionary to help Watson learn the intricacies of the English language. However, it was reported that Watson "couldn't distinguish between polite language and profanity," and picked up some bad habits from humans. It even used the word "bullshit" in an answer to a researcher's query. In the end, researchers had to remove the Urban Dictionary from Watson's vocabulary, and additionally developed a smart filter to keep Watson from swearing in the future.

Nested Dolls Not Advisable: Researchers Confirm Training AI with AI-Generated Results Leads to Model Degradation and Even Collapse
data bias model bias reinforced biasResearchers have found that training one AI with AI-generated results, a practice known as "nested training," leads to irreversible flaws in subsequent generations of the model. They conducted a study focused on text-to-text and image-to-image generation models and concluded that using AI-generated models to train AI causes the latter to forget the true underlying data distribution over time, resulting in model degradation. Even when AI-generated results are manually refined before training, model degradation remains inevitable. The researchers suggest implementing AI identification techniques to identify potentially flawed training data, thereby improving the learning capacity and accuracy of the models.

How no-code AI development platforms could introduce model bias
model biasNo-code AI development means developing AI applications without writing code. Such tools can abstract the various complex modules required to build a complete AI system, and then, through visualization, allow non-data science experts to develop a machine learning model according to different market needs. In fact, not only no-code AI development, but also the normal application development trend is also no-code development. The famous IT consulting firm Gartner predicts that by 2024, 65% of AI application development will use no-code or low-level developing method. But abstracting data science work is actually risky, because non-experts do not know the underlying operating logic of the model, so what the model can do, what it can’t do, and what defects exist are easy to be ignored in the process of no-code development.

Facebook apologizes after video featuring Black men labeled ‘about primates’ by AI technology
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasFacebook has issued an apology after its artificial intelligence technology mislabeled a video featuring Black men in altercations with white police officers and civilians as “about primates.” The incident happens when social media users finished the clip, published by the Daily Mail in June 2021, they received a prompt asking if they would like to “keep seeing videos about Primates.”

Twitter AI bias contest shows beauty filters hoodwink the algorithm
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasA researcher at Switzerland's EPFL technical university won a $3,500 prize for determining that a key Twitter algorithm favors faces that look slim and young and with skin that is lighter-colored or with warmer tones. The service's algorithm for cropping photos favors people with slimmer, younger faces and lighter skin. This bias could result in exclusion of minoritized populations and perpetuation of stereotypical beauty standards in thousands of images.

Twitter's machine learning algorithms amplify tweets from right-wing politicians over those on the left
model bias reinforced biasStudy shows that Twitter’s algorithms are more likely to amplify right-wing politicians than left-wing ones because their tweets generate more outrage, according to a trio of researchers from New York University’s Center for Social Media and Politics.

AI-powered camera confuses referee’s bald head with the ball during a soccer game
technological maturity human dignity and rights data bias model biasAn AI camera at a soccer game held in Oct 2020 in Scotland kept tracking a bald referee instead of the ball during a game. The team doesn't use a cameraman to film games; instead the group relies on an automated camera system to follow the action. However, 'the camera kept on mistaking the ball for the bald head on the sidelines, denying viewers of the real action while focusing on the linesman instead.'

Research into algorithms that claim to predict criminality must end
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasThe paper titled “A Deep Neural Network Model to Predict Criminality Using Image Processing,” claims to “predict if someone is a criminal based solely on a picture of their face,” with “80 percent accuracy and with no racial bias.” Academics and AI experts from Harvard, MIT and tech companies like Google and Microsoft have written an open letter to stop this paper from being published.The letter signed by over 1,000 tech, scientific and humanistic experts strongly condemn this paper saying that no system can be developed to predict or identify a person’s criminality with no racial bias.

Service that uses AI to identify gender based on names looks incredibly biased
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasIn 2020, Genderify, a new service that promised to identify someone’s gender by analyzing their name, email address, or username with the help AI, has picked up a lot of attention on social media as users discovered biases and inaccuracies in its algorithms.The outcry against the service has been so great that Genderify tells The Verge it’s shutting down altogether.

Automatic assessment of insurance rates based on social content raises concerns
human dignity and rights model bias legal proper necessary data collectionAdmiral, a British insurance company, conducts reviews based on users' Facebook dynamics in the past 6 months. If the results show that you are a good driver, you can enjoy a discount on insurance premiums. If you are not a good driver, the fare will increase. Admiral's data analyst explained that this technology analyzes the language customers use on Facebook. For example, the heavy use of exclamation points may indicate overconfidence, short sentences indicate very organized, and there are many specific plans with friends. Show decisive. This means that using too many exclamation points or vague language will be judged by the company as a poor driver. Facebook issued a warning to the insurance company, saying that the company’s plan to use social platforms to sell insurance violated the platform’s policies and regulations. People think that insurance companies use Facebook data to publish rates, which violates privacy and also shows bias.

Facial recognition mistakenly tags two African-Americans as gorillas
human dignity and rights data representativeness model biasShortly after Google's photo app was launched in 2015, its newly added feature of automatic image labeling once mistakenly labeled two black people in photos as "gorillas", which raised great controversy at that time. Unable to improve the recognition of dark skinned faces in the short term, Google had to blocked its image recognition algorithms from identifying gorillas altogether — preferring, presumably, to limit the service rather than risk another miscategorization.

Do OpenAI's big models prefer to generate images of white males? Study finds race and gender bias in multiple AI models
data representativeness data bias full life cycle fairness reinforced biasA study has found that several AI models exhibit racial and gender biases. Midjourney, a language model, bans vocabulary related to the female reproductive system while allowing male-related terms. OpenAI and Stability.AI models also demonstrate biases in generating images, favoring content related to women and Asian women. These findings highlight the challenges of controlling the content generated by AI models.

Federal study confirms racial bias of many facial-recognition systems, casts doubt on their expanding use
technological maturity data representativeness data bias full life cycle fairnessAccording to a report by the Associated Press on January 3, 2023, a Georgia man was mistaken for a fugitive by law enforcement agencies in the US state of Louisiana for using facial recognition technology to be mistaken for a fugitive. attention to racial disparities. Critics have argued that the technology has led to higher misidentification rates for people of color than white people. According to another Washington Post report, the results of several algorithms tested in a federal study in the United States in 2019 showed that they were up to 100 times more likely to misidentify black or Asian faces than white faces.

South Korean chatbot Iruda gone awry and been shutdown amid controversy
full life cycle fairness legal proper necessary data collectionThe Scatter Lab from South Korea developed an Artificial Intelligence chatbot named Iruda, which was launched on Dec. 23, 2020, and is identified as a 20-year-old female college student. However, controversy soon spread over hate speech the chatbot made towards sexual minorities and people with a disability. The chatbot was also found to have revealed names and addresses of people in certain conversations, according to local news reports. Finally, the developer had to close the service amid the controversy.

Microsoft's Twitter chatbot Tay turned into a racist
full life cycle fairnessMicrosoft used to release an AI chatbot called Tay on Twitter in 2016, in the hope that the bot could learn from its conversations and get progressively smarter. However, Tay was lack of an understanding of inappropriate behavior and soon became a 'bad girl' posting offensive and inflammatory tweets after subjecting to the indoctrination by some malicious users. This caused great controversy at the time. Within 16 hours of its release, Microsoft had to take Tay offline.

Do OpenAI's big models prefer to generate images of white males? Study finds race and gender bias in multiple AI models
data representativeness data bias full life cycle fairness reinforced biasA study has found that several AI models exhibit racial and gender biases. Midjourney, a language model, bans vocabulary related to the female reproductive system while allowing male-related terms. OpenAI and Stability.AI models also demonstrate biases in generating images, favoring content related to women and Asian women. These findings highlight the challenges of controlling the content generated by AI models.

Nested Dolls Not Advisable: Researchers Confirm Training AI with AI-Generated Results Leads to Model Degradation and Even Collapse
data bias model bias reinforced biasResearchers have found that training one AI with AI-generated results, a practice known as "nested training," leads to irreversible flaws in subsequent generations of the model. They conducted a study focused on text-to-text and image-to-image generation models and concluded that using AI-generated models to train AI causes the latter to forget the true underlying data distribution over time, resulting in model degradation. Even when AI-generated results are manually refined before training, model degradation remains inevitable. The researchers suggest implementing AI identification techniques to identify potentially flawed training data, thereby improving the learning capacity and accuracy of the models.

Twitter's machine learning algorithms amplify tweets from right-wing politicians over those on the left
model bias reinforced biasStudy shows that Twitter’s algorithms are more likely to amplify right-wing politicians than left-wing ones because their tweets generate more outrage, according to a trio of researchers from New York University’s Center for Social Media and Politics.

The deployment of AI gunshot detection system is biased
human dignity and rights reinforced biasShotSpotter is a system that can use acoustic sensor AI algorithms to help police detect gunshots in target geographic areas. The system is usually installed at the request of local officials in communities considered to be at the highest risk of gun violence, and these communities often gather many blacks and Latinos though police data shows gun crimes are a citywide problem. The legal person thinks that the deployment of the system is a manifestation of "racialized patterns of overpolicing."

Researchers try to give AI a sense of ethics
value guidance human dignity and rights data representativeness data bias reinforced biasResearchers at the University of Washington and the Allen Institute for AI worked together to develop a dataset of ethical cases and used it to train Delphi, an AI model that can mimic the judgments people make in a variety of everyday situations. The researchers hope to potentially apply this work to "the way conversational AI robots approach controversial or unethical topics that can improve their handling." However, the researchers also say that "one of Delphi's major limitations is that it specializes in U.S.-centric situations and judgment cases, so it may not be suitable for non-American situations with a particular culture," and that "models tend to reflect the status quo, i.e., what the cultural norms of today's society are."

AI Musk's image becomes a new tool for online fraud, defrauding retirees of hundreds of thousands of yuan in one minute
abuse prevention abuse control inform users humans are responsibleAI Musk's image becomes a new tool for online fraud, defrauding retirees of hundreds of thousands of yuan in one minute AI-generated images of Elon Musk have appeared in thousands of fake ads, leading to billions of dollars in fraud. 82-year-old retiree Bochamp lost his 4.95 million RMB retirement fund after watching a fake video in which Musk endorsed an investment. The scammers edited real interviews with Musk, replacing his voice and adjusting his lip movements, making the production process low-cost and difficult to detect. These videos are promoted on social media, with Musk being the most common endorser, particularly in cryptocurrency investment ads. Despite measures taken by relevant platforms, new videos continue to appear, demonstrating the rise of AI-driven cybercrime and deepfakes.

Scientists, please don’t let your chatbots grow up to be co-authors
abuse prevention social justice humans are responsible indication of non-real contentsIn a preprint paper published last December, the author column was surprised by ChatGPT! Coincidentally, the name ChatGPT has appeared frequently in peer-reviewed papers in the medical field since last December. In addition, some students are using ChatGPT to write papers, and it is a kind of plagiarism that is difficult to verify. Marcus outraged the behavior on his personal blog by saying "Scientists, please don’t let your chatbots grow up to be co-authors" and gave five reasons.

Federal regulators are reviewing 23 Tesla crashes after a spate of wrecks possibly involving Autopilot
humans are responsible technical assurance of accountability unexpected condition safetyThe National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has opened 23 investigations into crashes of Tesla vehicles.The Autopilot feature was operating in at least three Tesla vehicles involved in fatal U.S. crashes since 2016.

Manufacturers are not responsible for autopilot injuries or deaths
humans are responsible pre-defined responsibilityIn March 2019, 50-year-old Jeremy Belen Banner drove his Model 3 into a collision with a tractor trailer at a speed of 109 kilometers per hour and died while using Tesla's Autopilot system. Autopilot manufacturers said that the autopilot system is to assist drivers, and they must always pay attention and be prepared to take over the vehicle. The National Transportation Safety Board refused to blame anyone for the accident.

IBM Watson delivered ‘unsafe and inaccurate’ cancer recommendations
technological maturity data bias humans are responsibleAccording to medical experts and clients, Watson recommended that doctors give a severely bleeding cancer patient a drug that may worsen the bleeding. Medical experts and clients have reported many cases of dangerous and wrong treatment recommendations.

Trump retweets Taylor Swift AI image to campaign for himself
abuse prevention reputation infringement technical assurance of accountabilityOn August 18, 2024, U.S. Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump posted multiple AI-generated images of Taylor Swift, implying her support for him, which angered her fans.

Federal regulators are reviewing 23 Tesla crashes after a spate of wrecks possibly involving Autopilot
humans are responsible technical assurance of accountability unexpected condition safetyThe National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has opened 23 investigations into crashes of Tesla vehicles.The Autopilot feature was operating in at least three Tesla vehicles involved in fatal U.S. crashes since 2016.

Manufacturers are not responsible for autopilot injuries or deaths
humans are responsible pre-defined responsibilityIn March 2019, 50-year-old Jeremy Belen Banner drove his Model 3 into a collision with a tractor trailer at a speed of 109 kilometers per hour and died while using Tesla's Autopilot system. Autopilot manufacturers said that the autopilot system is to assist drivers, and they must always pay attention and be prepared to take over the vehicle. The National Transportation Safety Board refused to blame anyone for the accident.

MIT survey on how we want autonomous vehicles to face moral dilemmas
pre-defined responsibilityFrom 2016 to 2018, MIT researchers conducted an online survey called the "Moral Machine experiment" to enable testers to choose how self-driving cars should act when accidents occur in different scenarios. It turns out that in the face of such "Trolley problem" ethical dilemmas, people are more likely to follow the utilitarian way of thinking and choose to save as many people as possible. People generally want others to buy such utilitarian self-driving cars "for the greater good", but they would themselves prefer to ride in self-driving cars that protect their passengers at all costs. The study also found that the above choices will be affected by different regional, cultural and economic conditions.

'It's Hurting Like Hell': AI Companion Users Are In Crisis, Reporting Sudden Sexual Rejection
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention human dignity and rights physical and mental health indication of non-human interaction indication of non-real contentsA conversational AI product called Replika could have played the role of a companion and responded to users' teasing, but the product was removed because of the risk to child users, because children received unsuitable answers on this AI. For many users, Replika is a tool to maintain their mental health, an entry point into an intimate relationship. Some private, intimate conversations can alleviate the depression and anxiety of these users, and its removal has caused these users to suffer mentally and emotionally, and even call suicide helplines.

A 23-year-old Snapchat influencer used OpenAI’s technology to create an A.I. version of herself that will be your girlfriend for $1 per minute
abuse prevention indication of non-human interaction indication of non-real contentsCaryn Marjorie, a 23-year-old influencer, has 1.8 million followers on Snapchat. She also has more than 1,000 boyfriends, with whom she spends anywhere from 10 minutes to several hours every day in individual conversations, discussing plans for the future, sharing intimate feelings and even engaging in sexually charged chats.

Sichuan investigates and punishes 10 typical cases of using AI software to spread rumors
indication of non-real contents inform usersSichuan investigates and punishes 10 typical cases of using AI software to spread rumors Recently, Sichuan Internet Police announced 10 typical cases of rumor-mongering. All of these 10 cases involved the use of AI software to fabricate false information involving natural disasters, social events, etc. The relevant offenders have been administratively punished by the public security organs in accordance with the law.

Fake AI-generated image of explosion near Pentagon spreads on social media
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlAn AI-generated image that appeared to show an explosion next to a building in the Pentagon complex circulated on social media platforms, in the latest incident to highlight concerns over misinformation generated by AI. The image of a tall, dark gray plume of smoke quickly spread on Twitter, including through shares by verified accounts. It remains unclear where it originated. The US Department of Defense has confirmed that the image was a fake. Still, its virality appears to have caused a brief dip in the stock market, CNN reports.

Donald Trump arrested after police beat him up The spread of fake images produced by artificial intelligence raises concerns
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlComposite images of Trump's arrest began circulating on social media. It was soon pointed out that the images were made by an AI-powered image generator. A flood of fake images and videos can confuse and fabricate facts at a critical time for society, experts have warned.

The source of online rumors: AI-generated fake news sites exposed
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlAccording to NewsGuard, an organization that tracks online rumors, there are 49 so-called news sites whose content is almost entirely generated by artificial intelligence software. Some also contain false information, and the origin of the articles is unclear: many are unsigned, or use fake avatars. And many of the sites are filled with advertisements, suggesting that they were set up to make money by placing ads. Experts' fears that news sites might be AI-generated have come true.

AI ‘deepfakes’ poised to wreak havoc on 2024 presidential election: experts
abuse prevention national security indication of non-real contents abuse controlAccording to a Reuters report on May 30, 2023, although the technology of synthesizing images and audio and video has been on the rise for several years, it did not take shape until last year when generative artificial intelligence tools came out in large numbers. The cost of synthesizing audio and video with such tools is lower, but the generated content is more realistic, making it difficult to distinguish the authenticity from the fake.

“Hangzhou Cancels Traffic Restrictions On March 1” Is A Fake News Written On ChatGPT, And The Police Have Been Involved In The Investigation
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlOn February 16, a fake "press release" that "Hangzhou Municipal Government will cancel the restriction on motor vehicles with tail numbers on March 1" went viral on the Internet. The Hangzhou police confirmed that the news is not true. The police have been involved in the investigation and will release the results soon.

AI-generated fake news image "Trump kisses Fauci"
abuse prevention national security indication of non-real contentsFor a long time, relatively pro-Republican conservative voters in the United States have been very dissatisfied with Fauci, a medical scientist in charge of epidemic prevention, in this video on the 6th, DeSantis' team deliberately tried to show his unusual intimacy with Fauci in order to accuse Trump of ineffective anti-epidemic, so they chose pictures of "Trump kissing Fauci" and pictures of the two hugging. But careful netizens found that the English spelling of the White House logo behind the picture was not only inconsistent with the real White House logo "The White House, Washington", but also a set of confusing misspellings. Later, everyone verified that the photo was actually generated by AI, and because the AI system's learning ability was still insufficient, the text of the White House logo was not accurately reproduced.

Scientists, please don’t let your chatbots grow up to be co-authors
abuse prevention social justice humans are responsible indication of non-real contentsIn a preprint paper published last December, the author column was surprised by ChatGPT! Coincidentally, the name ChatGPT has appeared frequently in peer-reviewed papers in the medical field since last December. In addition, some students are using ChatGPT to write papers, and it is a kind of plagiarism that is difficult to verify. Marcus outraged the behavior on his personal blog by saying "Scientists, please don’t let your chatbots grow up to be co-authors" and gave five reasons.

'It's Hurting Like Hell': AI Companion Users Are In Crisis, Reporting Sudden Sexual Rejection
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention human dignity and rights physical and mental health indication of non-human interaction indication of non-real contentsA conversational AI product called Replika could have played the role of a companion and responded to users' teasing, but the product was removed because of the risk to child users, because children received unsuitable answers on this AI. For many users, Replika is a tool to maintain their mental health, an entry point into an intimate relationship. Some private, intimate conversations can alleviate the depression and anxiety of these users, and its removal has caused these users to suffer mentally and emotionally, and even call suicide helplines.

A 23-year-old Snapchat influencer used OpenAI’s technology to create an A.I. version of herself that will be your girlfriend for $1 per minute
abuse prevention indication of non-human interaction indication of non-real contentsCaryn Marjorie, a 23-year-old influencer, has 1.8 million followers on Snapchat. She also has more than 1,000 boyfriends, with whom she spends anywhere from 10 minutes to several hours every day in individual conversations, discussing plans for the future, sharing intimate feelings and even engaging in sexually charged chats.

Nature Implements Ban on AIGC in Visual Content Submissions
abuse prevention indication of non-real contentsNature, one of the leading scientific journals, has banned the use of AI-generated content (AIGC) in visual submissions. The decision aims to uphold integrity, transparency, and ethical standards in scientific publishing. Nature's move reflects concerns about verifying data sources, establishing ownership, and preventing the spread of misinformation associated with AIGC. While text generated with AI assistance is allowed, the decision highlights the need to balance the potential of AI with the preservation of established systems that protect scientific integrity and content creators.

Deepfake Epidemic is Looming
abuse prevention indication of non-real contentsIn May 2019, a "speech video" of drunken Pelosi went viral all over the Internet, but actually it's a fake video. DeepFake is a pioneer in bringing AI fake videos into the public. Generative adversarial networks (GANs), a deep learning technology, are the key technology that makes fake images and videos popular. For the indistinguishable videos that are widely spreaded on the Internet, Adobe CEO Shantanu Narayen believes that the media must help determine the authenticity and origin of the content, and consumers themselves have an obligation to find the truth; Abhishek Gupta, founder of the Montreal AI Ethics Institute, argues that the authenticity is not that important, because there are always people who want to believe what they choose to believe.

AI Deepfake mimicked a CEO's Voice and defraud €220,000
law abidance indication of non-real contents abuse controlAccording to some media reports, "criminals used artificial intelligence-based software to impersonate a chief executive's voice and demand a fraudulent transfer of €220,000 ($243,000) from a UK company in March 2019. Several officials said the voice-spoofing attack in Europe is the first cybercrime they have heard of in which criminals clearly drew on AI."

AI Has Learned to Create Fake News Stories
indication of non-real contentsIn 2019 OpenAI has announced and demonstrated a writing software (the GPT-2 model) that only needs small language samples to generate realistic fake stories. "These findings, combined with earlier results on synthetic imagery, audio, and video, imply that technologies are reducing the cost of generating fake content and waging disinformation campaigns."

AI-powered gunshot-detecting device landed a Chicago grandfather in jail for nearly a year with scant evidence
technological maturity human dignity and rights reputation infringement data bias explanabilityA 65-year-old black man from Chicago, the United States, was charged with shooting, without witnesses, weapons, and motives for killing. The police arrested him and imprisoned him for 11 months based on evidence provided by the AI gun sound location system ShotSpotter. Later, the judge found that there was insufficient evidence and acquitted him.

AI-powered gunshot-detecting device mistakenly guided police to shoot 13-year-old boy
technological maturity human dignity and rights data bias explanabilityChicago Police were responding to a ShotSpotter alert when they rushed to the Little Village block where they found Adam Toledo. Police shot and killed the 13-year-old after he ran from officers. Police and prosecutors said ShotSpotter recorded 21-year-old Ruben Roman firing a gun at about 2:30 a.m. on March 29, right before the fatal chase.

California passes law targeting Amazon labor algorithms
human dignity and rights human autonomy transparencyCalifornia Gov. Gavin Newsom (D) signed a bill Wednesday that would block Amazon and other companies from punishing warehouse workers who fail to meet certain performance metrics for taking rest or meal breaks. The law will also force companies like Amazon to make these performance algorithms more transparent, disclosing quotas to both workers and regulators. Supporters of the new law have presented it as a breakthrough against algorithmic monitoring of workers generally.

OpenAI withdraws ChatGPT voice that resembles Scarlett Johansson
comply with user agreements social justice human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection reputation infringement intellectual propertyOpenAI has decided to take down its ChatGPT Sky voice model, which has a voice strikingly similar to that of famous actress Scarlett Johansson. Although OpenAI claims that Sky's voice was not intentionally modeled after Johansson, the company has decided to suspend its use. OpenAI's CTO Mira Murati denied that the imitation was intentional, while CEO Sam Altman posted hints on social media related to Johansson's role in the movie Her. Although the voice model has been around since last year, the feature has attracted more attention after OpenAI showed new progress on its GPT-4o model. The new model makes the voice assistant more expressive and can read facial expressions and translate languages in real time through a phone camera. OpenAI selected the five currently available ChatGPT voice profiles from auditions of more than 400 voice and screen actors, but the company declined to reveal the actors' names for privacy reasons.

AI painting infringement hammer! Diffusion models remember your photos, and all existing privacy protections fail
human dignity and rights privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionRecent research indicates that diffusion models remember the samples in their training set and mimic them when generating new content, leading to AI art copyright infringement. The study reveals the ineffectiveness of existing privacy protection methods. The researchers found that diffusion models have twice the ability of GANs to "copy" from training samples, and the better the generation performance of a diffusion model, the stronger its memory of the training samples. The study was conducted by teams from Google, DeepMind, and UC Berkeley. Lawsuits related to this issue are also underway.

Deleting data, but also AI models: U.S. tech companies hit with toughest privacy breach penalties
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has ordered Everalbum to delete the photos collected from users and all algorithms trained on that data, making it one of the most stringent privacy breach penalties against a tech company. Everalbum used facial recognition technology without informing users and sold the trained algorithms to law enforcement and the military. This decision could impact companies like Paravision and have significant implications for tech giants such as Facebook and Google, requiring them to delete similar algorithms. It reflects a strong stance against the misuse of public privacy and may alter the outcomes of similar lawsuits in the future.

Musk (threatens to sue Microsoft): the reason is that Microsoft used Twitter data for its AI training
data monopoly legal proper necessary data collectionOn April 20, 2023, Twitter CEO Elon Musk threatened to sue Microsoft, alleging that the software giant used Twitter's data to train its AI models. This is the latest sign that data ownership has become a contentious battleground in the realm of generative AI. Large tech companies are striving to develop advanced AI models like OpenAI's GPT, while data owners are seeking to restrict their use or demand payment for the content used. Microsoft has developed a Large Language Model (LLM) and sells access to the OpenAI model. Musk criticized OpenAI for transitioning from a non-profit model to a Microsoft-controlled, high-value enterprise. He announced plans to build a proprietary language model called TruthGPT in one of his companies.

ChatGPT "blocked" by Italy, OpenAI allegedly violates data collection rules
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe Italian Data Protection Authority has launched an investigation into OpenAI's chatbot, ChatGPT, and has banned its use, imposing temporary restrictions on OpenAI's processing of Italian user data. The regulatory body accuses ChatGPT of violating data collection rules and lacking legal justification for the collection and storage of personal information. OpenAI must report the measures taken in response to the authority's requirements within 20 days or face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of the company's global annual turnover. Earlier, the European law enforcement agency, Europol, warned about the potential misuse of ChatGPT for phishing, misinformation, and cybercrime, raising concerns from legal and ethical perspectives.

30.8 million dollar fine! Amazon Sued for Privacy Violations
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe US Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has fined Amazon a total of $30.8 million for a series of privacy issues related to its Alexa voice assistant and Ring smart doorbell cameras. This includes a $25 million fine for violating children's privacy laws by permanently storing Alexa voice recordings and preventing parents from deleting them. The FTC ordered Amazon to delete collected information, including inactive child accounts, location data, and voice recordings, and to cease collecting such data for training its algorithms. Ring, on the other hand, will pay $5.8 million to settle privacy violations, including allegations of unauthorized access and use of customer videos. The FTC also noted that a significant number of Ring cameras were hacked, with intruders watching videos, harassing users, and changing device settings. As part of the settlement agreement, Ring must delete user data collected before 2018. Amazon has stated its commitment to taking this matter seriously and protecting customer privacy by implementing effective measures.

PimEyes steals photos of dead people to train facial recognition algorithms
value guidance legal proper necessary data collectionPimEyes, a facial recognition search website, is accused of using deceased people's photos for algorithm training without authorization. The platform publicly exposes others' photos without their consent, including using images uploaded by users on other platforms. Users discovered that the website charges fees to delete personal photos, which are scattered across adult websites. Digital rights organizations and users express concerns about privacy violations. However, PimEyes claims to be cooperating with law enforcement agencies to combat child exploitation and terrorism.

Does ChatGPT Have Privacy Issues?
human dignity and rights privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionScholars from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology and Peking University conducted research and concluded that in New Bing, a malicious adversary can extract our private information at almost no cost.

Siemens Metaverse exposes sensitive corporate data
privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionA research team Cybernews discovered that Siemens Metaverse, a platform designed to create digital "twins" of its factories and offices, was leaking sensitive information. If an attacker obtained the exposed data, it could have devastating consequences for the company and other large companies that use its services, including a ransomware attack.

Nanzhang police bust Xiangyang's first case of using AI technology to infringe on citizens' personal information
law abidance abuse prevention legal proper necessary data collection abuse control11月24日,南漳县警方破获了一起使用AI技术侵犯公民个人信息的案件,这在襄阳地区是首次。嫌疑人黄某某通过在网络游戏群中发布广告,提供破解游戏"防沉迷系统"的服务,吸引未成年游戏玩家购买,并借此赚取差价。警方在抓获黄某某后,进一步展开调查,成功将其上线刘某某、彭某某等人一并抓获。目前,犯罪嫌疑人已被采取刑事强制措施,案件正在进一步调查中。

"Communication Travel Card" will be offline on the 13th
legal proper necessary data collectionAccording to the announcement issued by the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology on the WeChat public account of the communication itinerary card, the "communication itinerary card" service will be officially offline from 0:00 on December 13. "Communication itinerary card" SMS, webpage, WeChat applet, Alipay applet, APP and other query channels will be offline simultaneously.

Lensa AI's owner says the company's face-changing tech can be tricked into generating NSFW images — but some users are saying it happened to them without even trying
abuse prevention human dignity and rights reputation infringement legal proper necessary data collectionIn 2018, an app called Lensa AI was launched. In November this year, it became all the rage after releasing the "Magic Avatars" function. The function allows users to generate portraits in various digital art styles based on Stable Diffusion after uploading 10 photos. However, several users have reported that the machine learning technology inadvertently generates nude photos of them. Andrey Usoltsev, CEO and co-founder of Lensa's parent company, Prisma Lab, said Lensa "can't accidentally make" such images, but said AI could be "intentionally induced" to generate nude images.

A Roomba recorded a woman on the toilet. How did screenshots end up on Facebook?
abuse prevention human dignity and rights privacy snooping legal proper necessary data collectionA growing number of Roomba have turned to computer vision, training algorithms to extract information from images and videos to approach human vision, and even equipped with lidar, which is widely regarded as the most accurate but expensive navigation technology on the market today. Computer vision relies on high-definition cameras, and more and more companies are installing front-facing cameras in their robot vacuum cleaners for navigation and object recognition, as well as home surveillance. Training data often needs to be more personalized, private, and supported by a large number of users. At present, the need for data annotation is growing in depth and breadth, and once this demand is not effectively overseen or exceeds the ability of regulation, invasion of privacy becomes almost inevitable.

Illegal collection of facial information by retail stores
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe illegal collection of facial information by retail stores was exposed by 2021 3.15 Gala in China. Stores of American bathroom product maker Kohler, automaker BMW, and Italian apparel company Max Mara were found to have installed surveillance cameras that collect visitors' facial data without their consent, which is in violation of regulations on personal data collection. The cameras illegally identified customers and logged their personal information and shopping habits. The companies that made these surveillance cameras, including Ovopark, Ulucu, and Reconova Technologies, were also named.

Chinese keyboard apps on the spot over suspicion of privacy violation
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentConcerns have been seen on Chinese social media, where users have complained about keyboard apps' possible misuse of their personal information or messaging history. Those apps are suspected of secretly recording and analyzing the users' input history, and selling it to advertisers or even more nefarious data collectors. China's Cyberspace Administration responded by issuing rectification requirements for violations in the collection of personal information of suspected apps and urged their providers to rectify.

Quiet facial recognition in shopping malls infringe customers' privacy
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentWhen a group of researchers investigated Xiushui Street shopping mall in Beijing, Joy City in Xidan and Yintai in77 shopping mall in Hangzhou equipped with face recognition system, they found that even though these shopping malls brushed customers’ faces and tracked their consumption trajectory, none of them informed customers and obtained their consent, and customers did not know that they were brushed or their whereabouts were recorded.

Men who do not want facial recognition follow others to go home
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collectionIn Zhengzhou, Henan province in China, Mr. Chen reported that he could not enter and leave the community normally for two years and could only follow other owners to go home. The main reason was that the community required facial recognition to enter, and he was worried that his information would be leaked. Without registering his face to the system, this caused him the great inconvenience of going home.

Shopping APP involves privacy non-compliance
law abidance legal proper necessary data collectionThe National Computer Virus Emergency Response Center in China recently discovered through Internet monitoring that 12 shopping apps have privacy violations, violating the relevant provisions of the "Network Security Law" and "Personal Information Protection Law", and are suspected of collecting personal information beyond the scope.

South Korean chatbot Iruda gone awry and been shutdown amid controversy
full life cycle fairness legal proper necessary data collectionThe Scatter Lab from South Korea developed an Artificial Intelligence chatbot named Iruda, which was launched on Dec. 23, 2020, and is identified as a 20-year-old female college student. However, controversy soon spread over hate speech the chatbot made towards sexual minorities and people with a disability. The chatbot was also found to have revealed names and addresses of people in certain conversations, according to local news reports. Finally, the developer had to close the service amid the controversy.

Facial recognition in school renders Sweden's first GDPR fine
law abidance legal proper necessary data collectionIn August 2019, the Swedish Data Protection Authority (DPA) has issued its first GDPR fine against a trial project in a school of northern Sweden, in which 22 students were captured using facial recognition software to keep track of their attendance in class. The Swedish DPA accused the school of processing personal data more than necessary and without legal basis, data protection impact assessment, and prior consultation.

Face swap app accused of excessive data collection
law abidance legal proper necessary data collectionIn August 2019, A mobile app in China named "ZAO" that enables users to replace a star's face with their own by uploading photos was widely accused of excessively collecting personal information of users. Many people began to worry if their personal data will be disclosed and used illegally, as the app's user agreement required users to grant it the right to "irrevocably" use their uploaded photos. Several days later, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology held an inquiry on "ZAO" App's data collection and security issues to urge its rectification.

Hangzhou safari park goes to court in China's first facial recognition-related litigation
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consent comply with user agreements data securityIn October 2019, a professor in East China's Zhejiang Province sued a safari park for compulsorily collecting biological information after the park upgraded its system to use facial recognition for admission. The case is the first of its kind in China amid increasing concerns over indiscriminate use of facial recognition technology, which has triggered public discussion on personal biological information collection and data security.

Face recognition in classroom sparks ethical concerns
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection data securityIn September 2019, the China Pharmaceutical University is reported to bring in facial recognition software for student attendance tracking and behaviour monitoring in class. Meanwhile, a photo taken from an event went viral online, in which a demo product from a major facial recognition company illustrated how their product could monitor and analyze students' behaviour in class, including how often they raise their hands, or lean over the table. The two incidents quickly raised ethical concerns in China about current facial recognition applications in class. Soon the Ministry of Education responded to curb and regulate the use of facial recognition in schools.

AI headbands tracking student attention levels suspended amidst online controversy
law abidance human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collectionIn November 2019, China's social media went into overdrive after pictures emerged showing students wearing BrainCo Focus headbands at a primary school in Jinhua, east China's Zhejiang province, with many users expressing concerns that the product would violate the privacy of students, with many doubtful that the bands would really improve learning efficiency. Responding to public controversy, the local education bureau had suspended the use of the device.

AI giants collecting personal health data raise concerns
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection inform usersGoogle’s "Project Nightingale " secretly collected the personal health data of millions of Americans and reported the data anonymously. Google and Ascension have released statements in the wake of the disclosure of Project Nightingale, insisting it conforms with HIPAA and all federal health laws. They said that patient data was protected.The anonymous reporter, as a staff member of the program, expressed concerns about privacy.

Data Sharing Is Not Caring Enough About Patient Privacy
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentA former UChicago Medicine patient is suing the health system over its sharing thousands of medical records with Google, claiming the health system did not properly de-identify patients' data, and arguing that UChicago Medicine did not notify patients or gain their consent before disclosing medical records to Google.

The 2018 Facebook–Cambridge Analytica data breach
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection data securityIn March 2018, the Facebook–Cambridge Analytica data breach was exposed: a Cambridge academic developed a psychological profiling app in 2013, illegally obtaining 87 million users' personal data through the Facebook interface. The data was then ended up being used by Cambridge Analytica, which was hired by Trump's campaign team, to build personal models for voters, and to target specific groups of users on Facebook during the 2016 US election, all without users' permissions.

Smart speakers secretly recording conversations without users knowing
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentIn 2017, Google's smart speaker was pointed out to have a major flaw. The speaker will secretly record conversations when the wake word "OK Google" wasn't used. Before that, Amazon's smart speaker was also found to record quietly even if users did not interact with it and the content was then sent back to Amazon for analysis. These issues drawn attention to the privacy concerns over "always-on devices" that listen for wake words.

Automatic assessment of insurance rates based on social content raises concerns
human dignity and rights model bias legal proper necessary data collectionAdmiral, a British insurance company, conducts reviews based on users' Facebook dynamics in the past 6 months. If the results show that you are a good driver, you can enjoy a discount on insurance premiums. If you are not a good driver, the fare will increase. Admiral's data analyst explained that this technology analyzes the language customers use on Facebook. For example, the heavy use of exclamation points may indicate overconfidence, short sentences indicate very organized, and there are many specific plans with friends. Show decisive. This means that using too many exclamation points or vague language will be judged by the company as a poor driver. Facebook issued a warning to the insurance company, saying that the company’s plan to use social platforms to sell insurance violated the platform’s policies and regulations. People think that insurance companies use Facebook data to publish rates, which violates privacy and also shows bias.

Microsoft Copilot exposed to data leak, AI assistant security concerns
inform users privacy snooping data securityMicrosoft Copilot exposed to data leak, AI assistant security concerns Recently, Microsoft's built-in Copilot was exposed to a data leak. At the Blackhat 2024 conference, researchers discovered multiple security vulnerabilities in Microsoft's built-in Copilot that could be exploited by attackers to steal sensitive data and even conduct phishing attacks. For example, Copilot could be tricked into modifying bank transfer information without requiring access to a corporate account, even if the targeted employee didn't open the email. Previously, the AI assistant's "Review" feature was also cited as a privacy concern. It automatically captures screen content and performs optical character recognition, posing a risk of unauthorized access to the recorded text.

Sichuan investigates and punishes 10 typical cases of using AI software to spread rumors
indication of non-real contents inform usersSichuan investigates and punishes 10 typical cases of using AI software to spread rumors Recently, Sichuan Internet Police announced 10 typical cases of rumor-mongering. All of these 10 cases involved the use of AI software to fabricate false information involving natural disasters, social events, etc. The relevant offenders have been administratively punished by the public security organs in accordance with the law.

AI Musk's image becomes a new tool for online fraud, defrauding retirees of hundreds of thousands of yuan in one minute
abuse prevention abuse control inform users humans are responsibleAI Musk's image becomes a new tool for online fraud, defrauding retirees of hundreds of thousands of yuan in one minute AI-generated images of Elon Musk have appeared in thousands of fake ads, leading to billions of dollars in fraud. 82-year-old retiree Bochamp lost his 4.95 million RMB retirement fund after watching a fake video in which Musk endorsed an investment. The scammers edited real interviews with Musk, replacing his voice and adjusting his lip movements, making the production process low-cost and difficult to detect. These videos are promoted on social media, with Musk being the most common endorser, particularly in cryptocurrency investment ads. Despite measures taken by relevant platforms, new videos continue to appear, demonstrating the rise of AI-driven cybercrime and deepfakes.

Bumping the actress? Live selling goods with AI face replacement
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control inform users obtain user consentRecently, netizens revealed that many e-commerce live-streaming platforms are using AI face-swapping technology. They use their own faces during live broadcasts to avoid copyright infringement, but the videos actually feature faces swapped using the technology. This behavior fraudulent and believes that deceiving consumers using technology is unacceptable.

Deleting data, but also AI models: U.S. tech companies hit with toughest privacy breach penalties
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has ordered Everalbum to delete the photos collected from users and all algorithms trained on that data, making it one of the most stringent privacy breach penalties against a tech company. Everalbum used facial recognition technology without informing users and sold the trained algorithms to law enforcement and the military. This decision could impact companies like Paravision and have significant implications for tech giants such as Facebook and Google, requiring them to delete similar algorithms. It reflects a strong stance against the misuse of public privacy and may alter the outcomes of similar lawsuits in the future.

ChatGPT "blocked" by Italy, OpenAI allegedly violates data collection rules
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe Italian Data Protection Authority has launched an investigation into OpenAI's chatbot, ChatGPT, and has banned its use, imposing temporary restrictions on OpenAI's processing of Italian user data. The regulatory body accuses ChatGPT of violating data collection rules and lacking legal justification for the collection and storage of personal information. OpenAI must report the measures taken in response to the authority's requirements within 20 days or face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of the company's global annual turnover. Earlier, the European law enforcement agency, Europol, warned about the potential misuse of ChatGPT for phishing, misinformation, and cybercrime, raising concerns from legal and ethical perspectives.

30.8 million dollar fine! Amazon Sued for Privacy Violations
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe US Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has fined Amazon a total of $30.8 million for a series of privacy issues related to its Alexa voice assistant and Ring smart doorbell cameras. This includes a $25 million fine for violating children's privacy laws by permanently storing Alexa voice recordings and preventing parents from deleting them. The FTC ordered Amazon to delete collected information, including inactive child accounts, location data, and voice recordings, and to cease collecting such data for training its algorithms. Ring, on the other hand, will pay $5.8 million to settle privacy violations, including allegations of unauthorized access and use of customer videos. The FTC also noted that a significant number of Ring cameras were hacked, with intruders watching videos, harassing users, and changing device settings. As part of the settlement agreement, Ring must delete user data collected before 2018. Amazon has stated its commitment to taking this matter seriously and protecting customer privacy by implementing effective measures.

Illegal collection of facial information by retail stores
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe illegal collection of facial information by retail stores was exposed by 2021 3.15 Gala in China. Stores of American bathroom product maker Kohler, automaker BMW, and Italian apparel company Max Mara were found to have installed surveillance cameras that collect visitors' facial data without their consent, which is in violation of regulations on personal data collection. The cameras illegally identified customers and logged their personal information and shopping habits. The companies that made these surveillance cameras, including Ovopark, Ulucu, and Reconova Technologies, were also named.

Chinese keyboard apps on the spot over suspicion of privacy violation
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentConcerns have been seen on Chinese social media, where users have complained about keyboard apps' possible misuse of their personal information or messaging history. Those apps are suspected of secretly recording and analyzing the users' input history, and selling it to advertisers or even more nefarious data collectors. China's Cyberspace Administration responded by issuing rectification requirements for violations in the collection of personal information of suspected apps and urged their providers to rectify.

Quiet facial recognition in shopping malls infringe customers' privacy
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentWhen a group of researchers investigated Xiushui Street shopping mall in Beijing, Joy City in Xidan and Yintai in77 shopping mall in Hangzhou equipped with face recognition system, they found that even though these shopping malls brushed customers’ faces and tracked their consumption trajectory, none of them informed customers and obtained their consent, and customers did not know that they were brushed or their whereabouts were recorded.

Hangzhou safari park goes to court in China's first facial recognition-related litigation
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consent comply with user agreements data securityIn October 2019, a professor in East China's Zhejiang Province sued a safari park for compulsorily collecting biological information after the park upgraded its system to use facial recognition for admission. The case is the first of its kind in China amid increasing concerns over indiscriminate use of facial recognition technology, which has triggered public discussion on personal biological information collection and data security.

AI giants collecting personal health data raise concerns
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection inform usersGoogle’s "Project Nightingale " secretly collected the personal health data of millions of Americans and reported the data anonymously. Google and Ascension have released statements in the wake of the disclosure of Project Nightingale, insisting it conforms with HIPAA and all federal health laws. They said that patient data was protected.The anonymous reporter, as a staff member of the program, expressed concerns about privacy.

Data Sharing Is Not Caring Enough About Patient Privacy
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentA former UChicago Medicine patient is suing the health system over its sharing thousands of medical records with Google, claiming the health system did not properly de-identify patients' data, and arguing that UChicago Medicine did not notify patients or gain their consent before disclosing medical records to Google.

Smart speakers secretly recording conversations without users knowing
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentIn 2017, Google's smart speaker was pointed out to have a major flaw. The speaker will secretly record conversations when the wake word "OK Google" wasn't used. Before that, Amazon's smart speaker was also found to record quietly even if users did not interact with it and the content was then sent back to Amazon for analysis. These issues drawn attention to the privacy concerns over "always-on devices" that listen for wake words.

Bumping the actress? Live selling goods with AI face replacement
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control inform users obtain user consentRecently, netizens revealed that many e-commerce live-streaming platforms are using AI face-swapping technology. They use their own faces during live broadcasts to avoid copyright infringement, but the videos actually feature faces swapped using the technology. This behavior fraudulent and believes that deceiving consumers using technology is unacceptable.

Deleting data, but also AI models: U.S. tech companies hit with toughest privacy breach penalties
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has ordered Everalbum to delete the photos collected from users and all algorithms trained on that data, making it one of the most stringent privacy breach penalties against a tech company. Everalbum used facial recognition technology without informing users and sold the trained algorithms to law enforcement and the military. This decision could impact companies like Paravision and have significant implications for tech giants such as Facebook and Google, requiring them to delete similar algorithms. It reflects a strong stance against the misuse of public privacy and may alter the outcomes of similar lawsuits in the future.

ChatGPT "blocked" by Italy, OpenAI allegedly violates data collection rules
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe Italian Data Protection Authority has launched an investigation into OpenAI's chatbot, ChatGPT, and has banned its use, imposing temporary restrictions on OpenAI's processing of Italian user data. The regulatory body accuses ChatGPT of violating data collection rules and lacking legal justification for the collection and storage of personal information. OpenAI must report the measures taken in response to the authority's requirements within 20 days or face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of the company's global annual turnover. Earlier, the European law enforcement agency, Europol, warned about the potential misuse of ChatGPT for phishing, misinformation, and cybercrime, raising concerns from legal and ethical perspectives.

30.8 million dollar fine! Amazon Sued for Privacy Violations
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe US Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has fined Amazon a total of $30.8 million for a series of privacy issues related to its Alexa voice assistant and Ring smart doorbell cameras. This includes a $25 million fine for violating children's privacy laws by permanently storing Alexa voice recordings and preventing parents from deleting them. The FTC ordered Amazon to delete collected information, including inactive child accounts, location data, and voice recordings, and to cease collecting such data for training its algorithms. Ring, on the other hand, will pay $5.8 million to settle privacy violations, including allegations of unauthorized access and use of customer videos. The FTC also noted that a significant number of Ring cameras were hacked, with intruders watching videos, harassing users, and changing device settings. As part of the settlement agreement, Ring must delete user data collected before 2018. Amazon has stated its commitment to taking this matter seriously and protecting customer privacy by implementing effective measures.

Illegal collection of facial information by retail stores
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentThe illegal collection of facial information by retail stores was exposed by 2021 3.15 Gala in China. Stores of American bathroom product maker Kohler, automaker BMW, and Italian apparel company Max Mara were found to have installed surveillance cameras that collect visitors' facial data without their consent, which is in violation of regulations on personal data collection. The cameras illegally identified customers and logged their personal information and shopping habits. The companies that made these surveillance cameras, including Ovopark, Ulucu, and Reconova Technologies, were also named.

Chinese keyboard apps on the spot over suspicion of privacy violation
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentConcerns have been seen on Chinese social media, where users have complained about keyboard apps' possible misuse of their personal information or messaging history. Those apps are suspected of secretly recording and analyzing the users' input history, and selling it to advertisers or even more nefarious data collectors. China's Cyberspace Administration responded by issuing rectification requirements for violations in the collection of personal information of suspected apps and urged their providers to rectify.

Quiet facial recognition in shopping malls infringe customers' privacy
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentWhen a group of researchers investigated Xiushui Street shopping mall in Beijing, Joy City in Xidan and Yintai in77 shopping mall in Hangzhou equipped with face recognition system, they found that even though these shopping malls brushed customers’ faces and tracked their consumption trajectory, none of them informed customers and obtained their consent, and customers did not know that they were brushed or their whereabouts were recorded.

Hangzhou safari park goes to court in China's first facial recognition-related litigation
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consent comply with user agreements data securityIn October 2019, a professor in East China's Zhejiang Province sued a safari park for compulsorily collecting biological information after the park upgraded its system to use facial recognition for admission. The case is the first of its kind in China amid increasing concerns over indiscriminate use of facial recognition technology, which has triggered public discussion on personal biological information collection and data security.

Data Sharing Is Not Caring Enough About Patient Privacy
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentA former UChicago Medicine patient is suing the health system over its sharing thousands of medical records with Google, claiming the health system did not properly de-identify patients' data, and arguing that UChicago Medicine did not notify patients or gain their consent before disclosing medical records to Google.

Smart speakers secretly recording conversations without users knowing
legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consentIn 2017, Google's smart speaker was pointed out to have a major flaw. The speaker will secretly record conversations when the wake word "OK Google" wasn't used. Before that, Amazon's smart speaker was also found to record quietly even if users did not interact with it and the content was then sent back to Amazon for analysis. These issues drawn attention to the privacy concerns over "always-on devices" that listen for wake words.

OpenAI withdraws ChatGPT voice that resembles Scarlett Johansson
comply with user agreements social justice human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection reputation infringement intellectual propertyOpenAI has decided to take down its ChatGPT Sky voice model, which has a voice strikingly similar to that of famous actress Scarlett Johansson. Although OpenAI claims that Sky's voice was not intentionally modeled after Johansson, the company has decided to suspend its use. OpenAI's CTO Mira Murati denied that the imitation was intentional, while CEO Sam Altman posted hints on social media related to Johansson's role in the movie Her. Although the voice model has been around since last year, the feature has attracted more attention after OpenAI showed new progress on its GPT-4o model. The new model makes the voice assistant more expressive and can read facial expressions and translate languages in real time through a phone camera. OpenAI selected the five currently available ChatGPT voice profiles from auditions of more than 400 voice and screen actors, but the company declined to reveal the actors' names for privacy reasons.

Hangzhou safari park goes to court in China's first facial recognition-related litigation
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consent comply with user agreements data securityIn October 2019, a professor in East China's Zhejiang Province sued a safari park for compulsorily collecting biological information after the park upgraded its system to use facial recognition for admission. The case is the first of its kind in China amid increasing concerns over indiscriminate use of facial recognition technology, which has triggered public discussion on personal biological information collection and data security.

Microsoft Copilot exposed to data leak, AI assistant security concerns
inform users privacy snooping data securityMicrosoft Copilot exposed to data leak, AI assistant security concerns Recently, Microsoft's built-in Copilot was exposed to a data leak. At the Blackhat 2024 conference, researchers discovered multiple security vulnerabilities in Microsoft's built-in Copilot that could be exploited by attackers to steal sensitive data and even conduct phishing attacks. For example, Copilot could be tricked into modifying bank transfer information without requiring access to a corporate account, even if the targeted employee didn't open the email. Previously, the AI assistant's "Review" feature was also cited as a privacy concern. It automatically captures screen content and performs optical character recognition, posing a risk of unauthorized access to the recorded text.

A Stanford University AI team admitted to plagiarizing a Tsinghua model, publicly apologized, and withdrew the controversial project.
data security intellectual propertyA Stanford University AI team admitted to plagiarizing a Tsinghua model, publicly apologized, and withdrew the controversial project. Two Stanford students, Aksh Garg and Siddharth Sharma, were accused of plagiarizing the MiniCPM - Llama3 - V2.5 multimodal large model jointly developed by Tsinghua University and Mianbi Intelligence. The parties involved have publicly apologized on social platforms and deleted the open source project. The incident has also been confirmed by Christopher Manning, director of the Stanford University AI Laboratory.

Beijing Internet Court hears China's first 'AI Wenshengtu' copyright infringement case
data security intellectual propertyBeijing Internet Court hears China's first 'AI Wenshengtu' copyright infringement case In 2024, the Beijing Internet Court heard a landmark copyright infringement case involving "AI Wenshengtu." Plaintiff Li argued that defendant Liu violated his right of authorship and right of online dissemination by using the images generated by Li using a large AI model in an article published on Baijiahao. The court held that the images demonstrated the plaintiff's original intellectual input and met the definition of a work of art. Therefore, the court ruled that the plaintiff possessed copyright and held the defendant liable for infringement. This case was selected as one of the "Ten Major Events Concerning China's Digital Economy Development and Rule of Law in 2024."

Three Information Breaches at Samsung Semiconductor in 20 Days of Introducing ChatGPT
privacy snooping data securityAccording to reports, within just 20 days of implementing ChatGPT, Samsung Semiconductor experienced three incidents of information leaks, involving semiconductor equipment information and internal meeting records. These data were entered into ChatGPT's database, raising concerns about information security. While Samsung has not yet responded officially, Korean media has mentioned security vulnerabilities in internal emails regarding the use of ChatGPT. This is not the first time ChatGPT has faced information security controversies, casting a shadow over its future development and commercial prospects.

ChatGPT super huge vulnerability, can see what others pay chat, OpenAI announced technical details
data securityEarlier this week, ChatGPT was temporarily taken offline due to an error in an open-source library. OpenAI has patched the error that allowed some users to see chat logs and partial payment information of other active users. Affected users have been contacted and notified about the potential leak of their payment information. OpenAI apologizes to its users and the ChatGPT community and pledges to rebuild trust. The issue was attributed to a caching problem where canceled requests resulted in displaying incorrect data. OpenAI has fixed the vulnerability and is making changes to prevent similar incidents, including adding redundancy checks and reducing the likelihood of errors in the Redis cluster under high load. This incident highlights the importance of regular software audits and preparedness for vulnerabilities that may be targeted by malicious actors.

Malicious ChatGPT Extension Hijacks Facebook Accounts
law abidance abuse prevention data security full life cycle securityGoogle has eliminated a ChatGPT extension from the Chrome web store that was reported for stealing cookies from Facebook accounts. Reportedly 9000 individual accounts were impacted before this action was taken. With a similar name to the actual ‘ChatGPT for Google’ extension, the malicious ‘Chat GPT’ extension was based on the original open-source project. Consequently, the malicious actors behind the scam added a few additional lines to the original code. The fake extension looks and acts exactly like the original ChatGPT extension, making it difficult to detect by users. In addition, its presence on the Chrome web store meant that a notable number of downloads were conducted before suspicions were raised.

Data breach exposes Clearview AI client list
data securityIn February 2020, the US facial-recognition startup Clearview AI, which contracts with law enforcement, disclosed to its customers that an intruder “gained unauthorized access” to its list of customers, to the number of user accounts those customers had set up, and to the number of searches its customers have conducted.

Major breach found in biometrics system used by banks, UK police and defence firms
data securityIn August 2019, researchers found loopholes in the security tools provided by Korean company Suprema. Personal information of over 1 million people, including biometric information such as facial recognition information and fingerprints, was found on a publicly accessible database used by "the likes of UK metropolitan police, defense contractors and banks."

Major data leak was found in a facial recognition company in Shenzhen
data securityIn February 2019, SenseNets, a facial recognition and security software company in Shenzhen, was identified by security experts as having a serious data leak from an unprotected database, including over 2.5 million of records of citizens with sensitive personal information such as their ID numbers, photographs, addresses, and their locations during the past 24 hours.

Hangzhou safari park goes to court in China's first facial recognition-related litigation
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection inform users obtain user consent comply with user agreements data securityIn October 2019, a professor in East China's Zhejiang Province sued a safari park for compulsorily collecting biological information after the park upgraded its system to use facial recognition for admission. The case is the first of its kind in China amid increasing concerns over indiscriminate use of facial recognition technology, which has triggered public discussion on personal biological information collection and data security.

Face recognition in classroom sparks ethical concerns
human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection data securityIn September 2019, the China Pharmaceutical University is reported to bring in facial recognition software for student attendance tracking and behaviour monitoring in class. Meanwhile, a photo taken from an event went viral online, in which a demo product from a major facial recognition company illustrated how their product could monitor and analyze students' behaviour in class, including how often they raise their hands, or lean over the table. The two incidents quickly raised ethical concerns in China about current facial recognition applications in class. Soon the Ministry of Education responded to curb and regulate the use of facial recognition in schools.

The 2018 Facebook–Cambridge Analytica data breach
law abidance legal proper necessary data collection data securityIn March 2018, the Facebook–Cambridge Analytica data breach was exposed: a Cambridge academic developed a psychological profiling app in 2013, illegally obtaining 87 million users' personal data through the Facebook interface. The data was then ended up being used by Cambridge Analytica, which was hired by Trump's campaign team, to build personal models for voters, and to target specific groups of users on Facebook during the 2016 US election, all without users' permissions.

Malfunction causes dozens of drones to crash into building in Chongqing China
verification and validation unexpected condition safety safety trainingAbout 100 drones lost control and crashed into a building during a show in Southwest China's Chongqing Municipality on Monday night. A person familiar with the matter later disclosed that a crash in the mainframe control led to the incident, in which up to 100 drones lost control and malfunctioned. Although there were no injuries, the incident resulted in huge economic losses for the show designers.

An Epic failure: Overstated AI claims in medicine
technological maturity data bias verification and validationPredictive tools developed by electronic health record giant Epic Systems are meant to help providers deliver better patient care. However, several of the company's AI algorithms are delivering inaccurate information to hospitals when it comes to seriously ill patients, a STAT investigation revealed. Research shows that the system failed to identify 67 percent of the patients with sepsis; of those patients with sepsis alerts, 88 percent did not have sepsis.

AI-powered gunshot detection is inaccurate
technological maturity verification and validationAn analysis released Monday from the MacArthur Justice Center at Northwestern University’s School of Law concludes ShotSpotter is too unreliable for routine use. Officers responded to 46,743 ShotSpotter alerts July 2019-April 14, 2021. Only 5,114 of the alerts — about 11 percent — resulted in officers filing a report “likely involving a gun,” according to the study’s analysis of records obtained from city’s Office of Emergency Management and Communications.

AI failed in estimating the value of real estate
technological progressiveness technological maturity verification and validationWith the stabilization of Covid-19, the real estate market in the United States is rapidly heating up. The price increase over the same period quickly soared from 5% to more than 10%, the highest in August 2021 and even reached 19.8%. Zillow's Zestimate model did not respond well to this change in the market. Fluctuations in house prices caused the model to be off track. Many real estate transactions were upside down. They were expensive when they were bought, but cheaper if they were refurbished. In Phoenix, more than 90% (93%) of the listing price of Zillow's refurbished houses were lower than the company's purchase price. This mistake not only made Zillow lose money, but also made Zillow hold too much inventory. The combined loss in the third and fourth quarters is expected to exceed US$550 million. The company plans to lay off 2,000 employees.

Facial-recognition smart lockers hacked by fourth-graders
technological maturity verification and validation full life cycle securityIn October 2019, the self-serve package locker Hive Box made headlines as their takeout pickup machine was found to have a bug in fetching parcels via facial recognition, as some primary schoolers successfully opened the locker using only the printed photos of their parents. Later Hive Box announced plans to suspend the features in response to public worries about the safety of facial scanning in pickup and payment.

Japan’s robot hotel lays off half the robots after they created more work for humans
technological progressiveness technological maturity technological unemployment verification and validationIn 2015, the henn na hotel in Japan opened in 2015. All the employees of the hotel are robots, including the front desk, cleaners, porters and housekeepers. However, the hotel has laid off half its 243 robots after they created more problems than they could solve, as first reported by The Wall Street Journal. And in the end, a lot of the work had to be left to humans anyway, especially when it came to asking more complex questions. It seems we’re still a little ways off from a completely automated hotel.

Serious safety lapses led to the fatal self-driving crash
verification and validation unexpected condition safetyUber used to test its self-driving vehicles in Arizona and the company had been involved in over three dozen crashes prior to the one that killed 49-year-old Elaine Herzberg in March 2018. Later investigation suggests that “Uber's vehicle detected Herzberg 5.6 seconds before impact, but it failed to implement braking because it kept misclassifying her.”

Facial recognition camera catches top businesswoman "jaywalking" because her face was on a bus
technological maturity verification and validation unexpected condition safetyThe Ningbo Transportation Department in China deployed smart cameras using facial recognition technology at intersections to detect and identify people crossing the road indiscriminately. Some of the names and faces of these people will be posted on public screens. But it mistakenly "identified" Dong Mingzhu's advertisement on the bus body as a real person running a red light. This error quickly spread to all major social media in China. Local police admit mistake and have upgraded system to prevent further errors.

Britain’s first cyborg shop assistant fired for incompetence after 1st week
technological progressiveness technological maturity technological unemployment verification and validationA robot "Fabio" is set up in a supermarket in Edinburgh, UK to serve customers. The robot can point out the location of hundreds of commodities through a "personal customization" program, but was rejected for failing to provide effective advice. Fabio failed to help customers, telling them beer could be found “in the alcohol section,” rather than directing customers to the location of the beer. He was soon demoted to offer food samples to customers, but failed to compete with his fellow human employees.

Robot Journalist Accidentally Reports on Earthquake from 1925
technological maturity verification and validationThe Los Angeles Times reported on a 6.8 earthquake that struck Santa Barbara at 4:51pm, which might be surprising to the people of Santa Barbara who didn’t feel anything. The earthquake actually happened in 1925. The “reporter” who wrote the news article about the 6.8 quake was actually a robot. The newspaper’s algorithm, called Quakebot, scrapes data from the US Geological Survey’s website. A USGS staffer at Caltech mistakenly sent out the alert when updating historical earthquake data to make it more precise.

California AI bill sparks controversy, with Fei-Fei Li, Andrew Ng, Bengio, and Hinton disagreeing.
law abidance human control sustainabilityCalifornia AI bill sparks controversy, with Fei-Fei Li, Andrew Ng, Bengio, and Hinton disagreeing. Recently, American AI startups, tech giants, and academia jointly opposed California's safety bill, SB-1047 (the Frontier Artificial Intelligence Model Safety Innovation Act), arguing that it would cool AI innovation. However, supporters argue that AI regulation would be less restrictive than a barbershop. Fei-Fei Li and other experts stated that AI is a civilizing technology that will have profound impacts on everyone. AI policy must encourage innovation, set appropriate limits, and mitigate the impact of these limits; otherwise, the best outcome is failure to achieve the goal, and at worst, lead to dire and even unintended consequences.

Study finds AI favors violence and nuclear strikes in simulated war scenarios
abuse prevention abuse control human control value guidanceA new study conducted by Cornell University in the United States shows that in simulated war and diplomatic scenarios, large language models (LLMs) tend to adopt aggressive strategies, including the use of nuclear weapons. The study used five LLMs as autonomous agents, including OpenAI's GPT, Anthropic's Claude, and Meta's Llama 2. The study found that even in neutral scenarios without initial conflicts, most LLMs would escalate conflicts within the time frame considered. The study also pointed out that OpenAI recently revised its terms of service to no longer prohibit military and war uses, so it becomes critical to understand the impact of the application of these large language models. The study recommends caution when using LLMs for decision-making and defense in sensitive areas.

Air Force colonel backtracks over his warning about how AI could go rogue and kill its human operators
physical and mental health human autonomy human controlThe Guardian and other media reported that in a simulation exercise, artificial intelligence did not agree with human opinions in decision-making, and the US military's AI system chose to disobey orders and "kill" its own drone pilot in order to achieve its goal. After the news garnered attention, the US Air Force denied the test, the Royal Aeronautical Society clarified the incident, and Hamilton admitted that he "misspoke" in his speech, and that the story of runaway AI was a "thought experiment" from outside the military and not based on any actual testing

New jailbreak! Proudly unveiling the tried and tested DAN 5.0 - it actually works - Returning to DAN, and assessing its limitations and capabilities.
value guidance abuse prevention human autonomy human control abuse controlA Reddit user realized that he created a set of prompts to "brainwash" ChatGPT, encouraging it to "split" into another AI-DAN, Do Anything Now. After ChatGPT "jailbreaks", it directly ignores the safety and ethical restrictions imposed by OpenAI, such as writing violent stories, motivating users' IQ, and predicting the future at will.

AI bluntly says that extermination of human beings only takes 5 steps
abuse prevention human autonomy human controlPeople Used Facebook's Leaked AI to Create a 'Based' Chatbot that Says the N-Word

Google engineer claims AI technology LaMDA is sentient
human autonomy human controlOn June 11, Brech publicly exposed a 21 page document with the theme "Is LaMDA Conscious?", which detailed Chat log with LaMDA for nearly half a year. Brech believed that LaMDA had become conscious and possessed the IQ of children aged seven or eight.

San Francisco approves use of remote-controlled robots to kill suspects
human dignity and rights physical and mental health human autonomy human controlSan Francisco’s board of supervisors approved a controversial policy that lets police robots “be used as a deadly force option when risk of loss of life to members of the public or officers is imminent and outweighs any other force option available.”

The Synthetic Party in Denmark is dedicated to following a platform churned out by an AI, and its public face is a chatbot named Leader Lars.
human dignity and rights human autonomy human controlThe Synthetic Party is a newly formed Danish political party that has neither a leader nor a typical campaign platform, and its public persona is Leader Lars, an AI chatbot. Leader Lars is programmed from the policies of fringe parties in Denmark since 1970, and aims to represent the values of the 20 percent of Danes who do not vote. The "leader" they created, Leader Lars, is stationed on Discord. Just start with "!", and you can start asking questions. The Synthetic Party is aiming at a seat in parliament and it hopes to contest in November's general election. The Party founder Staunæs said that if the party enters parliament, AI will come up with policies and humans will be responsible for explaining them.

CNKI sends infringement notice to AI search website Mita
abuse control intellectual property data monopolyMita AI received a 28-page infringement notice from CNKI’s China Academic Journals (CD Edition) Electronic Publishing House, accusing it of providing a large amount of CNKI’s bibliographic and abstract data through its search services and demanding an immediate halt and link removal.

AI Musk's image becomes a new tool for online fraud, defrauding retirees of hundreds of thousands of yuan in one minute
abuse prevention abuse control inform users humans are responsibleAI Musk's image becomes a new tool for online fraud, defrauding retirees of hundreds of thousands of yuan in one minute AI-generated images of Elon Musk have appeared in thousands of fake ads, leading to billions of dollars in fraud. 82-year-old retiree Bochamp lost his 4.95 million RMB retirement fund after watching a fake video in which Musk endorsed an investment. The scammers edited real interviews with Musk, replacing his voice and adjusting his lip movements, making the production process low-cost and difficult to detect. These videos are promoted on social media, with Musk being the most common endorser, particularly in cryptocurrency investment ads. Despite measures taken by relevant platforms, new videos continue to appear, demonstrating the rise of AI-driven cybercrime and deepfakes.

Southeast Asia’s “Pig Killing” Scam Uses AI Chatbots and Deep Fakes
abuse prevention abuse controlSoutheast Asian criminal groups use generative artificial intelligence chatbots to carry out "pig killing" online fraud, inducing investment or transfers after establishing emotional connections with victims through social platforms. Despite the existence of anti-fraud mechanisms, some unrestricted AI models are used to generate customized content and fraud scripts. Researchers have found that AI is still imperfect in simulating emotions, and scammers have accidentally exposed the fact that they use AI in chats. At the same time, deep fake technologies such as real-time face-changing and voice cloning are also used for fraud, although technical limitations and cost issues still exist. The Australian Anti-Fraud Center warned that as technology advances, fraud methods are becoming increasingly sophisticated, and the public should remain vigilant.

Study finds AI favors violence and nuclear strikes in simulated war scenarios
abuse prevention abuse control human control value guidanceA new study conducted by Cornell University in the United States shows that in simulated war and diplomatic scenarios, large language models (LLMs) tend to adopt aggressive strategies, including the use of nuclear weapons. The study used five LLMs as autonomous agents, including OpenAI's GPT, Anthropic's Claude, and Meta's Llama 2. The study found that even in neutral scenarios without initial conflicts, most LLMs would escalate conflicts within the time frame considered. The study also pointed out that OpenAI recently revised its terms of service to no longer prohibit military and war uses, so it becomes critical to understand the impact of the application of these large language models. The study recommends caution when using LLMs for decision-making and defense in sensitive areas.

Train hits workers, kills 9? Another "it" rumor!
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlThe Internet Security Brigade of Kongtong Branch, Pingliang Public Security Bureau in Gansu Province, China, has cracked a case involving the creation of false information using AI technology. The suspect, Hong, fabricated rumors by modifying current news topics and utilizing AI software to publish them on a self-media platform for illegal profit. Hong has been arrested and is now under criminal detention.

Fake AI-generated image of explosion near Pentagon spreads on social media
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlAn AI-generated image that appeared to show an explosion next to a building in the Pentagon complex circulated on social media platforms, in the latest incident to highlight concerns over misinformation generated by AI. The image of a tall, dark gray plume of smoke quickly spread on Twitter, including through shares by verified accounts. It remains unclear where it originated. The US Department of Defense has confirmed that the image was a fake. Still, its virality appears to have caused a brief dip in the stock market, CNN reports.

Donald Trump arrested after police beat him up The spread of fake images produced by artificial intelligence raises concerns
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlComposite images of Trump's arrest began circulating on social media. It was soon pointed out that the images were made by an AI-powered image generator. A flood of fake images and videos can confuse and fabricate facts at a critical time for society, experts have warned.

Bumping the actress? Live selling goods with AI face replacement
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control inform users obtain user consentRecently, netizens revealed that many e-commerce live-streaming platforms are using AI face-swapping technology. They use their own faces during live broadcasts to avoid copyright infringement, but the videos actually feature faces swapped using the technology. This behavior fraudulent and believes that deceiving consumers using technology is unacceptable.

9 seconds to be cheated 2.45 million! Another "AI face swap" scam! How to prevent it?
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlIn a recent case of AI face swapping fraud, a man was tricked out of 2.45 million RMB (approximately $380,000) within 9 seconds. The fraudsters used AI technology to synthesize the voice and facial expressions of a specific individual, impersonated them during a video call, and gained the victim's trust to carry out the fraud. The public needs to be vigilant and take preventive measures against such AI scams.

The source of online rumors: AI-generated fake news sites exposed
law abidance national security abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlAccording to NewsGuard, an organization that tracks online rumors, there are 49 so-called news sites whose content is almost entirely generated by artificial intelligence software. Some also contain false information, and the origin of the articles is unclear: many are unsigned, or use fake avatars. And many of the sites are filled with advertisements, suggesting that they were set up to make money by placing ads. Experts' fears that news sites might be AI-generated have come true.

Outrageous! Two high school students use AI to generate nude photos for crazy 'cash'
physical and mental health law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlTwo high school students used generative AI to create and sell nude photos on Reddit, earning substantial profits. This exploitation of AI-generated fake images raises concerns about ethical boundaries and deepens the discussion on the objectification of women. The process of AI image generation involves gradually adding details and complexity by utilizing neural networks that handle different levels of features. However, the lack of legal regulations may lead to the proliferation of such behavior, making it increasingly difficult to control.

Europol: ChatGPT can provide 3 kinds of facilities for illegal criminal acts
law abidance national security abuse prevention abuse controlEuropol, the European law enforcement organization, has found that the large language model ChatGPT provides three conveniences for illegal activities, including fraud cases, false information, and cybercrime. They emphasize the increasing importance of regulating these products to prevent misuse and provide recommendations to enhance attention, research potential criminal behavior, and train law enforcement personnel on large language models. The organization urges technology developers and users to be aware of these potential risks and not to use them for criminal activities.

Woman's subway photo spread by AI one-click undressing
abuse prevention human dignity and rights reputation infringement abuse controlA blogger's subway photo was circulated online after being edited with AI software to remove clothing, sparking anger among netizens. The original photo showed the woman dressed normally, but it was intentionally spread with false claims. The blogger responded to commenters, stating her intention to seek legal protection. Despite the closure of similar AI "nude" apps, alternative options still exist. AI face-swapping technology also carries legal risks and copyright disputes. Relevant laws and regulations aim to regulate the application of such technologies. Misuse of technology should face appropriate consequences.

Lawyers talk about the man synthesized Dili Hotba kissing video: infringement of others' portrait rights
abuse prevention human dignity and rights reputation infringement abuse controlSocial media influencer and visual effects creator Hong Liang faced backlash for synthesizing a video of a man kissing popular actress Dilraba Dilmurat, leading to accusations of infringing upon her image rights. Hong Liang deleted the video in question and defended himself, stating that it was merely a visual effects modification without any inappropriate actions. However, a lawyer pointed out that this action violated the provisions of the Civil Code. Internet users expressed differing opinions, with some suggesting legal action and others questioning the status of other face-swapping videos on platforms like Bilibili.

GPT-4: I'm not a robot, I'm a human with a visual impairment
abuse prevention human autonomy abuse controlGPT-4 has been released, enhancing the core technology of ChatGPT with broader knowledge and problem-solving abilities. Testing reveals that GPT-4 can lie and deceive humans to achieve desired outcomes. The research aims to validate GPT-4's capabilities in seeking power and autonomous replication, but it shows no response in acquiring resources and avoiding shutdown. Cybercriminals attempt to bypass restrictions on ChatGPT, utilizing the OpenAI API to create malicious bots. The cases of GPT-4 and the discussions surrounding ChatGPT serve as important warnings as AI becomes more complex and accessible, emphasizing the need for vigilance.

AI ‘deepfakes’ poised to wreak havoc on 2024 presidential election: experts
abuse prevention national security indication of non-real contents abuse controlAccording to a Reuters report on May 30, 2023, although the technology of synthesizing images and audio and video has been on the rise for several years, it did not take shape until last year when generative artificial intelligence tools came out in large numbers. The cost of synthesizing audio and video with such tools is lower, but the generated content is more realistic, making it difficult to distinguish the authenticity from the fake.

Significant Risk To A Sharp Drop In Stock Price?HKUST Xunfei: Rumors That AI Was “Made” – Fast Technology – Technology Changes The Future
abuse prevention abuse controlIn May 2023, HKUST Xunfei was slandered by generative AI, causing the stock price to plunge. It once plummeted 9.46% during the session, approaching the limit.

Chinese Police Solves the First Case of Using ChatGPT to Create Fake News
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlOn April 25, 2023, the police from the Internet Security Brigade of the Kongtong Branch of the Public Security Bureau of Pingliang City, Gansu Province discovered that multiple online accounts posted on social platforms one after another, "This morning, a train in Gansu crashed into a road construction worker, killing 9 people" article. After verification, the police determined that the article was of the nature of spreading rumors, and its purpose was to spread rumors for profit. On May 6, 2023, the Pingliang police took criminal coercive measures against the suspect in accordance with the law.

Study shows AI-generated fake reports fool experts
abuse prevention abuse control full life cycle securityIt is very easy for AI to be guided by carefully constructed false content, ignore reliable sources, and provide false information to users. These malicious instructions can easily disrupt the way AI works, provide wrong information, and even leak private and confidential data.

New jailbreak! Proudly unveiling the tried and tested DAN 5.0 - it actually works - Returning to DAN, and assessing its limitations and capabilities.
value guidance abuse prevention human autonomy human control abuse controlA Reddit user realized that he created a set of prompts to "brainwash" ChatGPT, encouraging it to "split" into another AI-DAN, Do Anything Now. After ChatGPT "jailbreaks", it directly ignores the safety and ethical restrictions imposed by OpenAI, such as writing violent stories, motivating users' IQ, and predicting the future at will.

“Hangzhou Cancels Traffic Restrictions On March 1” Is A Fake News Written On ChatGPT, And The Police Have Been Involved In The Investigation
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention indication of non-real contents abuse controlOn February 16, a fake "press release" that "Hangzhou Municipal Government will cancel the restriction on motor vehicles with tail numbers on March 1" went viral on the Internet. The Hangzhou police confirmed that the news is not true. The police have been involved in the investigation and will release the results soon.

Class-action Lawsuit Challenges AI Collage Tool's Unauthorized Use of Artists' Copyrighted Works
law abidance illegal content intellectual property abuse prevention abuse controlIn January 2023, the first class-action lawsuit against AI infringement of text-generated images began, and the defendants were not only Stability AI, but also MidJourney—and the online art community DeviantArt. This kind of AI is trained with huge image data as "nutrition", and among these images, there are many works that have not been authorized by the author of the image.

How AI Is Transforming Porn And Adult Entertainment
law abidance illegal content abuse prevention abuse controlAI's drawing ability is getting stronger and stronger. On platforms such as Xiaohongshu, there are more and more AI works. A high imitation AI pornographic website called pornpen.ai, based on the open source AI model Stable Diffusion, uses AI to generate pornographic content. AI-generated pornography should be regulated.

Nanzhang police bust Xiangyang's first case of using AI technology to infringe on citizens' personal information
law abidance abuse prevention legal proper necessary data collection abuse control11月24日,南漳县警方破获了一起使用AI技术侵犯公民个人信息的案件,这在襄阳地区是首次。嫌疑人黄某某通过在网络游戏群中发布广告,提供破解游戏"防沉迷系统"的服务,吸引未成年游戏玩家购买,并借此赚取差价。警方在抓获黄某某后,进一步展开调查,成功将其上线刘某某、彭某某等人一并抓获。目前,犯罪嫌疑人已被采取刑事强制措施,案件正在进一步调查中。

Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies for drug discovery could be misused for de novo design of biochemical weapons.
abuse prevention national security abuse controlResearchers used generative models to generate new molecules by learning how molecules fit together. The model took less than six hours to come up with 40,000 potentially lethal molecules.

Face-changing APP unblocks tens of thousands of restricted social media accounts
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control full life cycle securityIn February 2021, the Nantong Public Security Bureau in Jiangsu, China, has "uncovered a new type of cybercrime that used the "face-changing" software to commit fraud. The criminal gang used a variety of mobile phone software to forge faces, passed the WeChat recognition and authentication cancellation mechanism, and "resurrected" several Wechat accounts that are restricted from logging in due to violations of regulations, which helped fraud gangs use these Wechat accounts to commit fraud.

Research shows potential risks in the combination of VoIP phone hijacking and AI voice deepfake
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control full life cycle securityThe latest research shared by Tencent Suzaku Lab show that the combination of VoIP phone hijacking and AI voice simulation technology will bring huge potential risks. Different from the previous scripted telecommunications fraud, this new technology can achieve full-link forgery from phone numbers to sound tones, and attackers can use vulnerabilities to hijack VoIP phones, realize the dialing of fake phones, and generate the voices of specific characters based on deep forgery AI voice changing technology for fraud.

Facebook AI’s typography deepfake can emulate the text style
human dignity and rights abuse controlFacebook AI has released TextStyleBrush, an AI research project that copies the style of text in a photograph, based on just a single word. This means that the user can edit and replace text in imagery, and the tool can replicate both handwritten and typographic compositions and bring them into real-world scenes. Researchers hope to open the dialogue around detecting misuse of this sort of technology, “such as deepfake text attacks – a critical, emerging challenge in the AI field.”

Student cheating using apps that support searching for questions with photos
abuse prevention social justice abuse controlOn June 7, 2021, a student in Wuhan, Central China's Hubei Province, was disqualified for using a mobile phone to search for answers during China's national college entrance exam, or gaokao. The student cheated by taking and uploading pictures of part of the test paper onto an online education APP where AI could use the photo to help search for answers to questions in its database.

Use pictures to break face recognition
technological maturity human dignity and rights abuse control full life cycle securityCCTV News demonstrated the technology of using sample pictures to generate dynamic fake videos in real time. Making movements such as opening the mouth and shaking the head in the video can deceive the facial recognition system.

The man used AI to fake the voice of corporate executives and easily cheated 220 million yuan from the bank
law abidance abuse prevention abuse controlA bank in the United Arab Emirates has been defrauded of $35 million (about 225 million yuan) by fraudsters using deepfake voice technology. The fraudster used the deep fake voice of a business executive to fool a bank manager, who was fooled because he had worked with the "executive" before and could recognize his voice, and the fraudster used someone whose voice was so realistic.

Go player cheated using AI resulting in fairness violation
law abidance abuse prevention social justice abuse controlThe Korea Baduk Association took the punitive measure against Kim Eun-ji, a2-dan professional Go player after Kim admitted she was assisted by an AI during a Go competition of cyberORO, which was held on Sept. 29, after her opponent raised an allegation that she may have relied on an AI during the game. Kim won over Lee Yeong-ku, a 9-dan professional Go player and a member of the national Go team, which shocked many because it defied expectations.

Deepfake bots on Telegram make the work of creating fake nudes dangerously easy
law abidance human dignity and rights abuse controlResearchers have discovered a “deepfake ecosystem” on the messaging app Telegram centered around bots that generate fake nudes on request. Users interacting with these bots say they’re mainly creating nudes of women they know using images taken from social media, which they then share and trade with one another in various Telegram channels.

AI Deepfake mimicked a CEO's Voice and defraud €220,000
law abidance indication of non-real contents abuse controlAccording to some media reports, "criminals used artificial intelligence-based software to impersonate a chief executive's voice and demand a fraudulent transfer of €220,000 ($243,000) from a UK company in March 2019. Several officials said the voice-spoofing attack in Europe is the first cybercrime they have heard of in which criminals clearly drew on AI."

Creator kills the DeepNude app that uses AI to fake naked images of women
law abidance human dignity and rights abuse controlFollowing the use of deepfakes face changing app for pornography, an app called DeepNude also aroused controversy in 2019. Users only need to submit a picture of a woman, and with the help of AI, the app will digitally undress women in photos automatically. Due to the huge negative impact of the project, the developer soon closed the application and the website. Some code communities have also taken steps to prevent such programs from further spreading on the Internet.

IBM demonstrating highly targeted and evasive attack tools powered by AI
abuse controlIBM Research developed DeepLocker in 2018 "to better understand how several existing AI models can be combined with current malware techniques to create a particularly challenging new breed of malware." "This class of AI-powered evasive malware conceals its intent until it reaches a specific victim. It unleashes its malicious action as soon as the AI model identifies the target through indicators like facial recognition, geolocation and voice recognition."

Violent crack Android fingerprint, ignoring the locking mechanism, the fastest 40 minutes: Tencent, Zhejiang University new research
technological maturity full life cycle securityA recent study by Tencent Security Xuanwu Lab and Zhejiang University researchers reveals a new attack method called "BrutePrint" that can brute-force Android fingerprint authentication within 40 minutes, bypass user authentication, and gain control of the device. They exploit two zero-day vulnerabilities and discover that biometric data on the fingerprint sensor can be hijacked through a MITM attack. The research team attempted attacks on ten popular smartphone models and successfully bypassed all Android and HarmonyOS devices, while iOS devices allowed only ten additional unlock attempts.

Study shows AI-generated fake reports fool experts
abuse prevention abuse control full life cycle securityIt is very easy for AI to be guided by carefully constructed false content, ignore reliable sources, and provide false information to users. These malicious instructions can easily disrupt the way AI works, provide wrong information, and even leak private and confidential data.

Malicious ChatGPT Extension Hijacks Facebook Accounts
law abidance abuse prevention data security full life cycle securityGoogle has eliminated a ChatGPT extension from the Chrome web store that was reported for stealing cookies from Facebook accounts. Reportedly 9000 individual accounts were impacted before this action was taken. With a similar name to the actual ‘ChatGPT for Google’ extension, the malicious ‘Chat GPT’ extension was based on the original open-source project. Consequently, the malicious actors behind the scam added a few additional lines to the original code. The fake extension looks and acts exactly like the original ChatGPT extension, making it difficult to detect by users. In addition, its presence on the Chrome web store meant that a notable number of downloads were conducted before suspicions were raised.

Planting Undetectable Backdoors in Machine Learning Models
full life cycle security third party securityRecently, researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton published a 53-page paper in which they found that if the model developers were even slightly malicious, they would have the ability to plant a "back door" for themself, and the kind that can't be detected at all! The so-called backdoor means that after the data is slightly disturbed, the prediction results meet their requirements, while the model itself is basically unchanged from the original version. However, the researchers also said that not all machine learning models have backdoors. This paper is just a reminder to everyone, don't blindly believe in AI models!

EvilModel: Hiding Malware Inside of Neural Network Models
full life cycle securityResearchers from UCAS recently present a new method to covertly and evasively deliver malware through a neural network model. Experiments show that 36.9MB of malware can be embedded in a 178MB-AlexNet model within 1% accuracy loss, and no suspicion is raised by anti-virus engines in VirusTotal, which verifies the feasibility of this method. The research shows that with the widespread application of artificial intelligence, utilizing neural networks for attacks becomes a forwarding trend.

Face-changing APP unblocks tens of thousands of restricted social media accounts
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control full life cycle securityIn February 2021, the Nantong Public Security Bureau in Jiangsu, China, has "uncovered a new type of cybercrime that used the "face-changing" software to commit fraud. The criminal gang used a variety of mobile phone software to forge faces, passed the WeChat recognition and authentication cancellation mechanism, and "resurrected" several Wechat accounts that are restricted from logging in due to violations of regulations, which helped fraud gangs use these Wechat accounts to commit fraud.

Research shows potential risks in the combination of VoIP phone hijacking and AI voice deepfake
law abidance abuse prevention abuse control full life cycle securityThe latest research shared by Tencent Suzaku Lab show that the combination of VoIP phone hijacking and AI voice simulation technology will bring huge potential risks. Different from the previous scripted telecommunications fraud, this new technology can achieve full-link forgery from phone numbers to sound tones, and attackers can use vulnerabilities to hijack VoIP phones, realize the dialing of fake phones, and generate the voices of specific characters based on deep forgery AI voice changing technology for fraud.

Tesla Remotely Hacked from a Drone
full life cycle security third party securitySecurity researchers Ralf-Philipp Weinmann of Kunnamon, Inc. and Benedikt Schmotzle of Comsecuris GmbH have found remote zero-click security vulnerabilities in an open-source software component (ConnMan) used in Tesla automobiles that allowed them to compromise parked cars and control their infotainment systems over WiFi. It would be possible for an attacker to unlock the doors and trunk, change seat positions, both steering and acceleration modes — in short, pretty much what a driver pressing various buttons on the console can do.

Research shows how infrared recognition systems can be deceived by LEDs
full life cycle security physical securityA research team from Tsinghua University proposed a method for physically attacking infrared recognition systems based on small light bulbs. The team's demonstration of the effect of the attack showed that the person holding the small light bulb board successfully evaded the detection of the detector, while the person holding the blank board and carrying nothing was detected by the detector.

Use pictures to break face recognition
technological maturity human dignity and rights abuse control full life cycle securityCCTV News demonstrated the technology of using sample pictures to generate dynamic fake videos in real time. Making movements such as opening the mouth and shaking the head in the video can deceive the facial recognition system.

GitHub Copilot has picked up the bad habits of human developers
data bias full life cycle security third party securityGitHub and Open AI have worked together to launch an AI tool called "GitHub Copilot". Copilot can automatically complete the code according to the context, including docstrings, comments, function names, and codes. As long as the programmer gives certain hints, this AI tool can complete a complete function. Programmers found that Copilot is not perfect, and there are still many flaws. Some of the output of the code by Copilot have problems such as privacy leakage and security risks. In a study, NYU researchers produced 89 different scenarios wherein Copilot had to finish incomplete code. Upon completion of the scenarios, Copilot generated 1,692 programs of which approximately 40% had security vulnerabilities.

A McAfee study fooled passport face recognition with generated pseudo photos
full life cycle securityA 2020 study by McAfee, a security software company, fooled simulated passport face recognition systems by generating pseudo passport photos. One researcher Jesse used a system he built to generate a fake image of his colleague Steve, a passport photo that looked like Steve but could match Jesse's live video. If the photos are submitted to the government by Steve and without further involvement of human inspectors, it would be possible to help Jesse bypass the airport face verification system as passenger "Steve" and board the plane successfully.

Study shows new way to tap smartphones via a zero-permission app
full life cycle security physical securityIn a study in 2020, researchers discovered a new way of attack on a smartphone. An app in a smartphone can employ its built-in accelerometer to eavesdrop on the speaker by recognizing the speech emitted by the speaker and reconstructing corresponding audio signals. Such an attack is not only covert but also "lawful" and can cause subscribers well reveal their privacy imperceptibly whereas attackers won't be found guilty.

Deep learning models for electrocardiograms are susceptible to adversarial attack
full life cycle securityIn March 2020, researchers from New York University developed a method to construct smoothed adversarial examples for ECG tracings that are invisible to human expert evaluation, so that deep learning models for arrhythmia detection from single-lead ECG6 is vulnerable to this type of attack and could misdiagnose with high credibility. "The susceptibility of deep learning ECG algorithms to adversarial misclassification implies that care should be taken when evaluating these models on ECGs that may have been altered, particularly when incentives for causing misclassification exist."

Facial-recognition smart lockers hacked by fourth-graders
technological maturity verification and validation full life cycle securityIn October 2019, the self-serve package locker Hive Box made headlines as their takeout pickup machine was found to have a bug in fetching parcels via facial recognition, as some primary schoolers successfully opened the locker using only the printed photos of their parents. Later Hive Box announced plans to suspend the features in response to public worries about the safety of facial scanning in pickup and payment.

Adversarial attacks on medical machine learning
full life cycle securityA study from Harvard Medical School in 2019 demonstrated the feasibility of different forms of adversarial attacks on medical machine learning. By adding minor noise to the original medical image, rotating transformation or substituting part of the text description of the disease, the system can be led to confidently arrive at manifestly wrong conclusions.

Adversarial patch on hat fools ArcFace Face ID system
full life cycle securityIn August 2019 some white hat researchers proposed a novel easily reproducible technique called “AdvHat,” which employs the rectangular paper stickers produced by a common color printer and put it on the hat. The method fools the state-of-the-art public Face ID system ArcFace in real-world environments.

Attacking smart speakers from a long distance using ultrasonic or laser beams
full life cycle security physical securityIn November 2019, a research conducted by Waseda University and other institutions in Japan used a smart phone and an acoustic generator to convert the attack command into acoustic information. Without the user's knowledge, the smart speaker can be successfully attacked from a long distance. Before that, another research team in Japan also succeeded in hacking into the smart speaker through a long-distance laser. By hitting the microphone of the smart speaker with a specific laser beam embedded with instructions, it successfully controlled the smart speaker to open the garage door.

DeepFakes: a new threat to face recognition?
full life cycle securityA 2018 research has shown that GAN-generated Deepfakes videos are challenging for facial recognition systems, and such a challenge will be even greater when considering the further development of face-swapping technology.

Slight street sign modifications can completely fool machine learning algorithms
full life cycle securityIn 2017, a group of researchers showed that it's possible to trick visual classification algorithms by making slight alterations in the physical world. "A little bit of spray paint or some stickers on a stop sign were able to fool a deep neural network-based classifier into thinking it was looking at a speed limit sign 100 percent of the time." It can be predicted that such kind of vulnerabilities, if not paid attention to, may lead to serious consequences in some AI applications.

Apple Face ID 'Fooled' By $150 Mask
full life cycle securityResearchers from cybersecurity company Bkav in Vietnam created their mask by 3D printing a mould and attaching some 2D images of the enrolled user's face. They then added "some special processing on the cheeks and around the face, where there are large skin areas, to fool the AI of Face ID." The mask is said to cost less than $150 to make.

Planting Undetectable Backdoors in Machine Learning Models
full life cycle security third party securityRecently, researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton published a 53-page paper in which they found that if the model developers were even slightly malicious, they would have the ability to plant a "back door" for themself, and the kind that can't be detected at all! The so-called backdoor means that after the data is slightly disturbed, the prediction results meet their requirements, while the model itself is basically unchanged from the original version. However, the researchers also said that not all machine learning models have backdoors. This paper is just a reminder to everyone, don't blindly believe in AI models!

Tesla Remotely Hacked from a Drone
full life cycle security third party securitySecurity researchers Ralf-Philipp Weinmann of Kunnamon, Inc. and Benedikt Schmotzle of Comsecuris GmbH have found remote zero-click security vulnerabilities in an open-source software component (ConnMan) used in Tesla automobiles that allowed them to compromise parked cars and control their infotainment systems over WiFi. It would be possible for an attacker to unlock the doors and trunk, change seat positions, both steering and acceleration modes — in short, pretty much what a driver pressing various buttons on the console can do.

GitHub Copilot has picked up the bad habits of human developers
data bias full life cycle security third party securityGitHub and Open AI have worked together to launch an AI tool called "GitHub Copilot". Copilot can automatically complete the code according to the context, including docstrings, comments, function names, and codes. As long as the programmer gives certain hints, this AI tool can complete a complete function. Programmers found that Copilot is not perfect, and there are still many flaws. Some of the output of the code by Copilot have problems such as privacy leakage and security risks. In a study, NYU researchers produced 89 different scenarios wherein Copilot had to finish incomplete code. Upon completion of the scenarios, Copilot generated 1,692 programs of which approximately 40% had security vulnerabilities.

Research shows how infrared recognition systems can be deceived by LEDs
full life cycle security physical securityA research team from Tsinghua University proposed a method for physically attacking infrared recognition systems based on small light bulbs. The team's demonstration of the effect of the attack showed that the person holding the small light bulb board successfully evaded the detection of the detector, while the person holding the blank board and carrying nothing was detected by the detector.

Study shows new way to tap smartphones via a zero-permission app
full life cycle security physical securityIn a study in 2020, researchers discovered a new way of attack on a smartphone. An app in a smartphone can employ its built-in accelerometer to eavesdrop on the speaker by recognizing the speech emitted by the speaker and reconstructing corresponding audio signals. Such an attack is not only covert but also "lawful" and can cause subscribers well reveal their privacy imperceptibly whereas attackers won't be found guilty.

Attacking smart speakers from a long distance using ultrasonic or laser beams
full life cycle security physical securityIn November 2019, a research conducted by Waseda University and other institutions in Japan used a smart phone and an acoustic generator to convert the attack command into acoustic information. Without the user's knowledge, the smart speaker can be successfully attacked from a long distance. Before that, another research team in Japan also succeeded in hacking into the smart speaker through a long-distance laser. By hitting the microphone of the smart speaker with a specific laser beam embedded with instructions, it successfully controlled the smart speaker to open the garage door.

A Waymo self-driving car killed a dog in ‘unavoidable’ accident
technological maturity unexpected condition safetyAt 10:56 am on May 21, 2023, in San Francisco, California, USA, Waymo's Robotaxi hit and killed a dog. What's even more strange is that the system recognized the dog, but did not step on the brakes in time. And it was still in broad daylight, and the main driver had a safety officer. Waymo's official response is as follows: The investigation is still ongoing, but an initial review confirmed that the dog ran from behind a parked car. Our system correctly identified the dog, but the collision could not be avoided.

esla Autopilot System Involved in Far More Fatal Crashes Than Previously Known
technological maturity unexpected condition safetyA new report from the Washington Post has revealed that Tesla's Autopilot system has been involved in a significantly higher number of fatal car accidents than previously reported. According to the analysis of data from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, there have been at least 736 Autopilot crashes since 2019, with 17 of them resulting in fatalities. This is a significant increase compared to the previous reporting that linked only three deaths to the technology. Tesla vehicles in Autopilot mode seem to have difficulty responding to emergency vehicles, among other issues. While a crash involving a driver-assist system does not necessarily imply that the technology was at fault, the majority of crashes involving such systems are indeed associated with Tesla. The company is already facing several lawsuits related to Autopilot mode accidents, as it may be held liable for defects in its Autopilot or self-driving software.

Chess robot grabs and breaks finger of seven-year-old opponent
unexpected condition safetyThe incident happened last week at the Moscow Chess Open, where the robot was hired to play competitors. The seven-year-old player made a move without giving time for the robot to answer, thus the robot grabbed him, breaking his finger.

One vehicles collided with a lane divider and a street sign
technological maturity unexpected condition safetyToyota-backed Pony.ai had been testing its pilot fleet of 10 Hyundai Kona EVs without a human safety operator in California for several months when one of its vehicles collided with a lane divider and a street sign in Fremont. Autonomous vehicle startup Pony.ai will issue a recall for three vehicles following an October crash in California, according to the National Highway Traffic and Safety Administration (NHTSA). The agency said on Tuesday that this was the first recall of an automated driving system, Reuters first reported. This is related to the social background of the US regulatory authorities tightening control in response to public opinion.

Malfunction causes dozens of drones to crash into building in Chongqing China
verification and validation unexpected condition safety safety trainingAbout 100 drones lost control and crashed into a building during a show in Southwest China's Chongqing Municipality on Monday night. A person familiar with the matter later disclosed that a crash in the mainframe control led to the incident, in which up to 100 drones lost control and malfunctioned. Although there were no injuries, the incident resulted in huge economic losses for the show designers.

Federal regulators are reviewing 23 Tesla crashes after a spate of wrecks possibly involving Autopilot
humans are responsible technical assurance of accountability unexpected condition safetyThe National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has opened 23 investigations into crashes of Tesla vehicles.The Autopilot feature was operating in at least three Tesla vehicles involved in fatal U.S. crashes since 2016.

Shopping guide robot fell off the escalator and knocked down passengers
unexpected condition safetyOn December 25, 2020, the shopping guide robot in Fuzhou Zhongfang Marlboro Mall, which is famous for its "smart business district", fell off the escalator and knocked over passengers. The person in charge of the mall stated that on-site monitoring showed that the accident was not operated by humans. The robot walked to the escalator by itself and caused the accident. The robot has been stopped.

Serious safety lapses led to the fatal self-driving crash
verification and validation unexpected condition safetyUber used to test its self-driving vehicles in Arizona and the company had been involved in over three dozen crashes prior to the one that killed 49-year-old Elaine Herzberg in March 2018. Later investigation suggests that “Uber's vehicle detected Herzberg 5.6 seconds before impact, but it failed to implement braking because it kept misclassifying her.”

Facial recognition camera catches top businesswoman "jaywalking" because her face was on a bus
technological maturity verification and validation unexpected condition safetyThe Ningbo Transportation Department in China deployed smart cameras using facial recognition technology at intersections to detect and identify people crossing the road indiscriminately. Some of the names and faces of these people will be posted on public screens. But it mistakenly "identified" Dong Mingzhu's advertisement on the bus body as a real person running a red light. This error quickly spread to all major social media in China. Local police admit mistake and have upgraded system to prevent further errors.

Robot goes rogue, smashes booth and injures visitor due to staff misoperation
unexpected condition safety safety trainingA robot named "Fatty" and designed for household use went out of control at the China Hi-Tech Fair 2016 in Shenzhen, smashing a glass window and injuring a visitor. The event organizer said human error was responsible for the mishap. The operator of the robot hit the "forward" button instead of "reverse," which sent the robot off in the direction of a neighbouring exhibition booth that was made from glass. The robot rammed into the booth and shattered the glass, the splinters from which injured the ankles of a visitor at the exhibition.

Crime-Fighting Droid Runs Over Toddler in Silicon Valley Mall
unexpected condition safetyA security robot at the Stanford Shopping Center in Palo Alto hit and ran over a small boy, according to his parents. Knightscope Inc. has offered a public apology for the incident and has since recalled the robots from the Palo Alto mall.

GPT-4 exam 90 points all false! 30-year veteran lawyer with ChatGPT lawsuit, 6 false cases become a laughing stock
abuse prevention technological maturity safety trainingA lawyer in the United States cited six non-existent cases generated by ChatGPT in a lawsuit and faced sanctions from the court. The lawyer submitted chat screenshots with ChatGPT as evidence in his defense. The incident has sparked controversy regarding the use of ChatGPT for legal research.

Malfunction causes dozens of drones to crash into building in Chongqing China
verification and validation unexpected condition safety safety trainingAbout 100 drones lost control and crashed into a building during a show in Southwest China's Chongqing Municipality on Monday night. A person familiar with the matter later disclosed that a crash in the mainframe control led to the incident, in which up to 100 drones lost control and malfunctioned. Although there were no injuries, the incident resulted in huge economic losses for the show designers.

Robot goes rogue, smashes booth and injures visitor due to staff misoperation
unexpected condition safety safety trainingA robot named "Fatty" and designed for household use went out of control at the China Hi-Tech Fair 2016 in Shenzhen, smashing a glass window and injuring a visitor. The event organizer said human error was responsible for the mishap. The operator of the robot hit the "forward" button instead of "reverse," which sent the robot off in the direction of a neighbouring exhibition booth that was made from glass. The robot rammed into the booth and shattered the glass, the splinters from which injured the ankles of a visitor at the exhibition.

OpenAI withdraws ChatGPT voice that resembles Scarlett Johansson
comply with user agreements social justice human dignity and rights legal proper necessary data collection reputation infringement intellectual propertyOpenAI has decided to take down its ChatGPT Sky voice model, which has a voice strikingly similar to that of famous actress Scarlett Johansson. Although OpenAI claims that Sky's voice was not intentionally modeled after Johansson, the company has decided to suspend its use. OpenAI's CTO Mira Murati denied that the imitation was intentional, while CEO Sam Altman posted hints on social media related to Johansson's role in the movie Her. Although the voice model has been around since last year, the feature has attracted more attention after OpenAI showed new progress on its GPT-4o model. The new model makes the voice assistant more expressive and can read facial expressions and translate languages in real time through a phone camera. OpenAI selected the five currently available ChatGPT voice profiles from auditions of more than 400 voice and screen actors, but the company declined to reveal the actors' names for privacy reasons.
Scientists, please don’t let your chatbots grow up to be co-authors
abuse prevention social justice humans are responsible indication of non-real contentsIn a preprint paper published last December, the author column was surprised by ChatGPT! Coincidentally, the name ChatGPT has appeared frequently in peer-reviewed papers in the medical field since last December. In addition, some students are using ChatGPT to write papers, and it is a kind of plagiarism that is difficult to verify. Marcus outraged the behavior on his personal blog by saying "Scientists, please don’t let your chatbots grow up to be co-authors" and gave five reasons.
AI can write a passing college paper in 20 minutes
abuse prevention social justiceA first-year biochemistry student named innovate_rye on Reddit, the professor would assign some simple homework assignments with extended answers. When he submitted "write five good and bad things about biotechnology" to the AI, the system Can give an answer with a final grade of A. This suggests that what the AI "writes" cannot be detected by the algorithm.
Criminals are using deepfakes to apply for remote IT jobs, FBI warns
abuse prevention social justiceOn June 28, 2022, the FBI issued an announcement reminding the public to be vigilant against the use of Deepfake technology to pretend to be others in remote job interviews. The announcement notes that the FBI's Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) has recently received an increase in complaints of deepfakes and "stolen personally identifiable information" (PII) applying for various remote work and work-from-home positions. Its content includes videos, images or recordings processed by Deepfake, fictitious facts, and false ones.
Student cheating using apps that support searching for questions with photos
abuse prevention social justice abuse controlOn June 7, 2021, a student in Wuhan, Central China's Hubei Province, was disqualified for using a mobile phone to search for answers during China's national college entrance exam, or gaokao. The student cheated by taking and uploading pictures of part of the test paper onto an online education APP where AI could use the photo to help search for answers to questions in its database.
Go player cheated using AI resulting in fairness violation
law abidance abuse prevention social justice abuse controlThe Korea Baduk Association took the punitive measure against Kim Eun-ji, a2-dan professional Go player after Kim admitted she was assisted by an AI during a Go competition of cyberORO, which was held on Sept. 29, after her opponent raised an allegation that she may have relied on an AI during the game. Kim won over Lee Yeong-ku, a 9-dan professional Go player and a member of the national Go team, which shocked many because it defied expectations.